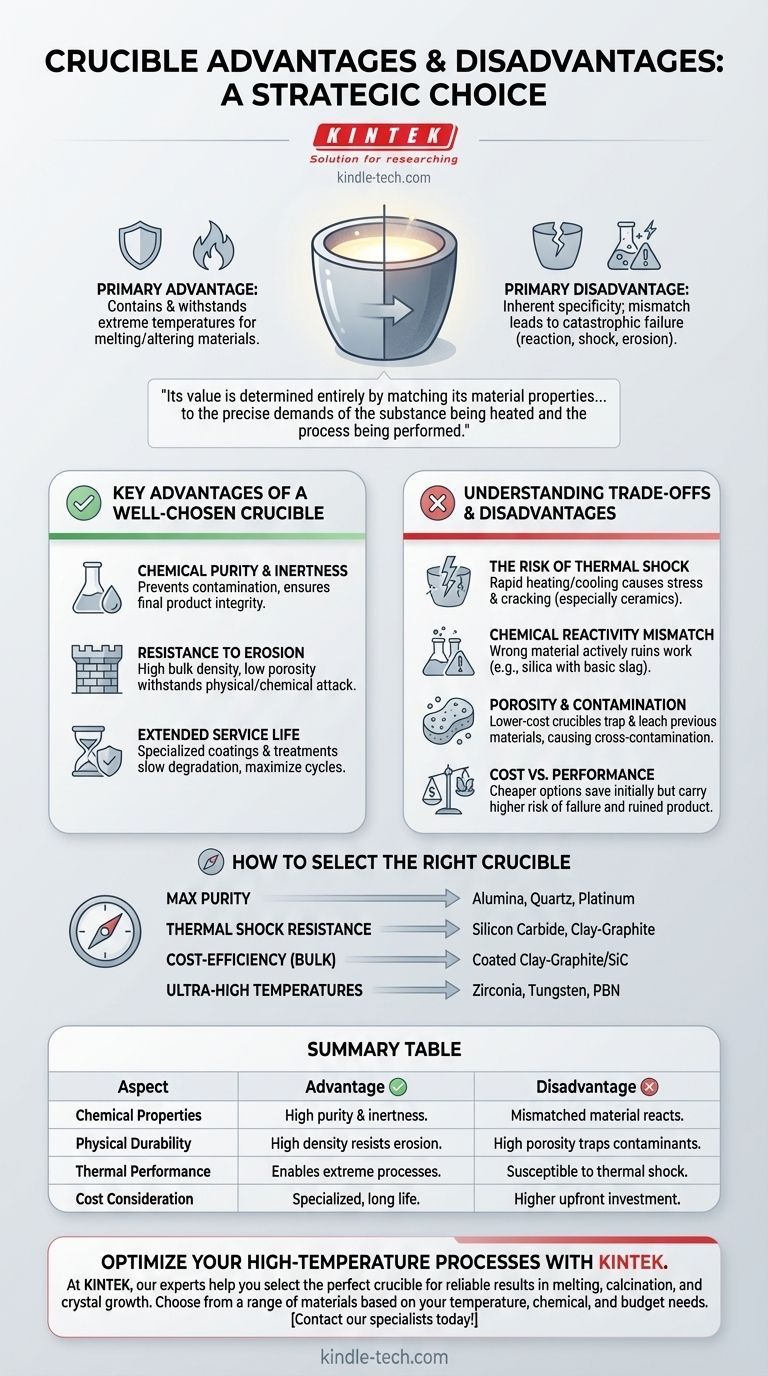
The primary advantage of a crucible is its ability to safely contain and withstand extreme temperatures required for melting or altering materials. However, its main disadvantage is its inherent specificity; a crucible that is perfect for one application can fail catastrophically in another due to chemical reactions, thermal shock, or material erosion.
The effectiveness of a crucible is not a given. Its value is determined entirely by matching its material properties—such as purity, density, and thermal resistance—to the precise demands of the substance being heated and the process being performed.

The Core Function: A Vessel for Transformation
A crucible is more than just a heat-proof bowl. It is a critical piece of technical equipment designed to facilitate a chemical or physical change at high temperatures without interfering with the process itself.
### Enabling High-Temperature Processes
The fundamental purpose of a crucible is to act as a stable container for materials being subjected to intense heat. This allows for processes like melting metals, calcining minerals, or growing crystals that would be impossible in standard containers.
### Maintaining Process Purity
A crucible's secondary, but equally critical, role is to be chemically inert. It must hold its contents without reacting with them, ensuring the final product is not contaminated by the container itself.
Key Advantages of a Well-Chosen Crucible
The benefits listed in technical specifications are not inherent to all crucibles, but rather the result of choosing the right type of high-performance crucible for a specific task, such as melting aluminum.
### Chemical Purity and Inertness
High-purity materials, such as the low-ash graphite mentioned for aluminum work, are essential for preventing contamination. When a crucible is pure, it doesn't leach volatile substances or impurities into the molten material, ensuring the quality and integrity of the final product.
### Resistance to Erosion
Materials with high bulk density and low porosity are designed to resist physical and chemical attacks. This structure prevents molten metals and reactive gases from penetrating or eroding the crucible walls, which would otherwise weaken the vessel and contaminate the melt.
### Extended Service Life
Specialized features like anti-oxidation treatments and protective coatings are not standard; they are value-added properties. These coatings create a barrier that dramatically slows down degradation from oxygen at high temperatures, maximizing the number of cycles a crucible can endure and lowering long-term operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
The advantages of a specialized crucible come with corresponding risks and considerations. A failure to understand these trade-offs is the most common source of process failure.
### The Risk of Thermal Shock
Perhaps the most universal vulnerability of crucibles, especially ceramic ones, is thermal shock. Heating or cooling a crucible too quickly creates internal stresses that can cause it to crack or shatter. This demands disciplined operational procedures.
### Chemical Reactivity Mismatch
The wrong crucible material will actively ruin your work. For example, using a silica (sand-based) crucible to melt a highly basic slag will cause the crucible to dissolve into the melt, contaminating the product and leading to vessel failure. Every material has a chemical counter-indicated for its use.
### Porosity and Contamination
Lower-cost or lower-quality crucibles often have higher porosity. This is a significant disadvantage, as the porous walls can absorb materials from a previous melt. When reused, these trapped materials can leach out, causing cross-contamination in subsequent batches.
### Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct trade-off between cost and performance. A high-purity, coated crucible designed for a specific application will be significantly more expensive upfront. Opting for a cheaper, general-purpose crucible may save money initially but carries a much higher risk of contamination, premature failure, and ruined product.
How to Select the Right Crucible
Choosing a crucible requires you to define your primary goal first. The material and design must serve your specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Select a crucible made from a material known to be inert to your sample, such as high-purity alumina, quartz, or platinum.
- If your primary focus is resistance to thermal shock: A silicon carbide or clay-graphite crucible often provides superior performance compared to more brittle ceramics.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for bulk processing: A durable, coated clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible often delivers the best balance of service life and upfront investment.
- If your primary focus is reaching ultra-high temperatures: You must use exotic materials like zirconia, tungsten, or pyrolytic boron nitride, which come with significant cost and specialized handling requirements.
Ultimately, viewing the crucible as an integral and active component of your process is the key to achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Properties | High purity and inertness prevents contamination. | Mismatched material can react, ruining the process. |
| Physical Durability | High bulk density resists erosion for longer life. | High porosity in low-cost options risks contamination. |
| Thermal Performance | Enables extreme temperature processes like metal melting. | Susceptible to cracking from thermal shock if heated/cooled too quickly. |
| Cost Consideration | Specialized, coated crucibles maximize performance and lifespan. | High-performance crucibles have a higher upfront cost. |
Ready to find the perfect crucible for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts understand that the right crucible is critical for achieving pure, reliable results in processes like metal melting, calcination, and crystal growth. We can help you select from a range of materials—including high-purity alumina, graphite, silicon carbide, and more—based on your needs for temperature, chemical resistance, and budget.
Let us help you optimize your high-temperature processes. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the efficiency of a crucible furnace? A Guide to Thermal Performance & Trade-offs
- Why are stainless steel reactors and graphite crucibles used for Nb-Ti alloys? Ensuring Purity in Magnesiothermic Reduction
- Is graphite crucible better than ceramic? The Definitive Guide to High-Temp Crucible Selection
- What are 2 uses of crucible? Mastering High-Temperature Melting and Analysis
- What is the function of crucible with cover in laboratory? Master High-Temperature Reactions
- What are the primary functions of alumina crucibles for calcining LLZO? Optimize Your Solid Electrolyte Synthesis
- What are the dual functions of a high-strength stainless steel crucible in a liquid metal electrochemical corrosion cell?
- Why are high-purity tantalum crucibles preferred when evaporating dielectric targets? Ensure Film Purity & Performance



















