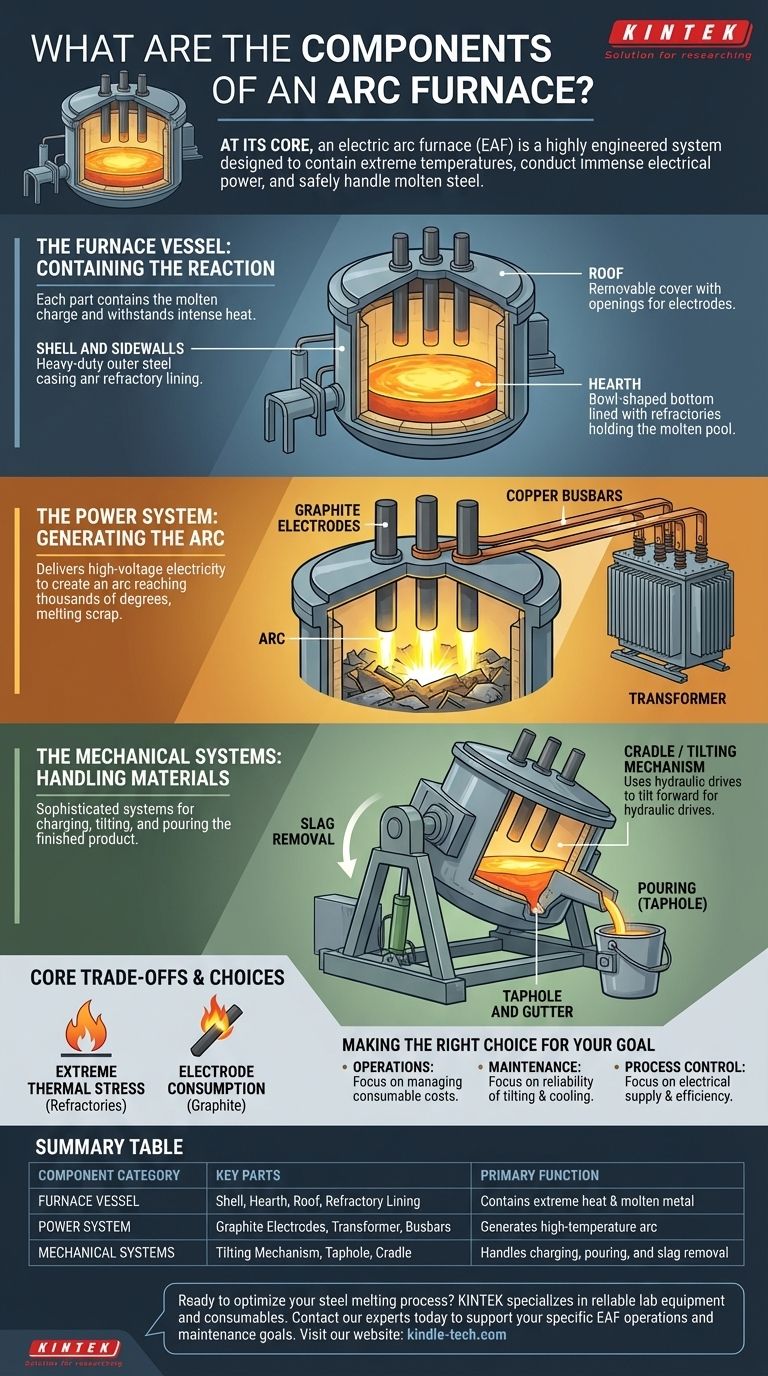
At its core, an electric arc furnace (EAF) consists of a refractory-lined steel vessel, a set of graphite electrodes to deliver energy, and mechanical systems for charging materials and pouring molten metal. Its primary components include the shell, hearth, roof, electrodes, and a tilting mechanism, all working together to contain and control an incredibly powerful electrical arc.
An electric arc furnace is not merely a container; it is a highly engineered system designed to perform three critical functions: contain extreme temperatures, conduct immense electrical power to melt scrap metal, and safely handle and discharge the resulting liquid steel.
The Furnace Vessel: Containing the Reaction
The main body of the furnace is a specialized vessel built to withstand the intense environment of steelmaking. Each part serves a distinct purpose in containing the molten charge.
The Shell and Sidewalls
The furnace's outer structure is a heavy-duty steel casing, often referred to as the shell. This provides the primary structural support for the entire apparatus.
Inside the shell, the sidewalls are lined with heat-resistant materials known as refractories. These linings are the first line of defense against the superheated molten metal and the intense radiant heat from the arc.
The Hearth
The hearth is the bowl-shaped bottom of the furnace. It is also heavily lined with specialized refractories designed to hold the pool of molten metal before it is discharged.
The Roof
The furnace is covered by a removable, refractory-lined roof. This roof has three circular openings that allow the electrodes to be lowered into the furnace.
Being removable is critical, as the roof is swung aside to allow a large bucket to load scrap metal—the primary raw material—into the furnace.
The Power System: Generating the Arc
The defining feature of an EAF is its ability to melt steel using electricity. This is accomplished through a robust power delivery system.
Graphite Electrodes
The heart of the furnace is the set of three graphite or carbon electrodes. These massive columns are lowered through the roof to a position just above the scrap metal.
A high-voltage electric current is passed through the electrodes, creating a powerful arc that leaps from the electrode tips to the metal charge. This arc can reach temperatures of several thousand degrees, rapidly melting the scrap.
Electrical Supply System
The electrodes are connected to a powerful transformer via heavy copper busbars and conductive electrode arms. This system is responsible for stepping down high-voltage electricity from the power grid and delivering the extremely high current required to sustain the arc.
The Mechanical Systems: Handling Materials
An EAF is not a static vessel. It requires sophisticated mechanical systems to charge raw materials, tilt the furnace, and pour out the finished product.
The Tilting Mechanism
The entire furnace shell rests on a massive cradle or "rocker" system. This mechanism uses powerful hydraulic or electric drives to tilt the furnace forward or backward.
Tilting forward allows the molten steel to be poured out, while tilting backward is used to remove the slag, which is the layer of impurities that floats on top of the molten steel.
The Taphole and Gutter
A taphole is a precisely located opening near the bottom of the furnace. When the steel is ready, the furnace is tilted, and the liquid metal flows out through the taphole and into a collection gutter or ladle below.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Operating an EAF involves managing a constant battle against extreme conditions. Understanding these challenges is key to understanding the furnace's design.
Extreme Thermal Stress
The refractory linings in the hearth, walls, and roof are consumable materials. They are under constant attack from thermal shock, chemical reactions with slag, and the physical force of the arc. Their lifespan is a critical operational and economic factor.
Electrode Consumption
The graphite electrodes are also consumable. They are gradually burned away by the intense heat and electrical current during operation. Replacing electrodes represents a significant portion of an EAF's operating cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your perspective on the EAF's components depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is on operations: Your concern will be managing the consumption of refractories and electrodes, as these are major cost drivers.
- If your primary focus is on maintenance: Your attention will be on the reliability of the tilting mechanism, the water-cooling systems, and the integrity of the shell and roof.
- If your primary focus is on process control: You will focus on the electrical supply system and electrode regulation to ensure an efficient and stable melting process.
Ultimately, each component is a critical link in a chain designed to transform solid scrap into liquid steel with precision and power.

Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Parts | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Vessel | Shell, Hearth, Roof, Refractory Lining | Contains the extreme heat and molten metal |
| Power System | Graphite Electrodes, Transformer, Busbars | Generates the high-temperature arc for melting |
| Mechanical Systems | Tilting Mechanism, Taphole, Cradle | Handles charging, pouring, and slag removal |
Ready to optimize your steel melting process? The right equipment is critical for managing consumables like electrodes and refractories, which are major operational cost drivers. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable solutions for efficient and controlled melting. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific EAF operations and maintenance goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the types of induction melting furnace? Coreless, Channel, and VIM Explained
- What are the different melting methods? A Guide to Choosing the Right Industrial Furnace
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials



















