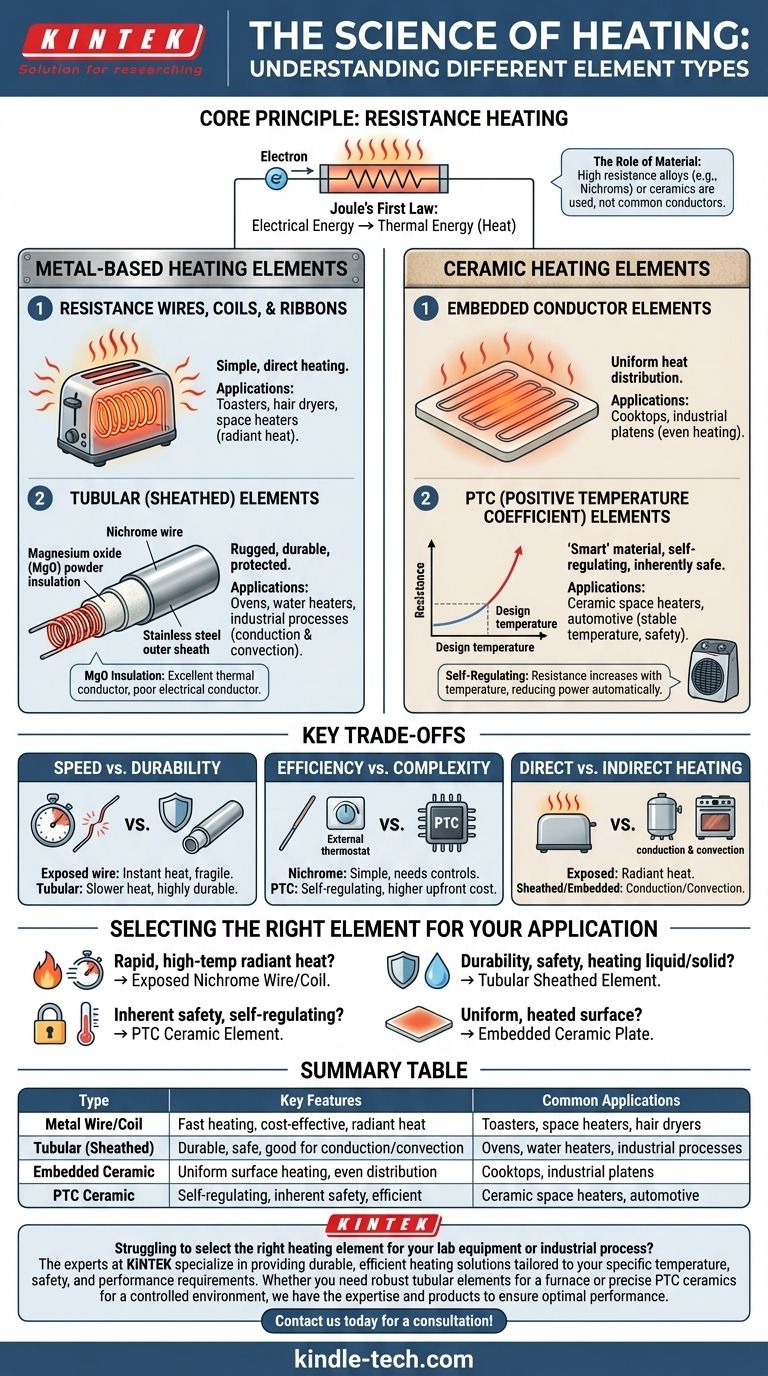
At their core, heating elements are transducers that convert electrical energy into heat energy through the principle of resistance. The main types are broadly categorized by their primary material and construction, most commonly falling into metal-based elements, like wires and tubes, and ceramic-based elements, which offer unique properties for specific applications.
The most critical factor in choosing a heating element is not its material alone, but how its construction and material properties align with the specific application's requirements for temperature, durability, and heat transfer efficiency.

The Principle: How Resistance Heating Works
Joule's First Law
All electric resistance heaters operate on a simple, fundamental principle known as Joule heating. As electric current passes through a material with electrical resistance, collisions between electrons and atoms convert electrical energy directly into thermal energy, or heat.
The Role of Material
The key is to use a material with high enough resistance to generate significant heat without melting or degrading quickly. This is why specialized alloys and ceramic compounds are used instead of common conductors like copper.
Metal-Based Heating Elements
Metal elements are the most common type, valued for their cost-effectiveness and versatility in a wide range of temperatures.
Resistance Wires, Coils, and Ribbons
This is the simplest form. A wire or ribbon, typically made of a Nichrome (nickel-chromium) alloy, is heated by an electric current.
These elements are found in applications like toasters, hair dryers, and space heaters where the glowing-hot element is directly exposed (or fanned) to heat the air or a surface via radiation.
Tubular (Sheathed) Elements
These are the rugged workhorses of the heating world. They consist of a fine Nichrome wire coil encased in a protective metal sheath, often stainless steel or Incoloy.
The coil is insulated from the outer sheath by a compacted ceramic powder, typically magnesium oxide, which is an excellent thermal conductor but a poor electrical conductor. This construction protects the resistance wire from moisture and oxidation, making it durable and safe for applications like oven elements, water heaters, and industrial processes.
Ceramic Heating Elements
Ceramic heaters are prized for their high efficiency, rapid heat transfer, and unique self-regulating properties in some variants.
Embedded Conductor Elements
In this design, a resistance wire or ribbon is embedded within a ceramic plate or structure. This allows the entire ceramic surface to heat up uniformly.
This uniform heating makes them ideal for applications requiring even heat distribution, such as certain types of cooktops or industrial platens.
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Elements
PTC ceramic is a "smart" material. Its electrical resistance increases sharply once it reaches a specific design temperature.
This behavior makes PTC heaters self-regulating. They heat up quickly and then automatically reduce their power consumption to maintain a stable temperature, eliminating the need for complex external control circuits and providing inherent protection against overheating. They are commonly used in small ceramic space heaters and automotive applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an element involves balancing performance, safety, and cost. There is no single "best" type.
Speed vs. Durability
Exposed wire or coil elements heat up almost instantly but are fragile and susceptible to damage and shorts. Tubular sheathed elements heat up more slowly but are vastly more durable and protected from the environment.
Efficiency vs. Complexity
Basic Nichrome wires are simple and cheap but often require external thermostats and safety cutoffs to prevent overheating. Self-regulating PTC ceramic elements are inherently safer and more efficient at maintaining a temperature but have a higher upfront cost and are limited to lower maximum temperatures.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Exposed elements are excellent for direct radiant heating (like a toaster). Sheathed and embedded elements are superior for conduction (heating a liquid in a tank) or convection (heating air inside an oven) where durability and safety are paramount.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the requirements of the task at hand.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature radiant heat: An exposed Nichrome wire or coil is the most direct solution.
- If your primary focus is durability, safety, and heating a liquid or solid: A tubular sheathed element is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is inherent safety and self-regulating temperature: A PTC ceramic element is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform, heated surface: An embedded ceramic plate provides the most even heat distribution.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental types empowers you to match the right tool to your specific thermal challenge.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Wire/Coil | Fast heating, cost-effective, radiant heat | Toasters, space heaters, hair dryers |
| Tubular (Sheathed) | Durable, safe, good for conduction/convection | Ovens, water heaters, industrial processes |
| Embedded Ceramic | Uniform surface heating, even distribution | Cooktops, industrial platens |
| PTC Ceramic | Self-regulating, inherent safety, efficient | Ceramic space heaters, automotive applications |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab equipment or industrial process? The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing durable, efficient heating solutions tailored to your specific temperature, safety, and performance requirements. Whether you need robust tubular elements for a furnace or precise PTC ceramics for a controlled environment, we have the expertise and products to ensure optimal performance. Contact us today for a consultation and let us help you solve your thermal challenge!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How long does a heating element last on the furnace? Understand Lifespan & Safety for Your System
- What role do Carbon-Carbon composite heaters play within densification equipment? High-Temp Thermal Stability Solutions
- Why are tungsten-rhenium (W/Re) thermocouples selected for monitoring the combustion synthesis of ferroalloys? - Up to 2400°C
- What is the best electric heating element? Match the Right Material to Your Application's Needs
- How are heating elements manufactured? A Guide to Precision, Safety, and Durability
- What role do laboratory heaters and thermocouples play in low-temperature nitriding? Achieve Precision Thermal Control
- What are the common materials used as heating elements? Find the Right Material for Your Temperature Needs
- Which material is suitable for use in heating elements? Match the Right Material to Your Temperature and Atmosphere












