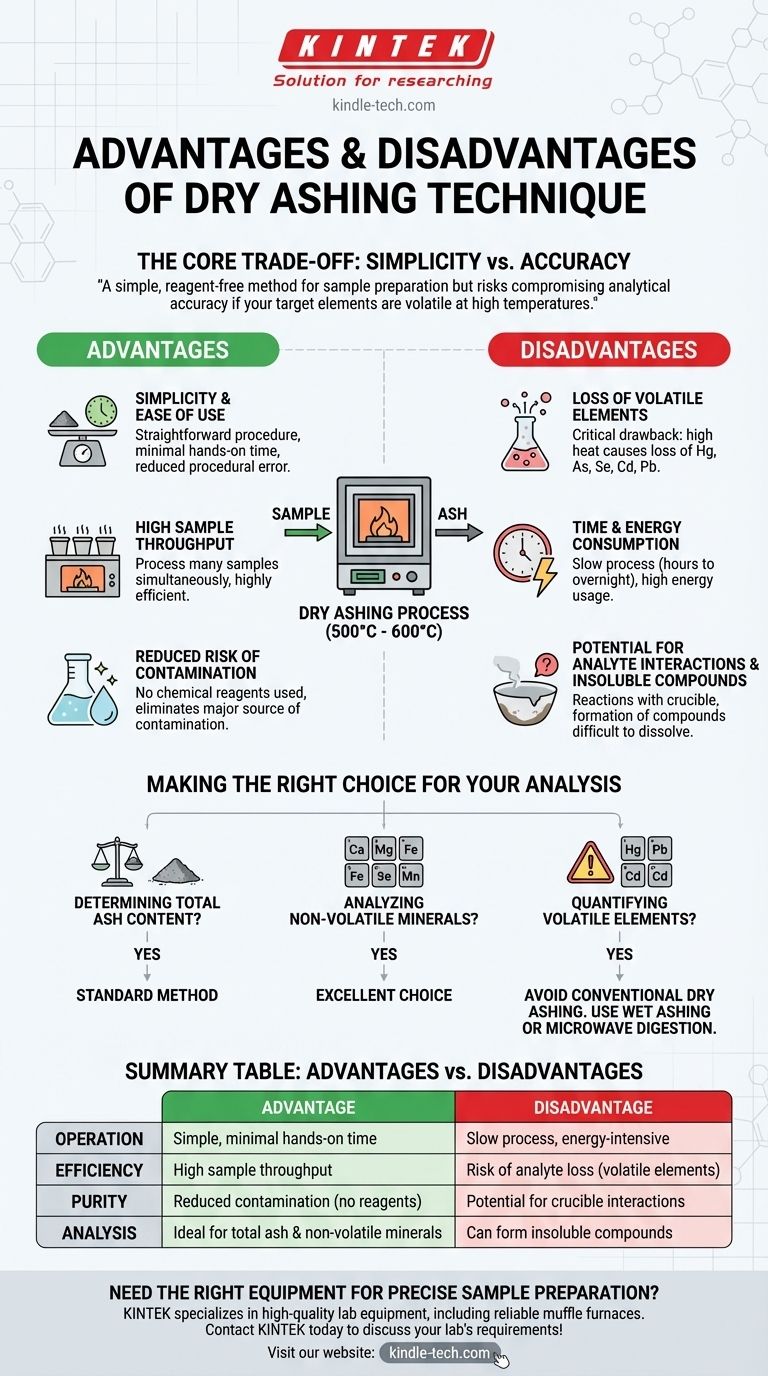
In analytical chemistry, dry ashing is a standard technique valued for its operational simplicity and ability to handle numerous samples at once. Its chief advantage is the effective removal of a sample's organic matrix through high-temperature combustion. However, its significant disadvantage is the potential for inaccurate results due to the loss of volatile mineral elements during the heating process.
The core trade-off of dry ashing is clear: it offers a simple, reagent-free method for sample preparation but risks compromising analytical accuracy if your target elements are volatile at high temperatures. The decision to use it hinges entirely on what you intend to measure.

The Principle of Dry Ashing
What Is the Goal?
The primary purpose of ashing is to remove the organic material (like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) from a sample. This isolates the inorganic residue, known as ash, which contains the sample's mineral elements.
How Does It Work?
The technique involves placing a sample in a crucible and heating it in a muffle furnace to high temperatures, typically between 500°C and 600°C. In the presence of air (oxygen), the organic matter is oxidized and burns away, primarily forming carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen gases.
What Is the Final Product?
The remaining ash consists of the non-combustible mineral content. These minerals are typically converted into more stable forms like oxides, sulfates, phosphates, and silicates, which can then be weighed or dissolved for further elemental analysis.
Key Advantages of the Dry Ashing Method
Simplicity and Ease of Use
The procedure is straightforward, requiring minimal hands-on time. An analyst weighs the sample, places it in the furnace, and weighs the resulting ash, reducing the potential for procedural error.
High Sample Throughput
A muffle furnace can typically hold many crucibles at once. This makes dry ashing highly efficient for laboratories that need to process a large number of samples simultaneously.
Reduced Risk of Contamination
Unlike wet ashing, which requires the addition of strong acids or oxidizing agents, dry ashing uses no chemical reagents. This eliminates a major source of potential contamination that could interfere with subsequent elemental analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
The Primary Concern: Loss of Volatile Elements
This is the most critical drawback of the technique. The high temperatures can cause volatile or semi-volatile elements to vaporize and escape, leading to an underestimation of their presence in the original sample.
Elements particularly susceptible to loss include mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), selenium (Se), cadmium (Cd), and lead (Pb).
Time and Energy Consumption
While the hands-on time is low, the entire process is slow. It can take several hours or even overnight for the furnace to heat up, hold the target temperature, and cool down safely. This process is also highly energy-intensive.
Potential for Analyte Interactions
At high temperatures, some mineral elements can react with the material of the crucible itself (e.g., porcelain or silica). This can cause the analyte to become "stuck" to the crucible, resulting in incomplete recovery and inaccurate measurements.
Formation of Insoluble Compounds
The intense heat can also convert some minerals into highly insoluble compounds. This poses a problem if the next step is to dissolve the ash in acid for analysis by techniques like ICP-OES or AAS, as some elements may not fully enter the solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Choosing the correct sample preparation method is fundamental to achieving accurate results. Use the following guidelines to determine if dry ashing is appropriate for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is determining total ash content: Dry ashing is the standard, most reliable method for this specific measurement.
- If your primary focus is analyzing non-volatile minerals (e.g., calcium, magnesium, iron, manganese): Dry ashing is an excellent and efficient choice, as these elements are stable at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is quantifying volatile elements (e.g., mercury, lead, cadmium): You must avoid conventional dry ashing. A lower-temperature method like wet ashing or microwave digestion is necessary to prevent analyte loss.
Ultimately, selecting the right technique requires a clear understanding of your target analytes and the inherent limitations of high-temperature oxidation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Simple, minimal hands-on time | Slow process, energy-intensive |
| Efficiency | High sample throughput | Risk of analyte loss (volatile elements) |
| Purity | Reduced contamination (no reagents) | Potential for crucible interactions |
| Analysis | Ideal for total ash & non-volatile minerals | Can form insoluble compounds |
Need the right equipment for precise sample preparation?
Choosing the correct ashing technique is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable muffle furnaces essential for dry ashing. We help laboratories like yours achieve efficient and contamination-free sample preparation.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution for your analytical needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- How do you control a muffle furnace? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- How do you check the temperature of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Monitoring
- What is the introduction of muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature, Contamination-Free Heating



















