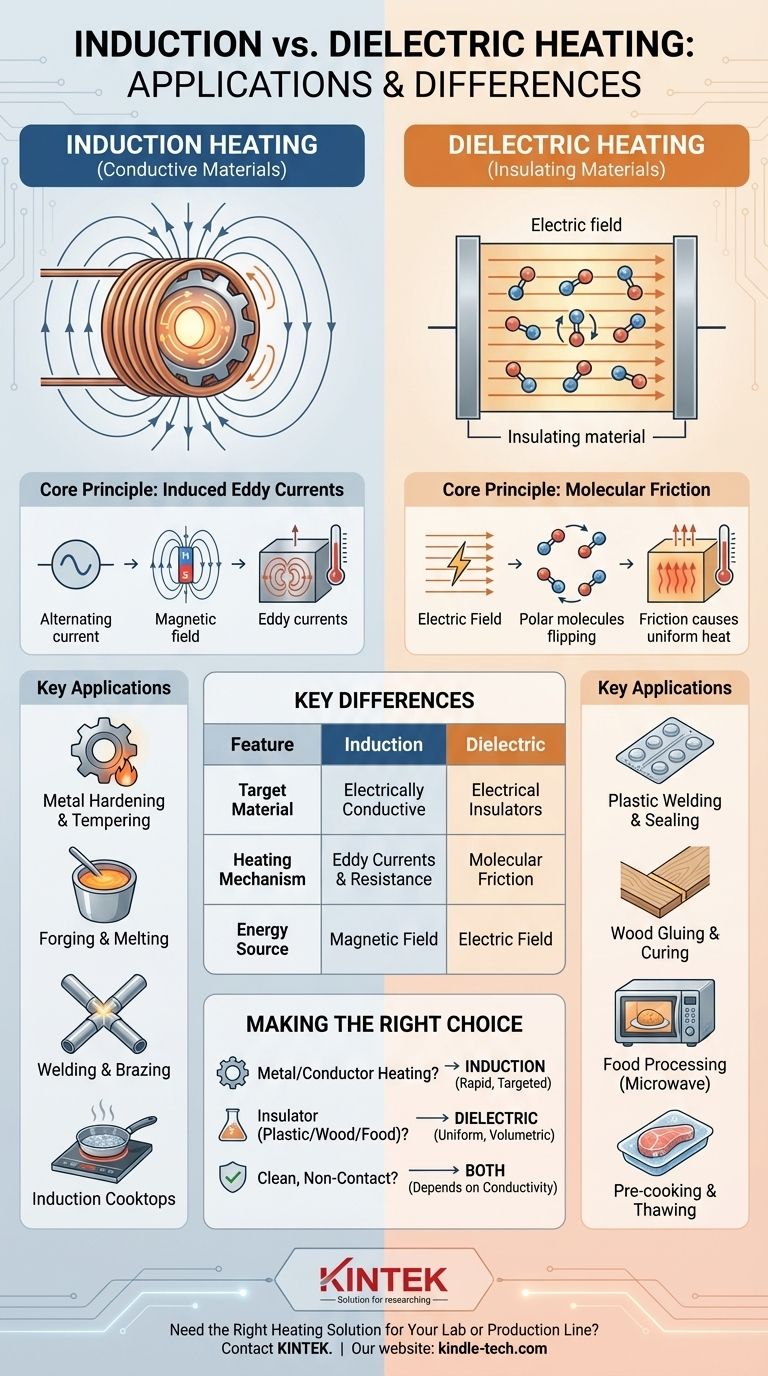
In simple terms, induction heating is used for electrically conductive materials like metals, while dielectric heating is used for electrical insulators like plastics, wood, and food. Induction heating uses a magnetic field to induce electrical currents inside the material, causing it to heat up from within. Dielectric heating, on the other hand, uses a high-frequency electric field to cause molecular friction within an insulating material, which generates the heat.
The fundamental difference lies in the material being heated. If the material conducts electricity, you use induction heating. If it is an insulator (a dielectric), you use dielectric heating. This single principle dictates every application.

How Induction Heating Works (And Where It's Used)
Induction heating is a non-contact process that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to produce heat directly inside a conductive object.
The Core Principle: Induced Eddy Currents
An alternating current is passed through a coil, creating a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive workpiece, like a piece of steel, is placed within this field, small, swirling electrical currents—known as eddy currents—are induced within the metal. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, localized heat.
Key Application: Metal Hardening and Tempering
This is one of the most common industrial uses. The surface of a metal part, like a gear or an engine crankshaft, can be heated with extreme speed and precision. This allows for selective hardening of wear-prone areas without altering the core properties of the part, dramatically increasing its durability.
Key Application: Forging and Melting
In forges and foundries, induction furnaces are used to heat metal billets to temperatures required for shaping or to melt metals for casting. Because the heat is generated within the metal itself and there is no direct contact with a flame, the process is extremely fast, clean, and non-polluting, preventing product contamination.
Key Application: Welding and Brazing
Induction heating provides the precise, rapid heat needed to join metal components. It's commonly used in manufacturing to braze or solder parts together, offering a highly repeatable and automated process.
Consumer Application: Induction Cooktops
A relatable example is the modern induction cooktop. The coil beneath the ceramic glass generates a magnetic field that directly heats the conductive metal of the pot or pan. The glass surface itself, being an insulator, remains cool to the touch.
How Dielectric Heating Works (And Where It's Used)
Dielectric heating targets materials that are electrical insulators. It's often described as the same principle that powers a household microwave oven.
The Core Principle: Molecular Friction
The insulating material is placed between two electrodes that create a high-frequency alternating electric field. If the material contains polar molecules (which have a positive and negative end, like water), these molecules attempt to rapidly align themselves with the changing field. This rapid flipping back and forth creates intermolecular friction, which generates uniform heat throughout the material's volume.
Key Application: Plastic Welding and Sealing
Dielectric heating is widely used to weld thermoplastic materials. It's the technology behind the seals on PVC blister packs, vinyl binders, and inflatable products. The process rapidly melts and fuses the plastic along a specific seam.
Key Application: Wood Gluing and Curing
In furniture manufacturing and lumber production, dielectric heating can cure glue lines almost instantly. The electric field selectively heats the moisture in the water-based glue, curing the joint from the inside out without overheating the wood itself.
Key Application: Food Processing
The microwave oven is the most famous application of dielectric heating. It uses an electric field to agitate the polar water molecules within food, cooking it quickly and evenly from within. This principle is also used on an industrial scale for pre-cooking, thawing, and pasteurizing food products.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Differences
While both methods are forms of high-frequency electric heating, they are not interchangeable. Choosing the wrong one will result in a process that is either completely ineffective or dangerously inefficient.
Target Material: Conductors vs. Insulators
This is the most critical distinction. Induction heating is only effective on materials that can conduct electricity. Dielectric heating is only effective on materials that are poor electrical conductors (insulators) but have polar molecules that can be agitated.
The Energy Source: Magnetic vs. Electric Field
Induction heating relies on a magnetic field to induce current. Dielectric heating relies on an electric field to cause molecular rotation.
Heating Mechanism: Current Flow vs. Molecular Friction
In induction heating, the heat comes from the material's resistance to eddy currents. In dielectric heating, the heat comes from the friction between oscillating molecules. This is why induction heating can heat a block of dry steel, while dielectric heating cannot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your decision is not a matter of preference but of physics. The electrical properties of your workpiece will determine the correct method.
- If your primary focus is heating a metal or other conductor: Induction heating is your only viable and highly efficient option for targeted, rapid heating.
- If your primary focus is heating an insulator like plastic, wood, or food: Dielectric heating is the correct method to generate uniform heat throughout the material's volume.
- If your primary focus is a clean, non-contact process: Both methods excel at this, but your choice is dictated entirely by the material's conductivity.
Ultimately, understanding whether your material conducts or insulates electricity is the key to selecting the right heating technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Dielectric Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Target Material | Electrically Conductive (e.g., Metals) | Electrical Insulators (e.g., Plastics, Wood, Food) |
| Heating Mechanism | Induced Eddy Currents & Resistance | Molecular Friction of Polar Molecules |
| Energy Source | Magnetic Field | Electric Field |
| Primary Applications | Metal Hardening, Forging, Brazing, Induction Cooktops | Plastic Welding, Wood Glue Curing, Food Processing (Microwaves) |
Need the Right Heating Solution for Your Lab or Production Line?
Understanding the difference between induction and dielectric heating is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need to implement these technologies effectively.
Whether you are working with conductive metals or insulating materials like plastics and composites, we can help you select the right system to ensure efficiency, repeatability, and superior results for your specific application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your processes. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual button battery sealing machine (digital display)
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of induction heating? High Cost & Geometric Limits Explained
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in HEA for nuclear fusion? Engineering Advanced Alloy Purity
- What is a high-frequency induction furnace? Achieve Fast, Clean, and Precise Metal Melting
- What is needed for induction heating? Build Your Efficient, Non-Contact Heating System
- What is an induction heater for forging metal? A High-Speed, Flameless Heating Solution
- Can an induction furnace melt titanium? Mastering the Challenge of Melting Reactive Metals
- What is the structure of an induction furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What is the primary function of a high-frequency induction melting furnace for CuNi alloys? Achieve Atomic Homogeneity














