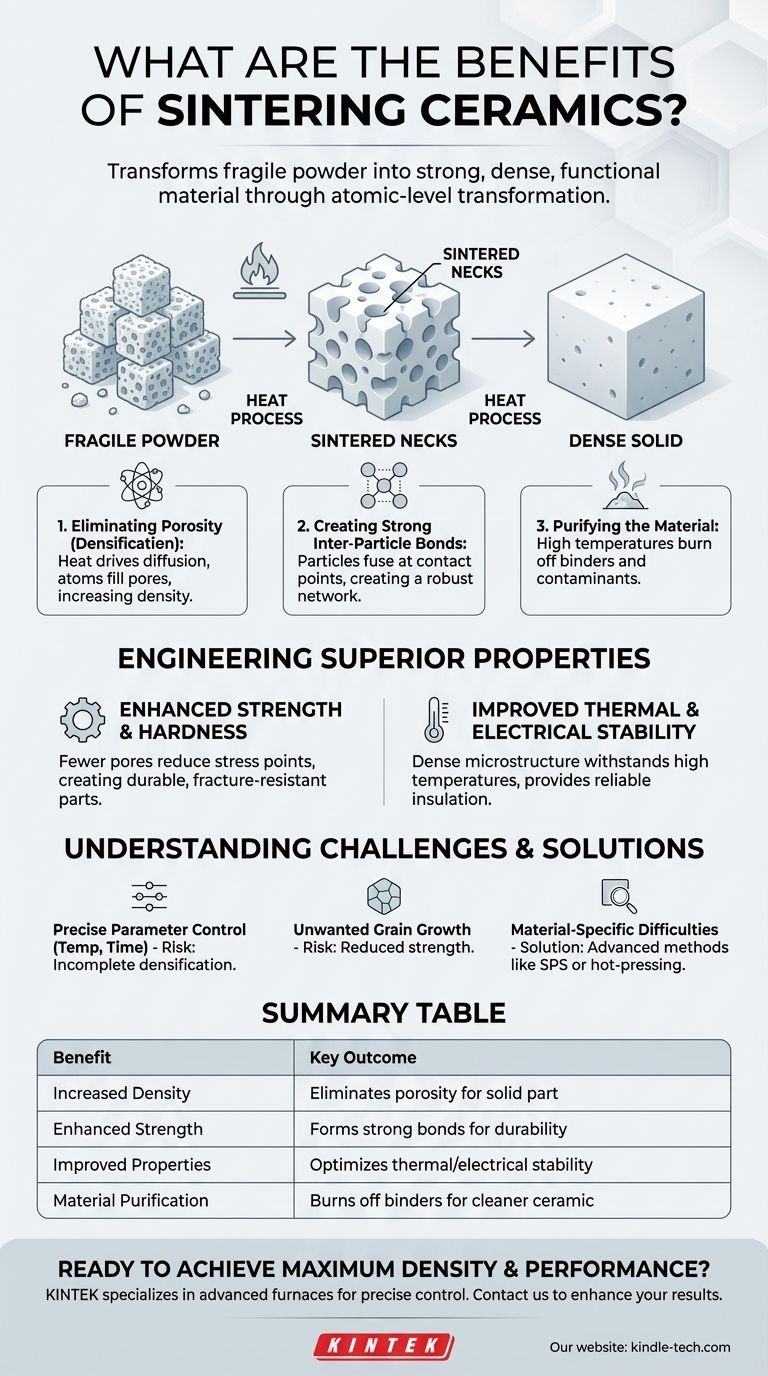
In essence, sintering transforms a fragile, compacted ceramic powder into a strong, dense, and functional material. This process is the most critical step in creating advanced ceramics, as it bonds individual particles together, eliminates internal pores, and develops the final microstructure that dictates the material's mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties.
Sintering is not merely a heating process; it is a controlled atomic-level transformation. It solves the fundamental problem of converting a loose collection of particles into a solid, engineered component with a uniform structure and superior performance characteristics.

The Fundamental Transformation: From Powder to Solid
Sintering creates a solid object by encouraging atoms to move between individual powder particles, fundamentally changing the material's structure from a loose compact to a dense polycrystalline solid.
Eliminating Porosity and Increasing Density
The primary goal of sintering is densification. The initial compacted powder, or "green body," is highly porous.
During sintering, heat drives a process called diffusion, where atoms migrate to fill the empty spaces (pores) between particles. This mass transfer dramatically increases the material's overall density.
For example, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) can achieve a relative density of 92.7% in BPO4 ceramics, compared to just 74.6% with conventional methods, highlighting its effectiveness in eliminating pores.
Creating Strong Inter-Particle Bonds
As particles are heated, they begin to fuse at their contact points. These initial connections are called sintered necks.
As the process continues, these necks grow wider, creating a strong, continuous network throughout the material. This is what transforms the fragile powder compact into a robust, monolithic part.
Purifying the Material
The sintering process often serves a dual purpose of purification. High temperatures help burn off and eliminate lubricants or binders that were used to form the initial powder shape.
It can also reduce surface oxygen and other contaminants, resulting in a cleaner, more chemically stable final ceramic.
Engineering Superior Material Properties
The microstructure created during sintering directly translates into enhanced performance. By carefully controlling the process, manufacturers can engineer ceramics for specific, demanding applications.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
The reduction of pores and the formation of strong inter-particle bonds directly lead to a significant increase in mechanical strength and hardness.
Fewer pores mean fewer stress concentration points where cracks can initiate, making the final ceramic part more durable and resistant to fracture. This is why sintered ceramics are used for cutting tools and refractory materials.
Improving Thermal and Electrical Stability
A dense, uniform microstructure improves a material's ability to withstand high temperatures and act as a reliable electrical insulator.
This thermal stability and insulating capability are critical for applications like furnace linings, spark plugs, and substrates for electronic circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While beneficial, sintering is a complex process that requires precise control to achieve the desired outcomes.
The Need for Precise Parameter Control
Sintering outcomes are highly sensitive to process parameters like temperature, time, and atmosphere.
Slight deviations can lead to incomplete densification, an undesirable microstructure, or even damage to the part. Achieving consistency requires sophisticated equipment and deep process knowledge.
The Risk of Unwanted Grain Growth
The same heat that drives densification can also cause the individual crystalline grains to grow larger. Excessive grain growth can be detrimental, often reducing the final material's strength and fracture toughness.
A key challenge is to achieve maximum density while minimizing grain growth, a balancing act that defines successful sintering.
Overcoming Material-Specific Difficulties
Some advanced ceramics, like silicon nitride (Si3N4) and silicon carbide (SiC), are notoriously difficult to densify using standard methods.
For these materials, specialized techniques are required. Liquid-phase sintering, where an additive melts to aid particle rearrangement, or hot-pressure sintering, which applies external pressure, are used to overcome these challenges and drive densification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The chosen sintering method depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard ceramics: Conventional solid-state sintering of materials like alumina or zirconia offers a reliable and well-understood path.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult, high-performance materials: Consider liquid-phase sintering or pressure-assisted methods like hot pressing to overcome natural resistance to densification.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in minimal time: Explore advanced methods like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), which can dramatically accelerate the process and improve final density.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is what unlocks the full potential of advanced ceramic materials.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Outcome |
|---|---|
| Increased Density | Eliminates porosity, creating a solid, monolithic part. |
| Enhanced Strength | Forms strong inter-particle bonds for superior durability. |
| Improved Properties | Optimizes thermal stability and electrical insulation. |
| Material Purification | Burns off binders and contaminants for a cleaner ceramic. |
Ready to achieve maximum density and performance for your ceramic components?
The sintering process is critical, and the right equipment makes all the difference. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and sintering solutions tailored for materials research and production. Our expertise helps you precisely control temperature, atmosphere, and pressure to perfect your ceramic's microstructure and properties.
Contact us today to discuss your specific ceramic sintering challenges and discover how our solutions can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a tubular furnace work? A Guide to Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















