For melting industrial materials, the four primary types of furnaces are induction furnaces, electric arc furnaces (EAF), cupola furnaces, and crucible furnaces. Each operates on a different principle and is suited for specific materials, scales of production, and purity requirements. While other furnace types exist, such as plasma or vacuum furnaces, they are typically used for more specialized thermal processes rather than general-purpose melting.
The most critical factor in choosing a furnace is not finding the "best" one, but matching the technology to your specific goal. The decision hinges on the trade-offs between production scale, material purity, energy efficiency, and operational cost.

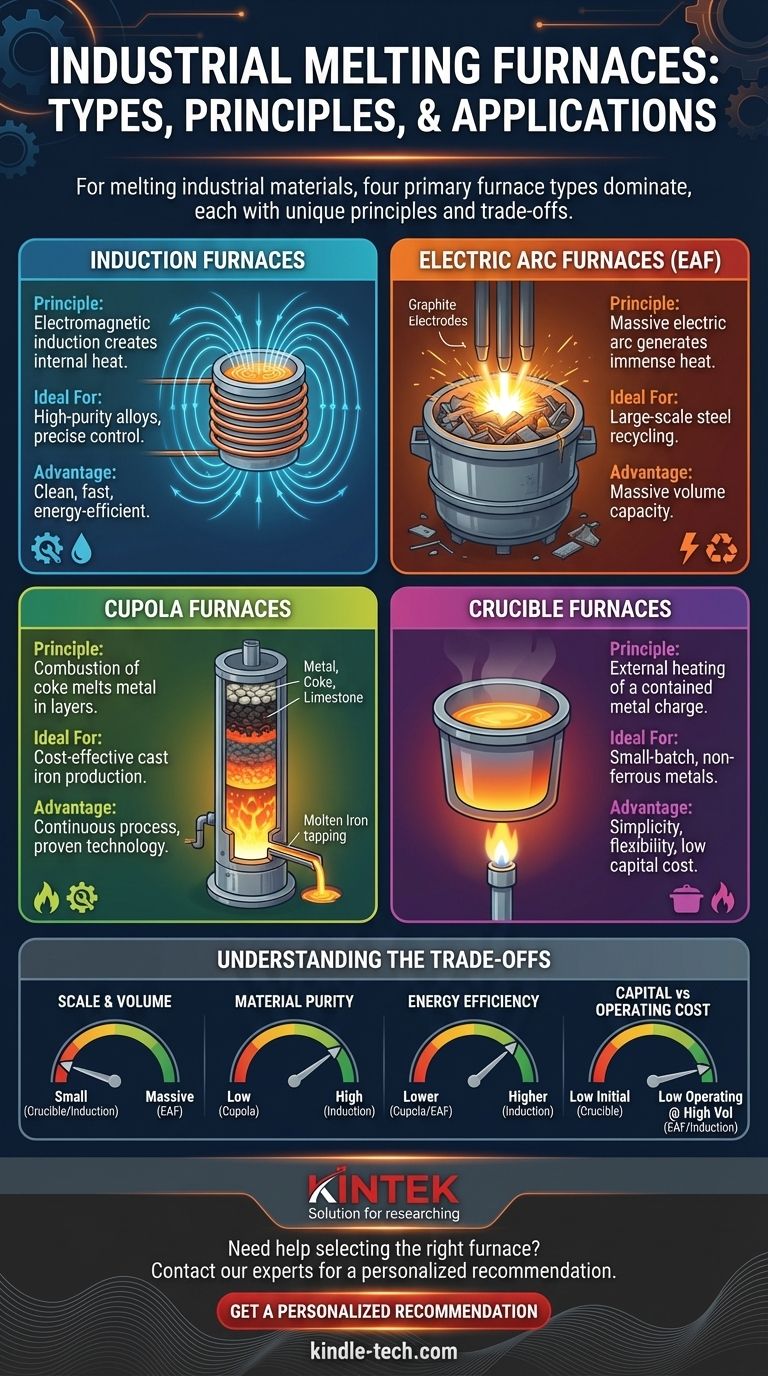
The Core Four: Industrial Melting Furnaces
The vast majority of industrial metal melting is handled by four main furnace designs. Understanding their core operating principles reveals their ideal applications.
Induction Furnaces
An induction furnace uses powerful, alternating electric currents to create a strong electromagnetic field around the metal. This field induces swirling electrical currents (eddy currents) within the metal itself, generating intense heat rapidly and cleanly.
Because the heat is generated directly within the material, the process is extremely fast, clean, and energy-efficient. This method also provides excellent temperature control and minimizes the loss of valuable alloying elements.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
An Electric Arc Furnace melts material by creating a massive electric arc between large graphite electrodes and the metal charge. The arc generates immense thermal energy, reaching temperatures high enough to melt tons of material in a short time.
EAFs are the workhorses of the steel industry, particularly for recycling steel scrap. Their primary advantage is the ability to handle very large volumes, making them essential for large-scale steel production.
Cupola Furnaces
A cupola is a tall, cylindrical vertical furnace. Layers of metal (like pig iron and scrap), coke (a high-carbon fuel), and limestone (a fluxing agent) are loaded from the top. As the coke burns, it melts the metal, which flows to the bottom to be tapped off.
While a more traditional technology, cupolas are still widely used for the cost-effective production of cast irons in foundries. They are a continuous process, unlike the batch processes of EAF or induction furnaces.
Crucible Furnaces
A crucible furnace is one of the simplest designs. It consists of a high-temperature-resistant container, or crucible, which holds the metal charge. The crucible is then heated externally by a flame or an electric heating element.
These furnaces are ideal for smaller batches and are commonly used for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze. Their simplicity and lower capital cost make them accessible for smaller foundries and workshops.
Specialized and Process-Specific Furnaces
Beyond the core four, other furnaces are used for highly specific applications, often focusing on advanced materials or processes other than simple melting.
Plasma Furnaces
Plasma furnaces use a jet of ionized gas (plasma) to generate extreme heat. They are used for materials that require very high melting points, such as ceramics or refractory metals. This technology can produce a very pure final product.
Tube and Vacuum Furnaces: For Thermal Processing
It is important to distinguish melting from other thermal processes. Tube and vacuum furnaces are critical tools, but they are generally not used to turn large volumes of solid metal into a liquid state for casting.
Instead, their function is heat treatment. This includes processes like annealing (softening metal), brazing (joining materials), purification, and aging, where precise temperature control in a controlled atmosphere is more important than bulk melting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single furnace technology is universally superior. The right choice depends entirely on balancing key operational factors.
Scale and Volume
EAFs are built for massive scale, melting over 100 tons of steel at a time. In contrast, induction and crucible furnaces are better suited for smaller, more flexible batch sizes, from a few kilograms to several tons.
Material Purity and Control
Induction furnaces offer the highest level of control and purity. The electromagnetic stirring action promotes a homogeneous mixture, and the lack of combustion byproducts ensures cleanliness. Cupolas, which burn coke directly with the metal, offer the least control over final chemistry.
Energy Source and Efficiency
Induction furnaces are recognized for their high energy efficiency, as they convert electrical energy directly into heat within the metal. EAFs are also electrically powered but consume enormous amounts of power due to their scale. Cupolas rely on a chemical fuel source (coke), which carries different cost and environmental considerations.
Capital vs. Operating Costs
Crucible furnaces typically have the lowest initial investment cost, making them accessible for small operations. Large-scale EAF and induction furnace installations represent significant capital expenditures but can offer lower operating costs per ton at high volumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by your end goal. Analyze your operational priorities to select the most effective technology.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel recycling: An Electric Arc Furnace is the industry standard for its massive volume capacity.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys and precise temperature control: An induction furnace provides unmatched cleanliness, efficiency, and control.
- If your primary focus is continuous, cost-effective cast iron production: A cupola furnace remains a robust and proven solution.
- If your primary focus is small-batch, non-ferrous melting: A crucible furnace offers simplicity, flexibility, and a low barrier to entry.
Ultimately, the most effective furnace is the one that aligns perfectly with your material, production scale, and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Ideal For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | High-purity alloys, precise control | Clean, fast, energy-efficient melting |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Large-scale steel recycling | Massive volume capacity |
| Cupola Furnace | Cost-effective cast iron production | Continuous process, proven technology |
| Crucible Furnace | Small-batch, non-ferrous metals | Simplicity, flexibility, low capital cost |
Still unsure which melting furnace is right for your lab or production line?
The team at KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including thermal processing solutions. We can help you analyze your specific material, volume, and purity requirements to select the perfect furnace technology for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and discover how the right equipment can enhance your efficiency, control, and final product quality.
Get a Personalized Recommendation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What are the different melting methods? A Guide to Choosing the Right Industrial Furnace
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















