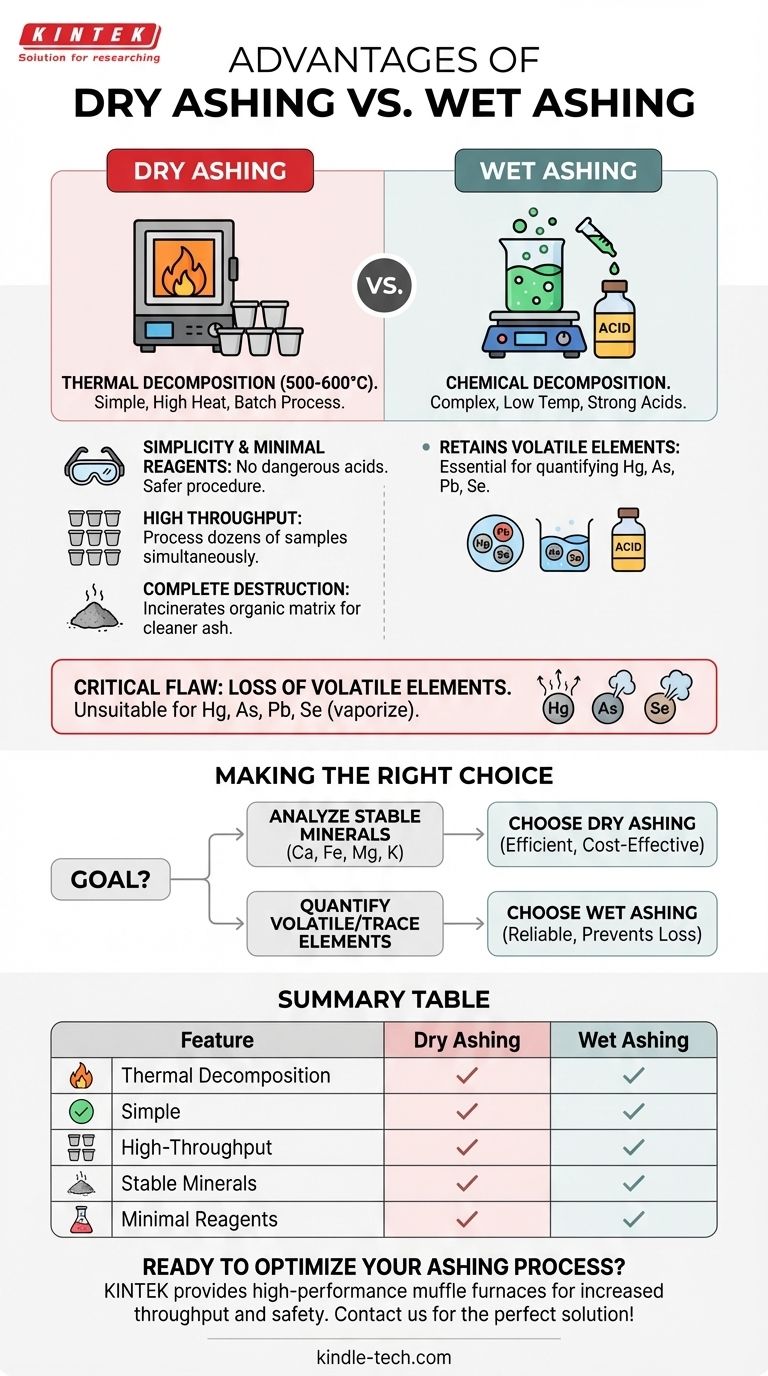
The primary advantages of dry ashing are its operational simplicity, minimal use of hazardous reagents, and its ability to process a large number of samples simultaneously. Unlike wet ashing, which requires careful handling of corrosive acids for each sample, dry ashing primarily involves placing samples in a high-temperature furnace, making it a more efficient method for labs with high throughput needs.
The choice between ashing methods is a critical trade-off. Dry ashing provides superior simplicity and batch processing capability, but it is unsuitable for volatile elements. Your decision must be guided by the specific elements you intend to analyze.

Understanding the Fundamental Processes
To grasp the advantages, it's crucial to understand how each method fundamentally works to remove the organic matrix and isolate the inorganic components (ash) for analysis.
How Dry Ashing Works
Dry ashing is a process of thermal decomposition. The sample is placed in a crucible and heated to very high temperatures, typically 500-600°C, in a muffle furnace.
At these temperatures, all organic matter is burned off in the presence of oxygen, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible minerals. These minerals are typically converted into their more stable oxide, sulfate, or phosphate forms.
How Wet Ashing Works
Wet ashing, also known as wet digestion, uses chemical decomposition instead of heat. The sample is heated at a much lower temperature in the presence of powerful liquid oxidizing agents.
Common reagents include concentrated nitric acid, sulfuric acid, or hydrogen peroxide. These chemicals break down and dissolve the organic matrix, leaving the mineral elements suspended in an aqueous solution.
Key Advantages of Dry Ashing
Dry ashing is often preferred in specific contexts due to several clear operational benefits.
Simplicity and Minimal Reagents
The procedure is straightforward: weigh the sample, place it in the furnace, and heat. This method eliminates the need to handle, measure, and dispose of large volumes of dangerous, corrosive acids, significantly improving lab safety and reducing procedural complexity.
High Throughput Capability
A single muffle furnace can hold dozens of crucibles at once. This allows a technician to prepare a large batch of samples for ashing simultaneously, making it highly efficient for routine quality control or large-scale studies. Wet digestion, by contrast, is often performed on samples individually or in very small batches.
Complete Organic Destruction
The extremely high temperatures of a muffle furnace are highly effective at completely incinerating the organic matrix. This can result in a "cleaner" ash, free from residual carbon that can sometimes interfere with subsequent analytical steps.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Flaw of Dry Ashing
No method is perfect. The primary advantage of dry ashing—its high heat—is also the source of its most significant limitation.
The Loss of Volatile Elements
The most critical drawback of dry ashing is the potential loss of volatile elements at high temperatures.
Elements like mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), lead (Pb), and selenium (Se) can vaporize and escape during the heating process. This makes dry ashing completely unsuitable if you need to accurately quantify these specific elements. Wet ashing, with its lower temperatures, is required to retain them in the sample solution.
Longer Processing Time
While throughput is high for a batch, the total time for a single dry ashing cycle can be very long. The heating, holding, and cooling phases of a furnace program can take many hours, often running overnight. For a single urgent sample, wet digestion can sometimes be faster.
Potential for Contamination
At high temperatures, there is a minor risk that elements from the sample could react with the crucible itself, or that trace elements from the furnace's interior could contaminate the sample. This is less common but remains a consideration for ultra-trace analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Selecting the correct method requires you to know exactly what you are trying to measure.
- If your primary focus is analyzing thermally stable minerals (like calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium) in many samples: Dry ashing is the most efficient, simple, and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is quantifying volatile or trace elements (like mercury, lead, or arsenic): Wet ashing is the only reliable choice to prevent their loss and ensure accurate results.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and minimizing hazardous waste: Dry ashing avoids the use of strong acids, making it an inherently safer procedure.
Ultimately, understanding the thermal stability of your target analytes is the key to selecting the correct ashing technique for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Dry Ashing | Wet Ashing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Method | Thermal decomposition (high heat) | Chemical decomposition (acids) |
| Key Advantage | Simple, high-throughput, safe | Retains volatile elements |
| Best For | Stable minerals (Ca, Fe, Mg, K) | Volatile elements (Hg, As, Pb, Se) |
| Reagent Use | Minimal to none | Significant (strong acids) |
| Sample Throughput | High (batch processing) | Low (individual/small batches) |
Ready to Optimize Your Ashing Process?
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for accurate and efficient sample preparation. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including high-performance muffle furnaces ideal for dry ashing.
We help laboratories like yours:
- Increase throughput with furnaces designed for high-volume batch processing.
- Enhance safety by minimizing the need for hazardous acid handling.
- Achieve consistent results with precise temperature control for complete organic destruction.
Let's discuss your lab's specific needs. Whether you're analyzing stable minerals or require a solution for volatile elements, our experts can guide you to the right equipment.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect sample preparation solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace required for post-treatment after the hot-press sintering of LLZO?
- What is the muffle furnace 1800 degree? High-Temp Precision for Advanced Materials
- What is the difference between oven and muffle furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Equipment
- What is the function of an annealing furnace in Na3PS4 synthesis? Achieve High-Conductivity Cubic-Phase Electrolytes
- Which of the following are the important temperature controls used in sintering furnace? Mastering Precise Thermal Profiles for Superior Materials
- What is the function of high-temperature digestion furnaces and lithium borate fluxes? Expert REE Sample Preparation
- What function does a high-temperature sintering furnace serve in biomass carbonization? Unlock Superior MFC Performance
- Why is precise temperature control in laboratory ovens critical for photocatalytic pigments? Protect Color & Function



















