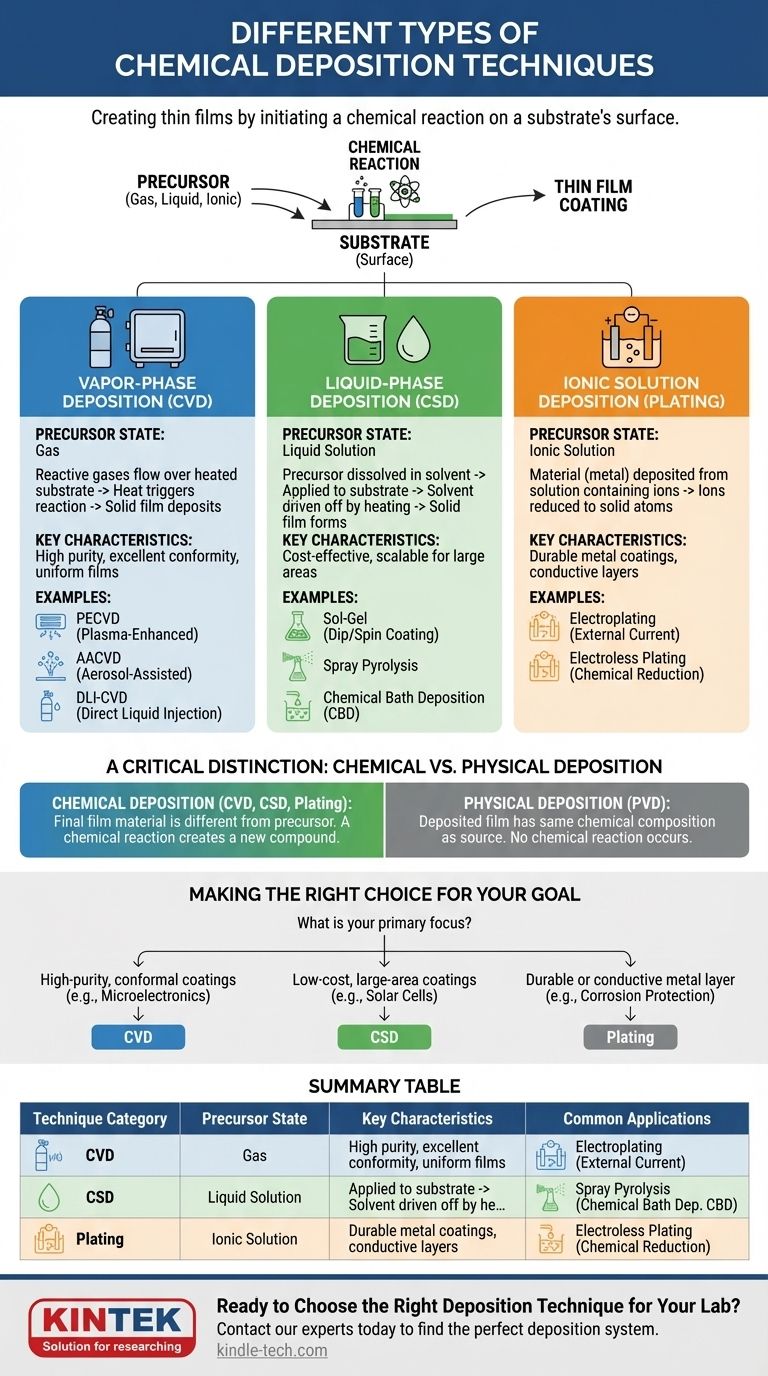
At its core, chemical deposition is a family of techniques used to create thin films and coatings by initiating a chemical reaction on a substrate's surface. The primary methods are categorized by the physical state of the chemical precursor: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) from a gas, Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) from a liquid, and Plating from an ionic solution.
The critical distinction between chemical deposition techniques is the phase of the precursor material—gas, liquid, or ion-rich solution. Understanding this fundamental difference is the key to selecting the right process for a specific material and application.
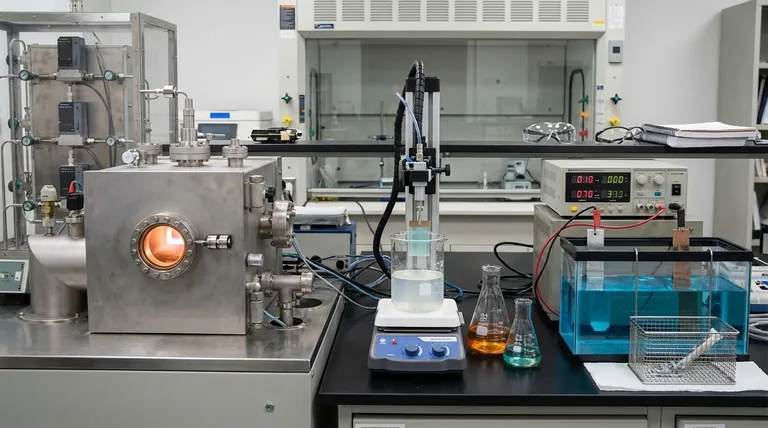

The Fundamental Categories of Chemical Deposition
To truly understand these methods, it's best to group them by the state of the starting material. This determines the equipment, process conditions, and the types of films you can create.
Vapor-Phase Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) involves flowing reactive precursor gases over a heated substrate. The heat triggers a chemical reaction, causing a solid material to deposit as a thin film onto the substrate surface.
This method is prized for its ability to create highly pure, dense, and uniform films that conform perfectly to even the most complex surface shapes.
There are several specialized forms of CVD:
- Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Uses plasma (an ionized gas) to energize the chemical reaction. This allows deposition to occur at much lower temperatures than traditional CVD, which is crucial for temperature-sensitive substrates.
- Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD): The chemical precursor is first dissolved in a solvent and then aerosolized into tiny droplets. This aerosol is then delivered into a heated chamber, where it vaporizes and reacts.
- Direct Liquid Injection (DLI-CVD): A liquid precursor is directly injected into a heated vaporization chamber. This provides precise control over the precursor delivery rate, leading to highly reproducible film growth.
Liquid-Phase Deposition (CSD)
Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) encompasses a broad set of techniques where the precursor is dissolved in a solvent to create a chemical solution. This solution is then applied to a substrate, and the solvent is driven off through heating, leaving behind a solid film.
CSD methods are often simpler, cheaper, and more scalable for large areas than CVD, though film quality can sometimes be less uniform.
Common CSD techniques include:
- Sol-Gel: A chemical solution (the "sol") undergoes a transition to form a gel-like network. This can be applied to a substrate via dip-coating or spin-coating before being heated to form a dense, often ceramic or glass-like, film.
- Spray Pyrolysis: The chemical solution is sprayed as a fine mist onto a heated substrate. The droplets undergo thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) upon hitting the hot surface, forming the desired film.
- Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD): A substrate is immersed in a dilute chemical solution. The film forms slowly on the substrate surface as a result of a controlled chemical reaction and precipitation within the bath.
Ionic Solution Deposition (Plating)
Plating involves depositing a material, typically a metal, onto a conductive surface from a solution containing its ions. The process relies on reducing these ions into solid metal atoms.
This is a very common industrial process for creating conductive layers, corrosion-resistant coatings, or decorative finishes.
The two main types of plating are:
- Electroplating: An external electrical current is used to drive the reduction of metal ions onto the substrate (the cathode). This allows for fast and precise control over the thickness of the deposited layer.
- Electroless Plating: The deposition is driven by a chemical reaction using a reducing agent contained within the plating solution itself. This process does not require an external power source and can uniformly coat complex shapes and even non-conductive surfaces (after initial activation).
A Critical Distinction: Chemical vs. Physical Deposition
It is common to see chemical deposition compared to another major category: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). Understanding their difference is essential for navigating material science.
Chemical Deposition (CVD)
In all forms of chemical deposition, the final film material is different from the precursor. A chemical reaction occurs to create a new compound on the substrate. This is why it's called "chemical" deposition.
Physical Deposition (PVD)
In PVD methods like sputtering or evaporation, a target material is physically ejected (e.g., via ion bombardment) or boiled off. This vapor then travels and condenses on the substrate. No chemical reaction occurs; the deposited film has the same chemical composition as the source material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a technique depends entirely on your material requirements, budget, and the geometry of the part you are coating.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, conformal coatings for complex microelectronics: CVD is the industry standard due to its unmatched precision and film quality.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, large-area coatings like solar cells or architectural glass: CSD techniques like spray pyrolysis or sol-gel offer excellent scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is applying a durable or conductive metal layer: Plating (either electroplating or electroless) is the most direct and well-established method.
By understanding the fundamental state of the precursor—gas, liquid, or ion—you can effectively navigate the landscape of deposition techniques and select the optimal path for your project.
Summary Table:
| Technique Category | Precursor State | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Gas | High purity, excellent conformity, uniform films | Microelectronics, complex 3D parts |
| Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) | Liquid | Cost-effective, scalable for large areas | Solar cells, architectural glass |
| Plating (Electro & Electroless) | Ionic Solution | Durable metal coatings, can coat non-conductors | Conductive layers, corrosion protection |
Ready to Choose the Right Deposition Technique for Your Lab?
Navigating the world of CVD, CSD, and plating can be complex. The right equipment is critical to achieving the high-purity, uniform coatings your research or production demands.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the reliable deposition tools and expert support to ensure your success. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics or applying durable coatings, we have the solution for you.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect deposition system for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















