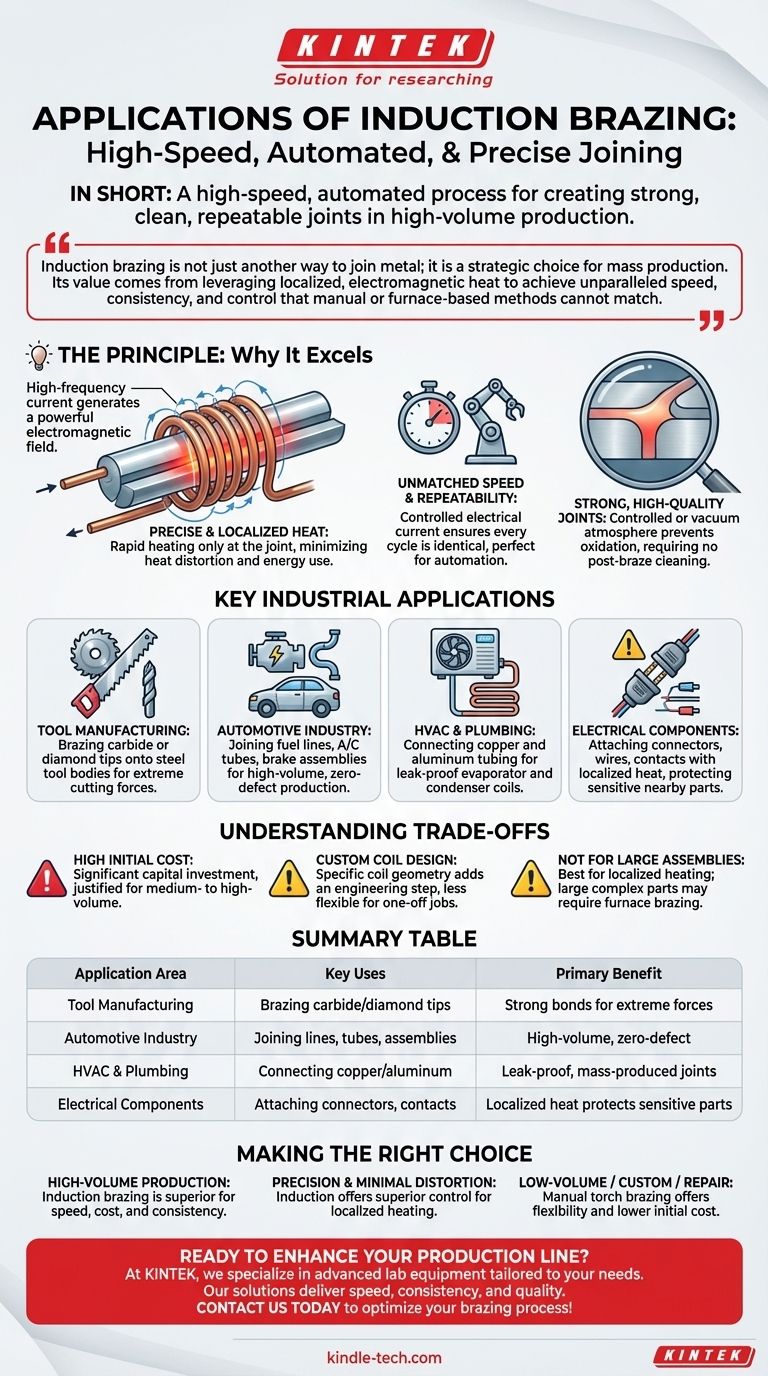
In short, induction brazing is a high-speed, automated process used extensively in manufacturing for creating strong, clean, and highly repeatable joints. Its applications are most common in high-volume production lines where precision is critical, such as attaching carbide tips to cutting tools, joining fuel lines in the automotive industry, or connecting tubing in HVAC systems.
Induction brazing is not just another way to join metal; it is a strategic choice for mass production. Its value comes from leveraging localized, electromagnetic heat to achieve unparalleled speed, consistency, and control that manual or furnace-based methods cannot match.
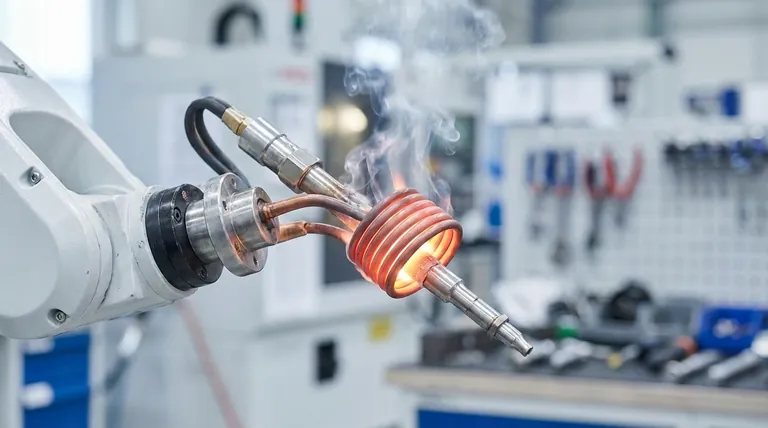

The Principle: Why Induction Brazing Excels
To understand its applications, you must first understand its core advantage: targeted, non-contact heating. The process uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil.
Precise and Localized Heat
This current generates a powerful electromagnetic field around the parts to be joined. This field induces electrical currents directly within the metal parts, causing them to heat up rapidly right at the joint area.
Unlike a furnace that heats the entire assembly, induction heating is extremely focused. This minimizes the risk of heat distortion in the rest of the part and consumes far less energy.
Unmatched Speed and Repeatability
Because the heating is controlled by an electrical current, the process is incredibly fast and precisely repeatable. Once calibrated, every cycle delivers the exact same amount of heat for the exact same duration.
This makes induction brazing perfect for automation and robotic integration, enabling the production of thousands of identical components per day.
Strong, High-Quality Joints
The process allows for brazing in a controlled or even a vacuum atmosphere, which prevents oxidation and results in clean, strong joints that often require no post-braze cleaning. The filler metal flows evenly due to the uniform heating, creating a durable metallurgical bond.
Key Industrial Applications
The combination of speed, precision, and repeatability makes induction brazing the go-to method in several key industries.
Tool Manufacturing
This is a classic application. Induction is used to braze carbide or diamond tips onto steel tool bodies for items like saw blades, drill bits, and mining tools. The process is fast and creates a bond strong enough to withstand extreme cutting forces.
Automotive Industry
Automotive manufacturing relies on high-volume, zero-defect processes. Induction brazing is used for joining fuel lines, A/C tubes, brake line assemblies, and even certain engine and transmission components made from steel, aluminum, and copper.
HVAC and Plumbing
In the production of air conditioning and refrigeration systems, induction is used to join copper and aluminum tubes reliably. The speed and repeatability are essential for mass-producing leak-proof evaporator and condenser coils.
Electrical Components
The electronics industry uses induction brazing to attach connectors, wires, and contacts to electrical terminals. The localized heating is critical to avoid damaging sensitive nearby components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Induction heating systems and the associated automation represent a significant capital investment. The cost is typically only justified for medium- to high-volume production runs where the return on investment can be realized through speed and reduced labor.
Custom Coil Design
The induction coil, which generates the magnetic field, must be designed and shaped specifically for the geometry of the part being brazed. This adds an engineering step and makes the process less flexible for one-off jobs or highly varied part shapes.
Not Ideal for Very Large or Complex Assemblies
Induction is best for localized heating around a joint. For brazing large, intricate assemblies where the entire part needs to be heated slowly and uniformly to prevent stress, other methods like vacuum furnace brazing are often superior.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right brazing method depends entirely on your production goals, part geometry, and budget.
- If your primary focus is high-volume mass production: Induction brazing is the superior choice for its unmatched speed, low per-unit cost, and process consistency.
- If your primary focus is precision with minimal heat distortion: Induction brazing's localized heating offers superior control over furnace brazing, protecting the integrity of the overall assembly.
- If your primary focus is low-volume, custom work, or repair: Manual torch brazing offers far greater flexibility and lower initial cost, making it more practical for non-production environments.
Ultimately, selecting the correct joining process is about aligning the method's strengths with your specific manufacturing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Manufacturing | Brazing carbide/diamond tips to tool bodies | Strong bonds for extreme cutting forces |
| Automotive Industry | Joining fuel lines, A/C tubes, brake assemblies | High-volume, zero-defect production |
| HVAC & Plumbing | Connecting copper/aluminum tubing for coils | Leak-proof, mass-produced joints |
| Electrical Components | Attaching connectors, wires, and contacts | Localized heat protects sensitive parts |
Ready to enhance your production line with precision induction brazing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your manufacturing needs. Whether you're in automotive, HVAC, or tool manufacturing, our solutions deliver the speed, consistency, and quality your high-volume production requires.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your brazing process and drive efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing



















