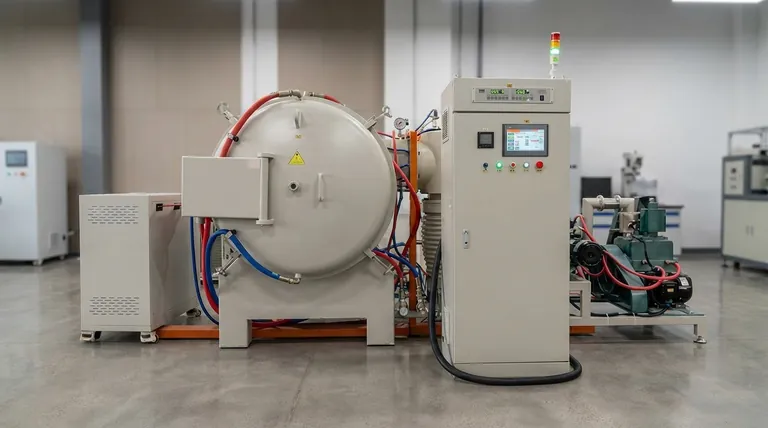
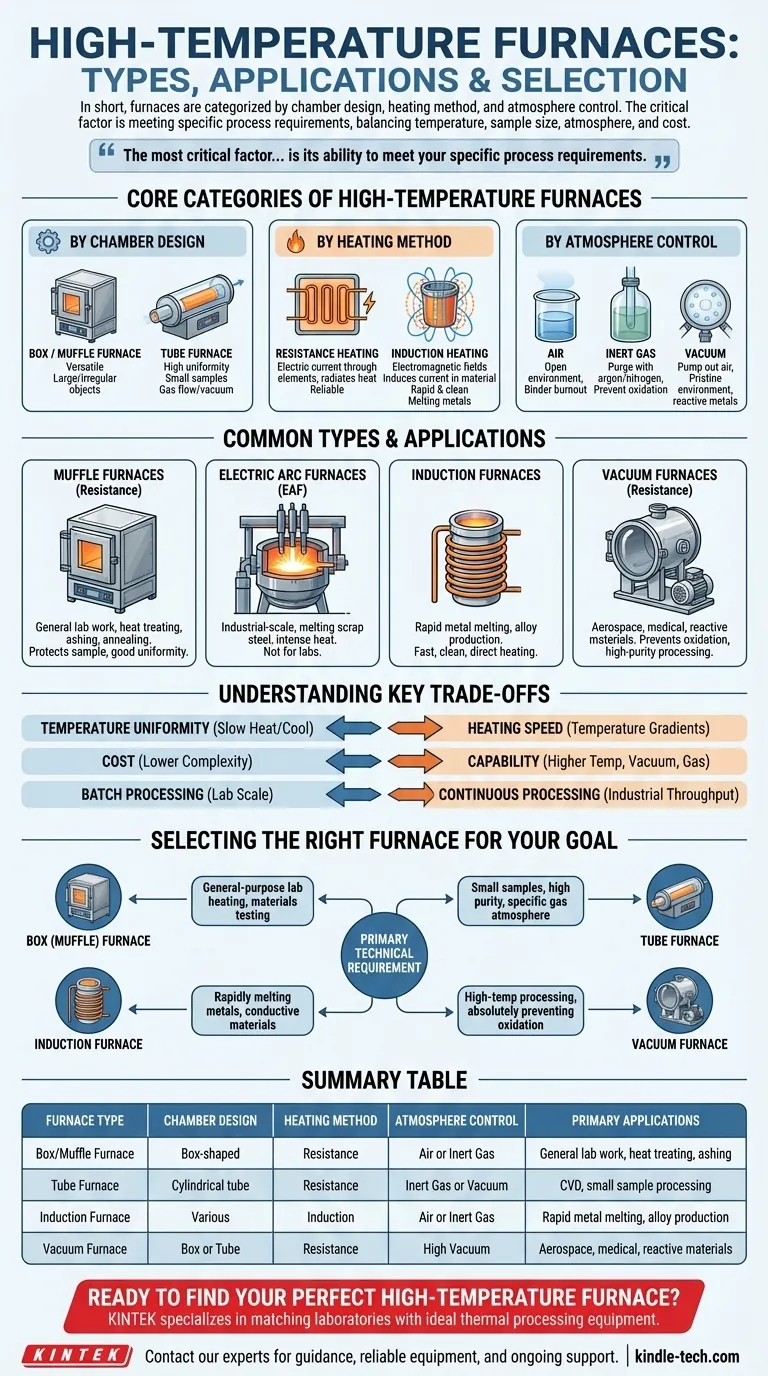
In short, high-temperature furnaces are primarily categorized by their chamber design (like box or tube furnaces), their heating method (such as resistance or induction), and the type of atmospheric control they provide (air, inert gas, or vacuum). While dozens of specific models exist, these core characteristics are what distinguish one from another for technical applications.
The most critical factor in selecting a high-temperature furnace is not its name, but its ability to meet your specific process requirements. The choice always comes down to a trade-off between temperature, sample size, atmospheric control, and cost.

Core Categories of High-Temperature Furnaces
To truly understand the landscape, it's best to think of furnaces in terms of their fundamental design principles rather than a long list of names. The primary differentiators are the chamber's shape, how it generates heat, and how it controls the internal atmosphere.
By Chamber Design: Box vs. Tube
Box furnaces, also known as muffle furnaces, feature a box-shaped chamber. This design is highly versatile and ideal for general-purpose lab work, heat treating, or firing larger or irregularly shaped objects.
Tube furnaces use a cylindrical tube (often ceramic or quartz) as their chamber. This configuration excels at achieving high temperature uniformity for smaller samples and is the standard for processes requiring a controlled flow of gas or a vacuum, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
By Heating Method: Resistance vs. Induction
Most common lab and industrial furnaces are resistance furnaces. They work by passing an electric current through high-resistance heating elements surrounding the chamber, which glow hot and radiate heat. This is a reliable and well-understood technology.
Induction furnaces operate on a completely different principle. They use powerful electromagnetic fields to directly induce an electric current within the conductive material itself, causing it to heat rapidly from the inside out. This method is exceptionally fast and clean, making it ideal for melting metals.
By Atmosphere Control: Air, Inert Gas, and Vacuum
The simplest furnaces operate in ambient air. These are sufficient for processes like binder burnout or simple materials testing where oxidation is not a concern.
For materials sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures, a furnace must offer atmosphere control. This allows you to purge the air and replace it with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, preventing oxidation and unwanted chemical reactions.
Vacuum furnaces represent the highest level of atmospheric control. By pumping out nearly all the air, they create a pristine environment essential for processing highly reactive metals, sintering advanced ceramics, and high-purity brazing.
Common Furnace Types and Their Applications
With the core categories understood, we can now place the more specific furnace types into context.
Muffle Furnaces (Resistance Heating)
These are the workhorses of the laboratory. The "muffle" is an inner chamber that protects the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, ensuring better temperature uniformity and preventing contamination. They are used for everything from ashing biological samples to annealing steel parts.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
These are industrial-scale behemoths used primarily for melting scrap steel. They use a high-power electric arc between electrodes to generate intense heat, capable of melting tons of metal at a time. They are not typically found in a laboratory setting.
Induction Furnaces
Used for melting metals with exceptional speed and purity, induction furnaces are common in foundries and specialty alloy production. Because they heat the material directly, there is less risk of contamination from the furnace walls or heating elements.
Vacuum Furnaces
As discussed, these are specialized systems for high-value processes. Their ability to prevent oxidation makes them critical in the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries for applications like heat treating titanium alloys or sintering tungsten carbide.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" type; there is only the best fit for your objective and budget.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Heating Speed
A well-insulated box furnace with heating elements on all sides provides excellent temperature uniformity across the chamber. However, it will heat up and cool down slowly. Conversely, an induction furnace offers incredible heating speed but may create temperature gradients within the material.
Cost vs. Capability
A simple air atmosphere box furnace is relatively inexpensive. As you add capabilities—higher maximum temperatures, gas-handling manifolds, or high-vacuum pumping systems—the complexity and cost increase dramatically. A high-vacuum furnace can easily cost ten times more than a basic muffle furnace of the same size.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Most laboratory furnaces (box, tube) are batch furnaces, where you load a sample, run a cycle, and unload it. For industrial production, continuous furnaces like conveyor belt, roller hearth, or pusher furnaces are used to process a constant flow of material, increasing throughput.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Goal
Base your decision on the primary technical requirement of your work.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating or materials testing: A box (muffle) furnace offers the best combination of versatility, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is processing small samples with high purity or a specific gas atmosphere: A tube furnace provides superior atmospheric control and temperature uniformity for this scale.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting metals or other conductive materials: An induction furnace is the most efficient and fastest technology for the job.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing while absolutely preventing oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the necessary tool, despite its higher cost and complexity.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one whose technical capabilities are precisely matched to your process objective.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Chamber Design | Heating Method | Atmosphere Control | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Box/Muffle Furnace | Box-shaped | Resistance | Air or Inert Gas | General lab work, heat treating, ashing |
| Tube Furnace | Cylindrical tube | Resistance | Inert Gas or Vacuum | CVD, small sample processing |
| Induction Furnace | Various | Induction | Air or Inert Gas | Rapid metal melting, alloy production |
| Vacuum Furnace | Box or Tube | Resistance | High Vacuum | Aerospace, medical, reactive materials |
Ready to Find Your Perfect High-Temperature Furnace?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to your lab's success. The wrong choice can lead to inconsistent results, material waste, and costly downtime. KINTEK specializes in matching laboratories with the ideal equipment for their specific thermal processing needs.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our team will help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature uniformity, heating speed, atmosphere control, and cost.
- Reliable Equipment: From robust muffle furnaces for daily lab work to advanced vacuum systems for high-purity applications.
- Ongoing Support: We ensure your furnace continues to perform at its best, maximizing your research and production efficiency.
Don't leave your results to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation. Let KINTEK help you select the furnace that will drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature gasification reactor in biomass-to-hydrogen? Maximize Hydrogen Yield
- What type of ore are subjected for calcination? Purify Carbonate & Hydrated Ores
- What are the factors that control the sintering process? Master Temperature, Time, Pressure & Material
- What are the disadvantages of nitriding? Key Limitations of Each Process Method
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- What is the temperature of a vacuum brazing furnace? Key metrics for precision joining
- What are the specific control requirements for heating furnaces in zero-reforming DRI? Optimize Your Heat Management
- What role do electric vacuum laboratory furnaces play in LBE corrosion tests? Ensure Precision Reactor Simulations



















