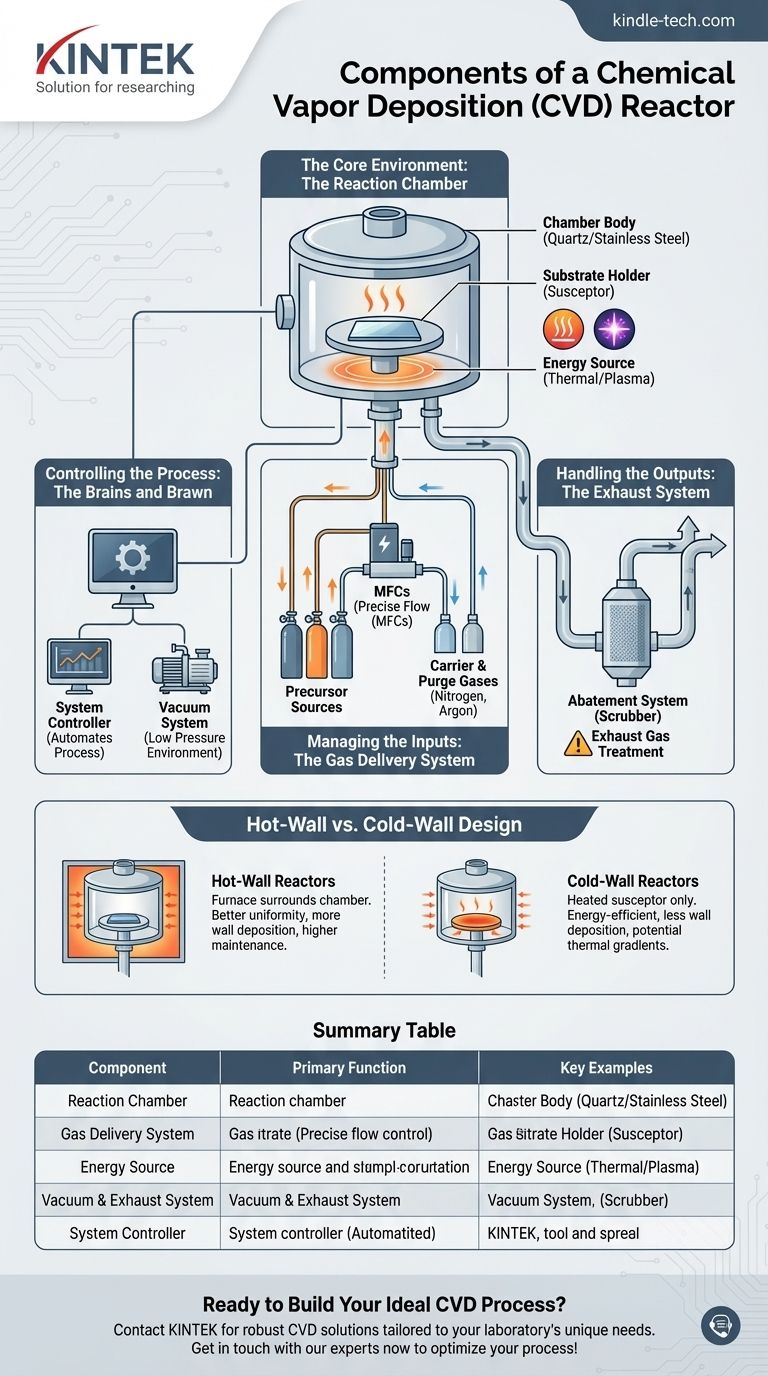
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reactor is an integrated system of components designed to create a highly controlled environment. The main functional units include a gas delivery system to introduce chemical precursors, a reaction chamber where the deposition occurs, an energy source to drive the chemical reaction, and a vacuum and exhaust system to control pressure and remove byproducts. These elements are all managed by a central process controller.
A CVD reactor is not merely a container; it is a precision instrument. Every component works in concert to precisely manage the flow of gases, temperature, and pressure, which are the fundamental levers for controlling the growth and quality of a thin film on a substrate.

The Core Environment: The Reaction Chamber
The reaction chamber is the heart of the CVD system, where the actual deposition takes place. Its design is critical for ensuring process stability and film uniformity.
The Chamber Body
The chamber itself is a sealed vessel that contains the reaction. It is typically made from materials that are inert to the process chemicals and can withstand high temperatures, such as quartz or stainless steel. The "quartz tube" often seen in university labs is a classic example of a chamber body for a low-pressure CVD (LPCVD) system.
The Substrate Holder (Susceptor)
Inside the chamber, a platform holds the material to be coated, known as the substrate. This holder, often called a susceptor, is frequently the component that is directly heated to bring the substrate to the correct process temperature.
The Energy Source
A CVD reaction requires energy to proceed. This is most commonly thermal energy supplied by a furnace surrounding the chamber or by heating lamps focused on the susceptor. In other configurations, like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), the energy is supplied by an RF source to create a plasma.
Managing the Inputs: The Gas Delivery System
This system is responsible for delivering precise amounts of chemical gases (precursors) into the reaction chamber. Accuracy here is paramount for creating a film with the desired composition.
Precursor Sources
The raw materials for the film are stored as gases or volatile liquids in cylinders. These chemicals are known as precursors, as they are the predecessors to the final solid film.
Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs)
The single most critical component for process control is the Mass Flow Controller (MFC). An MFC is a sophisticated valve that measures and controls the flow rate of each gas with extreme precision, ensuring the chemical recipe is followed exactly.
Carrier and Purge Gases
In addition to reactive precursors, inert gases like nitrogen or argon are used. They act as carrier gases to transport the precursors into the chamber and as purge gases to clear the chamber of air before a run or reactive gases after a run.
Controlling the Process: The Brains and Brawn
The control systems ensure that the recipe—the specific sequence of temperatures, pressures, and gas flows—is executed perfectly.
The Vacuum System
Most CVD processes operate at pressures far below atmospheric levels. A vacuum system, consisting of one or more pumps, is used to remove air from the chamber before the process begins and to maintain the precise low-pressure environment required for high-quality film growth.
The System Controller
The system controller is the central computer that automates and monitors the entire process. It orchestrates the MFCs, the energy source, and the vacuum pumps, adjusting all factors in real-time to ensure the deposition runs according to the specified recipe.
Handling the Outputs: The Exhaust System
What goes into the reactor must come out. The exhaust system manages the byproducts of the reaction safely.
Exhaust Gas Treatment
The unreacted precursor gases and chemical byproducts are often toxic, corrosive, or flammable. The exhaust stream is therefore passed through an abatement system (or "scrubber") that neutralizes these harmful compounds before they are safely vented.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hot-Wall vs. Cold-Wall Design
The physical arrangement of the heating source and the chamber creates a fundamental design trade-off.
Hot-Wall Reactors
In a hot-wall design, a furnace surrounds the entire reaction chamber. This provides excellent temperature uniformity for multiple substrates but also causes the desired film to deposit on the chamber walls, leading to particle contamination and requiring frequent cleaning.
Cold-Wall Reactors
In a cold-wall design, only the substrate holder (susceptor) is heated. The chamber walls remain cool. This is more energy-efficient and minimizes unwanted deposition on the walls, but it can create thermal gradients that may affect film uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The configuration of these components directly impacts the system's capabilities. Understanding your primary goal is key to selecting the right type of reactor.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform films (e.g., for semiconductors): You will need an LPCVD or PECVD system with high-precision Mass Flow Controllers and a robust, multi-stage vacuum system.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and lower cost (e.g., for simple protective coatings): An Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) system, which forgoes the complex vacuum system, is often the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., polymers or plastics): A Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) system is necessary, as its plasma energy source enables deposition at much lower temperatures than purely thermal methods.
Ultimately, understanding how each component contributes to the process environment empowers you to control the synthesis of materials at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Chamber | Sealed environment for deposition | Quartz tube, stainless steel vessel |
| Gas Delivery System | Precise precursor introduction | Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs), precursor cylinders |
| Energy Source | Drives chemical reaction | Furnace, heating lamps, RF plasma source |
| Vacuum & Exhaust System | Controls pressure & removes byproducts | Vacuum pumps, gas abatement scrubbers |
| System Controller | Automates and monitors entire process | Central computer managing recipe execution |
Ready to Build Your Ideal CVD Process?
Understanding the components is the first step; implementing them for your specific application is the next. Whether you require high-purity semiconductor films, high-throughput protective coatings, or low-temperature deposition on sensitive materials, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment can guide you.
We specialize in providing robust CVD solutions and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our systems can help you achieve precise, atomic-level control over your thin film synthesis.
Get in touch with our experts now to optimize your CVD process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating



















