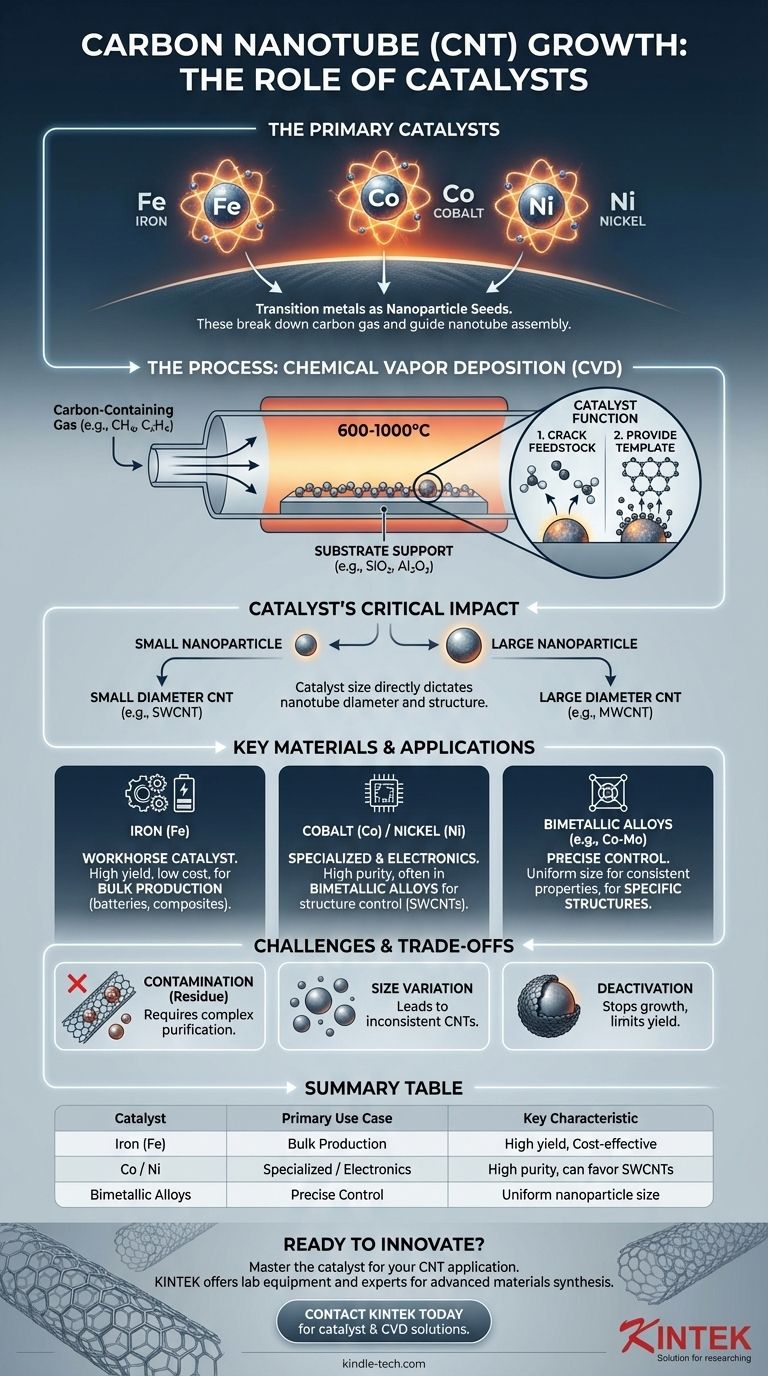
The primary catalysts for carbon nanotube (CNT) growth are transition metals, most commonly iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni). These materials are used in the form of nanoparticles, which serve as the "seeds" for nanotube formation. During synthesis, these metallic particles break down a carbon-containing gas and provide a catalytic surface upon which the carbon atoms assemble into the cylindrical, hexagonal lattice structure of a nanotube.
The choice of catalyst is not just about a specific element; it is about controlling the size, composition, and state of catalyst nanoparticles. These tiny particles directly dictate the diameter, structure, and quality of the resulting carbon nanotubes, making catalyst engineering the most critical step in the entire production process.
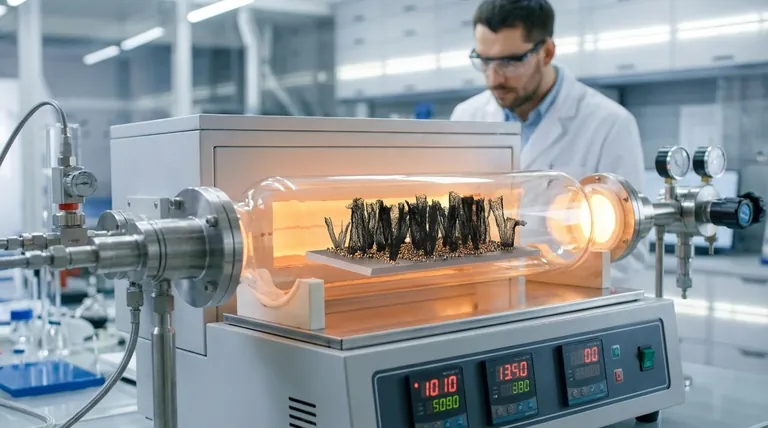

The Fundamental Role of a Catalyst in CNT Synthesis
Carbon nanotubes do not form spontaneously. Their synthesis is a carefully controlled process where the catalyst acts as the essential intermediary between a simple carbon source and the complex final structure.
Why a Catalyst is Necessary
The catalyst performs two critical functions. First, it cracks the feedstock, breaking down the bonds of a carbon-containing gas (like methane, ethylene, or acetylene). Second, it provides a high-energy, nanoscale template where carbon atoms can precipitate and arrange themselves into the stable hexagonal structure of a nanotube.
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Process
The most common synthesis method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In this process, a substrate coated with catalyst nanoparticles is heated to high temperatures (typically 600-1000°C). A carbon-containing gas is then flowed over the substrate, where it decomposes on the catalyst surface, initiating CNT growth.
Catalyst Nanoparticles: The Seed of Growth
The size of the catalyst nanoparticle directly correlates with the diameter of the nanotube that grows from it. A smaller nanoparticle will produce a smaller diameter nanotube. This relationship is crucial for producing specific types of CNTs, such as single-wall or multi-wall varieties.
Key Catalytic Materials and Their Properties
While many metals show some catalytic activity, a select few have become the industry standard due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Iron (Fe): The Workhorse Catalyst
Iron is by far the most widely used catalyst for CNT production. It offers a superb balance of high catalytic activity, high yield, and low cost, making it ideal for the bulk production required for applications like lithium-ion batteries.
Cobalt (Co) and Nickel (Ni)
Cobalt and nickel are also highly effective catalysts. They are often used in specialized applications or as part of bimetallic alloys (e.g., Fe-Co, Co-Mo) to fine-tune the growth process, increase yield, or preferentially grow specific types of CNTs like single-wall nanotubes (SWCNTs).
The Substrate's Role
The catalyst nanoparticles are typically deposited on a stable, inert substrate support material, such as silicon dioxide (SiO₂), magnesium oxide (MgO), or alumina (Al₂O₃). This support prevents the nanoparticles from clumping together (sintering) at high synthesis temperatures, ensuring a high density of active growth sites.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, the catalyst also introduces the primary challenges in producing high-quality CNTs for demanding applications.
Catalyst Purity and Contamination
The single biggest challenge is residual catalyst contamination. After synthesis, metallic particles remain embedded within the CNT material. These impurities degrade the electrical and mechanical properties and must be removed through a complex and costly acid purification process, especially for electronics or battery applications.
Controlling Nanoparticle Size
Achieving a uniform distribution of catalyst nanoparticle sizes is difficult. A wide size distribution results in a mix of CNTs with varying diameters and properties, which is undesirable for high-performance applications that demand consistency.
Catalyst Deactivation
During growth, the catalyst particle can become encapsulated in layers of amorphous carbon or other byproducts. This deactivates the catalyst, stopping CNT growth and limiting the final length and yield of the nanotubes. Process parameters like temperature, gas concentration, and residence time must be optimized to mitigate this effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a catalyst system is driven entirely by the intended application and the desired properties of the final carbon nanotube product.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, bulk production (e.g., for composites or battery additives): An iron-based catalyst on an alumina support is the industry standard due to its unmatched cost-effectiveness and high yield.
- If your primary focus is high purity for electronics: A nickel-based catalyst might be preferred, often combined with a growth method and rigorous purification process designed to minimize metallic residue.
- If your primary focus is controlling CNT structure (e.g., specific single-wall nanotubes): The strategy shifts to bimetallic alloys (like Co-Mo) and advanced techniques to create catalyst nanoparticles with extremely precise, uniform diameters.
Ultimately, mastering the catalyst is the key to unlocking the transformative potential of carbon nanotubes for any application.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Bulk Production (e.g., batteries, composites) | High yield, cost-effective, industry standard |
| Cobalt (Co) / Nickel (Ni) | Specialized applications, high purity electronics | Often used in bimetallic alloys, can favor SWCNT growth |
| Bimetallic Alloys (e.g., Co-Mo) | Precise structure control (e.g., specific SWCNTs) | Enables uniform nanoparticle size for consistent CNT properties |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or product development? The right catalyst system is critical for achieving the specific CNT diameter, structure, and purity your application demands. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for advanced materials synthesis, including CNT growth. Our experts can help you select the right tools for your catalyst engineering and CVD processes. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation in nanotechnology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















