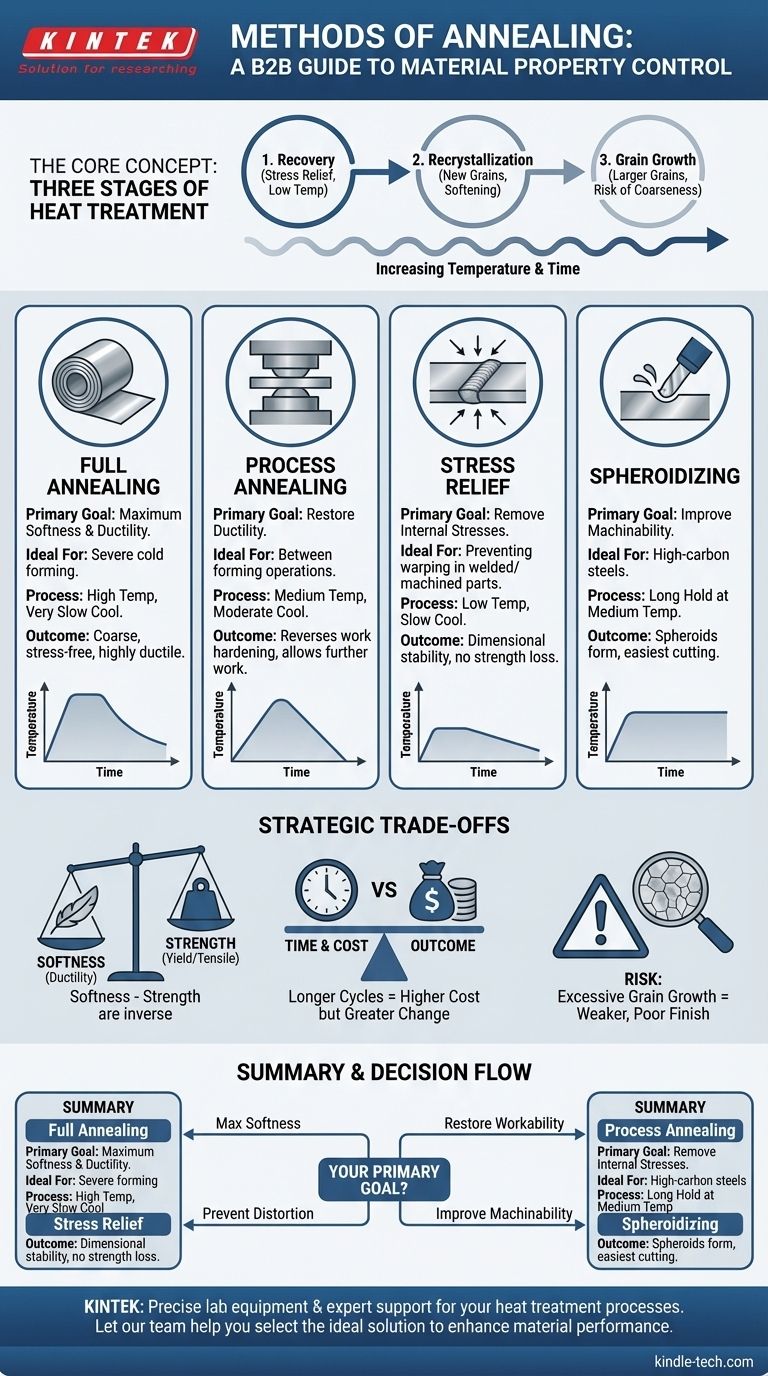
At its core, annealing is not one single process but a family of heat treatments, each with a specific goal. The primary methods include full annealing, process annealing, stress relief, and spheroidizing, all designed to alter a material's microstructure by heating it to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it at a controlled rate. The chosen method depends entirely on the desired outcome, from achieving maximum softness to simply removing internal stresses.
The specific annealing method you choose is a strategic decision dictated by your end goal. It's about balancing the need to reduce hardness, relieve internal stress, or improve machinability against considerations of time, cost, and the material's final required strength.

The Foundation: Three Stages of Annealing
Before examining the different methods, it's crucial to understand the three fundamental stages that occur within the material as heat is applied. Every annealing process manipulates these stages to achieve its goal.
Stage 1: Recovery
This is the low-temperature stage where the primary effect is stress relief. During recovery, the heat allows atoms within the crystal lattice to move, reducing the number of internal defects (dislocations) and relieving internal stresses caused by processes like cold working or welding.
The material's mechanical properties, such as hardness and strength, do not change significantly during this stage.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
As the temperature increases, the process enters the recrystallization stage. Here, new, strain-free grains begin to form and grow, replacing the deformed, defect-laden grains created during cold work.
This is the stage where the effects of work hardening are reversed. The material becomes significantly softer, more ductile, and its strength decreases as the new grain structure takes over.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
If the material is held at the annealing temperature for too long or the temperature is too high, the newly formed grains will continue to grow. Smaller grains merge into larger ones.
While this can further increase ductility, excessive grain growth can be detrimental, leading to a coarse structure with reduced strength and a poor surface finish if the part is later formed.
A Breakdown of Key Annealing Methods
Each method uses a specific temperature and cooling cycle to target different stages and produce a distinct outcome.
Full Annealing
This process is used to make a material as soft and ductile as possible. The material is heated well above its upper critical temperature, held long enough for its internal structure to fully transform, and then cooled very slowly, often by leaving it in the furnace to cool overnight.
This results in a coarse microstructure that is extremely soft, ductile, and free of internal stress, making it ideal for severe cold forming operations.
Process Annealing
Also known as intermediate annealing, this method is used to restore ductility to a work-hardened part between forming operations. The material is heated to a temperature just below its lower critical point, which is high enough to cause recrystallization but not a full phase change.
This reverses the effects of work hardening, allowing for further drawing, stamping, or bending without fracturing the material. Because it uses a lower temperature, it is faster and cheaper than full annealing.
Stress Relief Annealing
This is a low-temperature process designed solely to remove internal stresses caused by welding, casting, or heavy machining. The temperature is kept low enough to avoid any significant changes to the material's mechanical properties.
The primary goal is dimensional stability. By relieving internal stress, you prevent the part from warping, cracking, or changing shape over time or during subsequent machining. It primarily utilizes the recovery stage.
Spheroidizing
This method is specific to high-carbon steels to improve their machinability. The steel is heated to a temperature just below the lower critical point and held for an extended period (often over 24 hours).
This long cycle causes the hard carbide layers in the steel's microstructure to break up and form small, round particles (spheroids) within the softer iron matrix. A spheroidized structure offers minimal resistance to a cutting tool, drastically improving machinability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an annealing process involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these compromises is key to making the right engineering decision.
Softness vs. Strength
The core trade-off in annealing is strength for ductility. A full anneal produces the softest possible state, but this comes at the cost of significantly reduced yield and tensile strength. If the final part requires a certain level of strength, a full anneal may be inappropriate.
Time and Cost vs. Outcome
More complex annealing cycles, like full annealing and spheroidizing, require slow cooling or long hold times. This consumes significant furnace time and energy, increasing the cost. A simpler process like stress relief is much faster and cheaper but provides none of the softening benefits.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
Pushing for maximum softness by using too high a temperature or holding for too long can backfire. Excessive grain growth (Stage 3) can lead to a material that is not only weaker but may also have poor fatigue life and a rough surface finish known as "orange peel" if it is subsequently formed.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Goal
Your choice must be driven by the specific properties you need in the material at a given stage of production.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness for severe forming: Use full annealing to create the most ductile, stress-free state possible.
- If your primary focus is restoring workability between cold-working steps: Use process annealing as a fast and cost-effective way to regain ductility.
- If your primary focus is preventing distortion in a finished part: Use stress relief annealing to remove internal stresses without altering strength.
- If your primary focus is improving the machinability of high-carbon steel: Use spheroidizing to transform the microstructure for easier cutting.
Mastering these methods provides precise control over a material's properties, turning a raw component into one perfectly suited for its intended function.
Summary Table:
| Annealing Method | Primary Goal | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Full Annealing | Maximum softness & ductility | Severe cold forming operations |
| Process Annealing | Restore ductility between forming steps | Reversing work hardening |
| Stress Relief | Remove internal stresses | Preventing warping in welded or machined parts |
| Spheroidizing | Improve machinability | High-carbon steels before cutting |
Need to precisely control the properties of your materials? The right annealing process is critical to achieving the perfect balance of strength, ductility, and stability for your lab work or production. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and expert support needed for all your heat treatment processes. Let our team help you select the ideal solution to enhance your material's performance and ensure reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a muffle furnace? Unlock the Core Systems for Precise, Safe Heating
- What do you use a muffle furnace for? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the 3 types of heat transfer? Master Conduction, Convection & Radiation for Your Lab
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Unlock Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the design and construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Isolated Heating Chamber



















