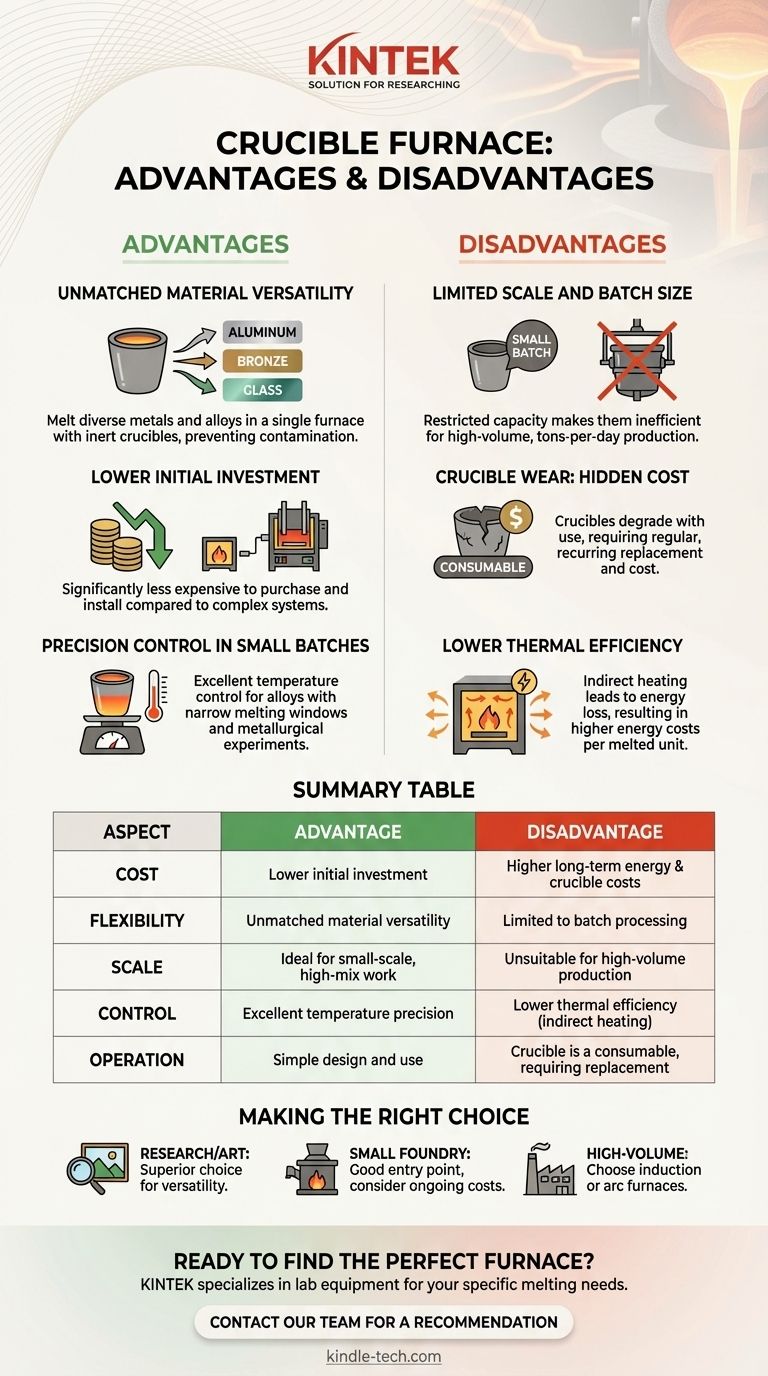
Crucible furnaces are valued for their operational simplicity and material flexibility. They are a foundational tool in metallurgy, offering a cost-effective method for melting a wide range of materials in smaller quantities. Key advantages include their lower initial cost and versatility, while their primary disadvantages center on limited batch sizes and the ongoing cost of replacing the crucibles themselves.
The decision to use a crucible furnace is a strategic one. It represents a trade-off between upfront investment and operational efficiency, making it an ideal choice for small-scale, high-mix applications but less suitable for high-volume, single-material production.

The Core Advantages of a Crucible Furnace
A crucible furnace's design is straightforward: a refractory-lined chamber heats a removable pot, or crucible, which contains the material to be melted. This simple mechanism is the source of its primary benefits.
Unmatched Material Versatility
Because the molten material is entirely contained within the inert crucible, the furnace itself does not come into direct contact with the charge. This separation prevents contamination and allows a single furnace to melt a vast array of different metals, alloys, and even glass simply by swapping crucibles.
This makes it perfect for environments like research labs, art foundries, or custom jewelers who may need to melt aluminum one day and bronze the next.
Lower Initial Investment
Compared to more complex systems like induction or arc furnaces, crucible furnaces are significantly less expensive to purchase and install. Their technology is mature, their construction is simpler, and their compact footprint reduces space requirements.
This low barrier to entry makes them an excellent starting point for new businesses, small foundries, or educational institutions.
Precision Control in Small Batches
Crucible furnaces, whether powered by gas or electricity, offer excellent temperature control. This precision is critical when working with alloys that have narrow melting windows or when conducting metallurgical experiments where exact temperatures are paramount.
The ability to manage a small, contained melt allows for a level of hands-on control that is difficult to achieve in larger, industrial-scale furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The same simplicity that makes crucible furnaces so accessible also creates inherent limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for making an informed investment.
The Challenge of Scale and Batch Size
The most significant disadvantage is limited capacity. Crucible furnaces are, by design, batch-process tools. Their size is restricted by the physical dimensions of the crucible, making them inefficient for applications requiring high-volume output.
For industrial production runs measured in tons, a crucible furnace is simply not a practical or cost-effective solution.
Crucible Wear: The Hidden Operational Cost
The crucible is a consumable component. It endures extreme thermal shock and chemical attack from molten metal during every cycle. Crucibles made from graphite, silicon carbide, or clay-graphite will inevitably degrade, crack, or fail over time.
This means crucibles must be replaced regularly, creating a recurring operational expense that must be factored into the total cost of ownership. A failed crucible can also be a significant safety hazard.
Lower Thermal Efficiency
Heating in a crucible furnace is indirect. The energy source (burners or electric elements) heats the furnace chamber, which then radiates heat to the crucible, which in turn transfers that heat to the metal. Each step in this process involves energy loss.
This makes crucible furnaces less energy-efficient than direct-heating methods like induction furnaces, where the electromagnetic field heats the metal itself. Over time, this translates to higher energy costs per kilogram of metal melted.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology requires a clear understanding of your primary goals, from production volume to material flexibility.
- If your primary focus is research, prototyping, or art: The unmatched versatility, precision control, and low initial cost of a crucible furnace make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is starting a small-scale foundry: A crucible furnace is an excellent entry point, but you must build a business model that accounts for the recurring costs of crucible replacement and higher energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: An induction or arc furnace will provide the speed, efficiency, and lower per-unit operational cost necessary to be competitive at scale.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can confidently select the right melting technology for your specific operational needs and budget.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher long-term energy & crucible costs |
| Flexibility | Unmatched material versatility | Limited to batch processing |
| Scale | Ideal for small-scale, high-mix work | Unsuitable for high-volume production |
| Control | Excellent temperature precision | Lower thermal efficiency (indirect heating) |
| Operation | Simple design and use | Crucible is a consumable, requiring replacement |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment for your specific melting and material processing needs. Whether you're in research, jewelry making, or starting a small-scale foundry, our experts can help you select the ideal crucible furnace to balance cost, versatility, and performance.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















