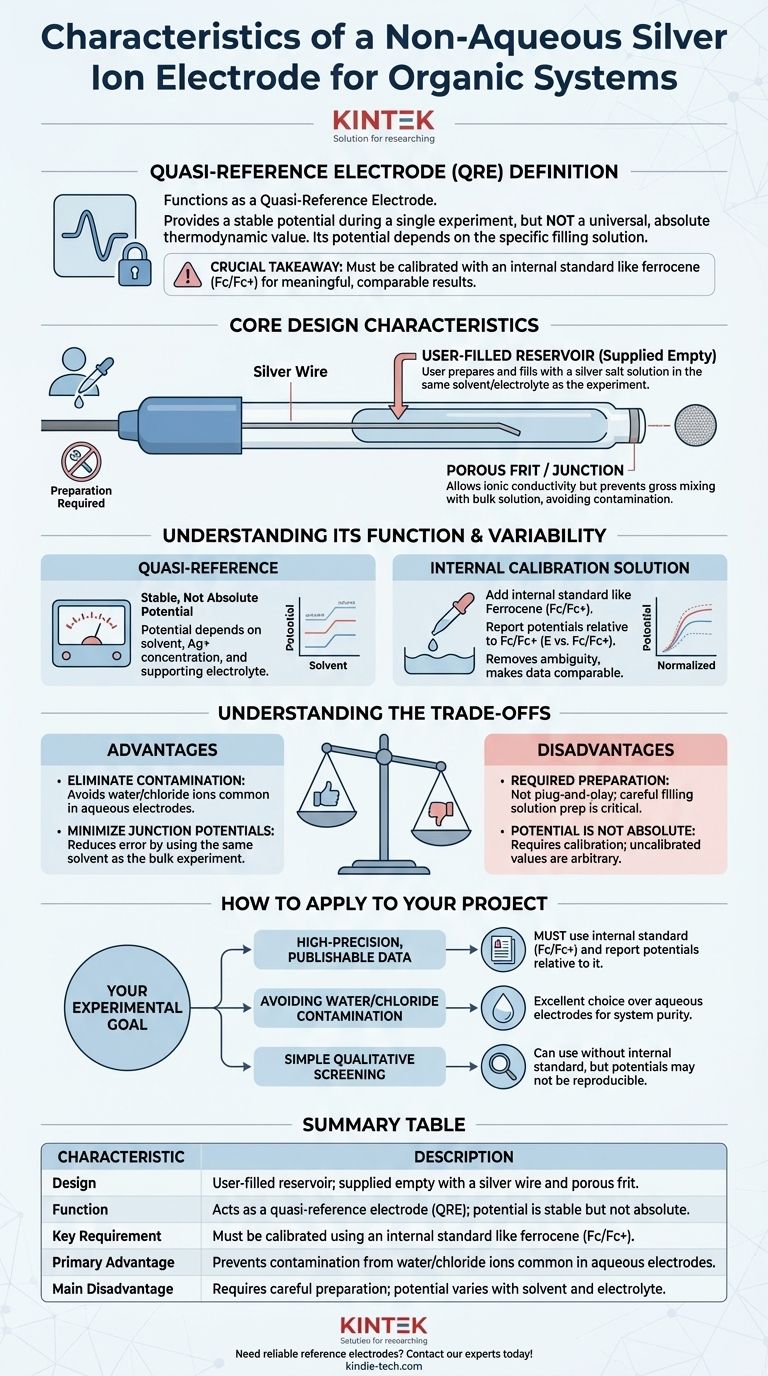
A non-aqueous silver ion electrode is a highly specialized reference electrode designed specifically for electrochemical measurements in organic solvents. Its defining characteristic is its user-configurable design; it is supplied empty, requiring the user to prepare and add a filling solution. This makes it a flexible but demanding tool that provides a stable potential within a single experiment, rather than a universal, absolute potential like its aqueous counterparts.
The crucial takeaway is that a non-aqueous silver ion electrode functions as a quasi-reference electrode (QRE). Its potential is not fixed but depends on the specific filling solution you prepare. For results to be meaningful and comparable, you must calibrate its potential during each experiment using an internal standard like ferrocene.

Core Design Characteristics
The unique physical and chemical nature of this electrode dictates how it must be handled and used to ensure reliable measurements.
User-Filled Reservoir
The most notable feature is that the electrode is supplied empty. It consists of a silver wire housed within a glass or polymer body that you must fill with an appropriate solution. This is a deliberate design choice, not a cost-saving measure.
The Role of the Filling Solution
You create the reference potential by preparing a filling solution, typically a known concentration of a silver salt (e.g., silver nitrate, AgNO₃, or silver triflate, AgOTf) dissolved in the same solvent and containing the same supporting electrolyte as your main experiment. This preparation is the most critical step in using the electrode correctly.
Isolation from the Bulk Solution
The electrode tip features a porous frit or junction. This allows for ionic conductivity between the internal filling solution and the bulk solution in your electrochemical cell, which is necessary to complete the electrical circuit. However, it prevents gross mixing of the two solutions, which would contaminate your experiment and destabilize the reference potential.
Understanding its Function as a Quasi-Reference Electrode (QRE)
The term "quasi-reference electrode" perfectly describes the behavior of a user-filled silver ion electrode in organic systems.
What is a QRE?
A QRE provides a stable potential during a single, continuous experiment. However, this potential is not based on a standardized, universally agreed-upon thermodynamic value. It is "quasi" because its value depends entirely on the composition and concentration of the filling solution you prepared.
The Problem of Potential Variability
The potential of your Ag/Ag+ QRE will differ based on the solvent used, the concentration of the silver salt, and the specific supporting electrolyte. This means a potential of "+0.5 V" in one experiment is not directly comparable to "+0.5 V" in another experiment if the conditions or filling solution were even slightly different.
The Solution: Internal Calibration
To obtain meaningful, reproducible, and publishable data, you must calibrate the QRE in situ. This is done by adding a small amount of an internal standard with a well-known redox potential to your analyte solution.
In non-aqueous electrochemistry, the ferrocene/ferrocenium (Fc/Fc+) couple is the universally accepted standard. After your experiment, you simply report all measured potentials relative to the observed potential of the Fc/Fc+ couple (E vs. Fc/Fc+). This practice removes the ambiguity of the QRE and makes your results comparable to research from any other laboratory.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using a non-aqueous QRE involves a clear set of advantages and disadvantages that you must weigh for your specific application.
Advantage: Eliminating Contamination
The primary reason to use a non-aqueous reference electrode is to avoid contaminating your sensitive organic system with water or chloride ions, which are unavoidable when using standard aqueous electrodes like Ag/AgCl or SCE.
Advantage: Minimizing Junction Potentials
Using a filling solution with the same solvent as your bulk experiment dramatically reduces the liquid junction potential. This large, unstable, and unknown potential, which forms at the interface of two different solvents (e.g., water and acetonitrile), is a major source of error when using aqueous electrodes in organic media.
Disadvantage: Required Preparation
This electrode is not "plug-and-play." It requires careful preparation of the filling solution. An improperly prepared or contaminated solution will result in an unstable, drifting potential that invalidates your entire measurement.
Disadvantage: Potential is Not Absolute
As discussed, the potential is only stable, not absolute. Failing to calibrate against an internal standard like ferrocene means your potential values are arbitrary and cannot be reliably compared or reproduced.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The correct use of this electrode depends entirely on your experimental goals.
- If your primary focus is high-precision, publishable data: You must use an internal standard like ferrocene and report all potentials relative to the Fc/Fc+ redox couple.
- If your primary focus is avoiding water/chloride contamination: This electrode is an excellent choice over any aqueous alternative, ensuring the purity of your organic system.
- If your primary focus is simple qualitative screening: You may use the electrode without an internal standard, but you must accept that the potentials may not be perfectly reproducible between experiments.
Properly prepared and calibrated, the non-aqueous silver ion electrode is an indispensable tool for reliable electrochemical analysis in organic media.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Design | User-filled reservoir; supplied empty with a silver wire and porous frit. |
| Function | Acts as a quasi-reference electrode (QRE); potential is stable but not absolute. |
| Key Requirement | Must be calibrated using an internal standard like ferrocene (Fc/Fc+). |
| Primary Advantage | Prevents contamination from water/chloride ions common in aqueous electrodes. |
| Main Disadvantage | Requires careful preparation; potential varies with solvent and electrolyte. |
Need reliable reference electrodes for your organic electrochemistry work? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrodes designed for precise, contaminant-free measurements in non-aqueous systems. Our products help researchers like you achieve accurate, reproducible results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying
- Which solvent is normally used in IR spectroscopy? Optimize Your Sample Prep for Clearer Results
- Do cannabinoids evaporate? How to Preserve Potency and Prevent Degradation
- What precautions should be taken in a chemistry lab? Master the RAMP Framework for Ultimate Safety














