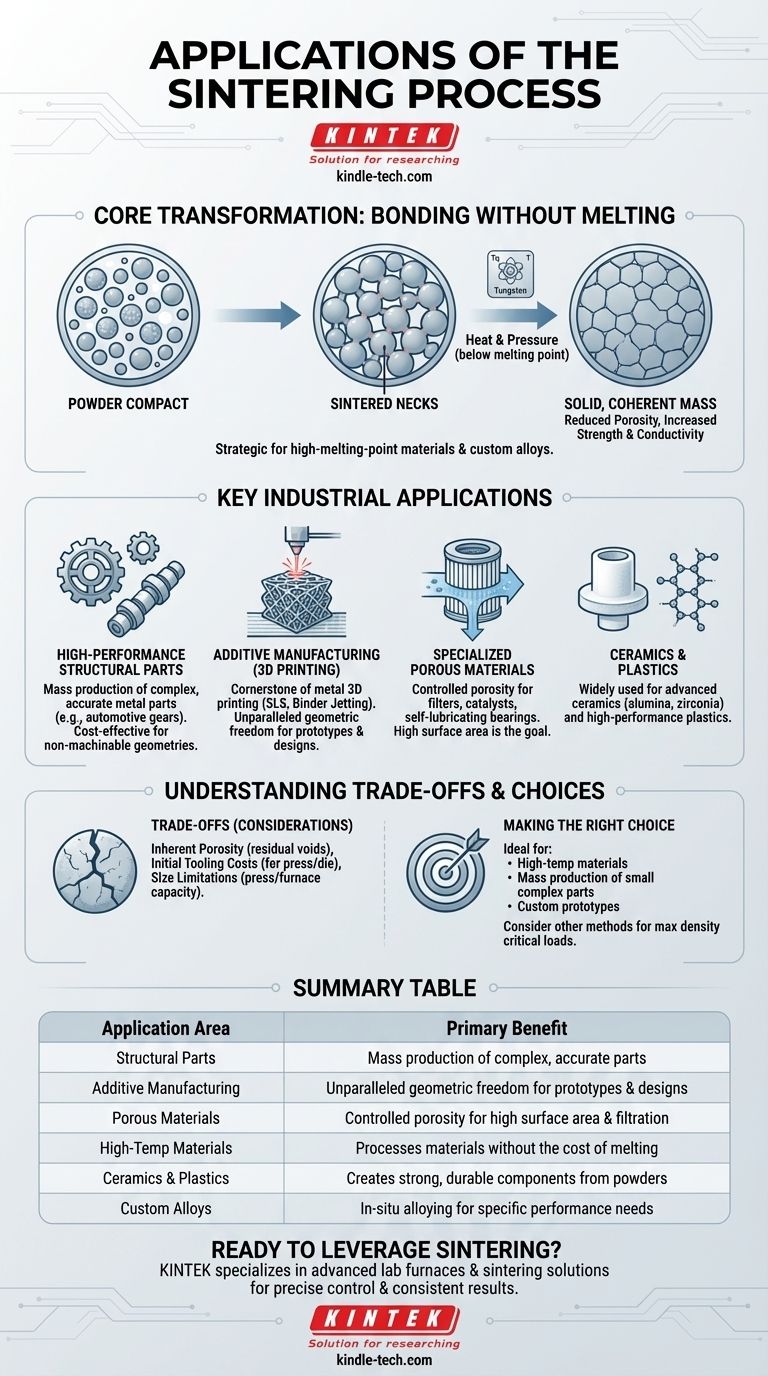
At its core, the sintering process is used to transform powdered material into a solid, coherent mass using heat and pressure, without melting it. Its key applications include fabricating parts from high-melting-point metals, creating complex components via 3D printing, and precisely controlling a material's final properties like density, strength, and conductivity.
Sintering is not just an alternative to melting; it is a strategic manufacturing choice. Its primary value lies in creating high-performance parts with material combinations and complex geometries that are often impossible or uneconomical to achieve through traditional casting or machining.

How Sintering Fundamentally Transforms Materials
To understand its applications, you must first understand how sintering alters a material at the particle level. The process is chosen specifically for the changes it imparts.
Bonding Without Melting
Sintering heats a compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together and forming strong "sintered necks" that give the final part its structural integrity.
This is especially critical for materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten or molybdenum, where melting is impractical or prohibitively expensive.
Reducing Porosity for Enhanced Strength
The initial powder compact is full of tiny voids. During sintering, particles fuse and rearrange, significantly reducing this porosity and increasing the material's density.
This densification directly improves mechanical properties like strength and durability. It also enhances electrical and thermal conductivity by creating a more continuous path through the material.
Creating Custom Alloys In-Situ
Sintering provides a unique opportunity to create alloys by simply mixing powders of different elements. For example, powders of iron, copper, and graphite can be blended and then sintered.
During the heating process, the elements diffuse into one another, forming a homogenous alloy throughout the part. This allows for the creation of custom materials tailored to specific performance requirements.
Key Industrial Applications
The principles of sintering translate into several powerful manufacturing applications across various industries.
High-Performance Structural Parts
Sintering is a cost-effective method for the mass production of small, complex, and highly accurate metal parts. This is common in the automotive industry for gears, camshaft lobes, and bearing races.
The process excels at creating non-machinable geometries, offering design freedom that would be too costly or technically impossible with traditional subtractive manufacturing.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Sintering is a cornerstone of metal 3D printing (e.g., Selective Laser Sintering, SLS, or Binder Jetting). A laser or binding agent is used to selectively sinter powder layer by layer, building a complex part from a digital model.
This application provides unparalleled control, consistency, and energy savings compared to melting, enabling the creation of intricate, one-of-a-kind metal forms.
Specialized Porous Materials
While many applications aim to eliminate porosity, some leverage sintering to control and preserve it.
By only partially sintering a powder, it's possible to create a strong but porous structure. These materials are ideal for use as filters, catalysts, or self-lubricating bearings, where a high surface area or gas absorbency is the primary goal.
Ceramics and Plastics
Though often associated with metals, the sintering process is also widely used for manufacturing advanced ceramics, such as alumina and zirconia, and certain high-performance plastics. The fundamental principle of fusing particles without melting remains the same.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is without limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging where sintering may not be the optimal choice.
Inherent Porosity
Even with advanced techniques, achieving 100% density is difficult. Most sintered parts retain a small amount of residual porosity, which can be the starting point for cracks in highly stressed applications. For critical components requiring maximum fatigue life, forged or wrought materials are often superior.
Initial Tooling Costs
For powder metallurgy applications that use a press and die, the initial tooling cost can be significant. This makes the process most cost-effective for large production volumes where the tooling cost can be amortized over thousands of parts.
Size Limitations
The size of a part that can be produced is often limited by the capacity of the press used for compaction and the ability of the furnace to provide uniform heat. Very large components are typically not suitable for conventional sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials: Sintering is ideal as it avoids the extreme energy costs and technical challenges of melting.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex, small parts: Sintering offers excellent repeatability and cost-effectiveness compared to machining each individual part.
- If your primary focus is creating custom prototypes or intricate designs: Sintering, especially within 3D printing, provides unparalleled geometric freedom.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density for critical loads: You must consider that sintering may leave residual porosity, and other methods like forging might be superior.
By understanding its core principles and trade-offs, you can leverage sintering to solve manufacturing challenges that other processes simply cannot address.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Cases | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Parts | Gears, bearings, automotive components | Mass production of complex, accurate parts |
| Additive Manufacturing | Metal 3D printing (SLS, Binder Jetting) | Unparalleled geometric freedom for prototypes & designs |
| Porous Materials | Filters, catalysts, self-lubricating bearings | Controlled porosity for high surface area & filtration |
| High-Temp Materials | Tungsten, molybdenum components | Processes materials without the cost of melting |
| Ceramics & Plastics | Alumina, zirconia, high-performance polymers | Creates strong, durable components from powders |
| Custom Alloys | Tailored material properties (e.g., Iron-Copper-Graphite) | In-situ alloying for specific performance needs |
Ready to leverage sintering for your next project?
Whether you are developing high-performance metal components, exploring the possibilities of metal 3D printing, or need to create custom porous materials, the right equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and sintering solutions that deliver precise temperature control and uniform heating for consistent, high-quality results.
Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you:
- Achieve optimal density and strength in your sintered parts.
- Experiment with custom material combinations and complex geometries.
- Scale your R&D efforts to production with reliable and efficient furnaces.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials



















