At its core, induction heating is categorized not just by the equipment, but by the application and architecture of the system. The two primary architectures, especially in industrial melting, are the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. Each leverages the same physical principle but is designed for fundamentally different operational needs.
The key distinction lies in how the electromagnetic energy is coupled to the material. A coreless furnace acts like a large transformer with the metal charge as the core, while a channel furnace uses a loop of molten metal as a closed secondary circuit.

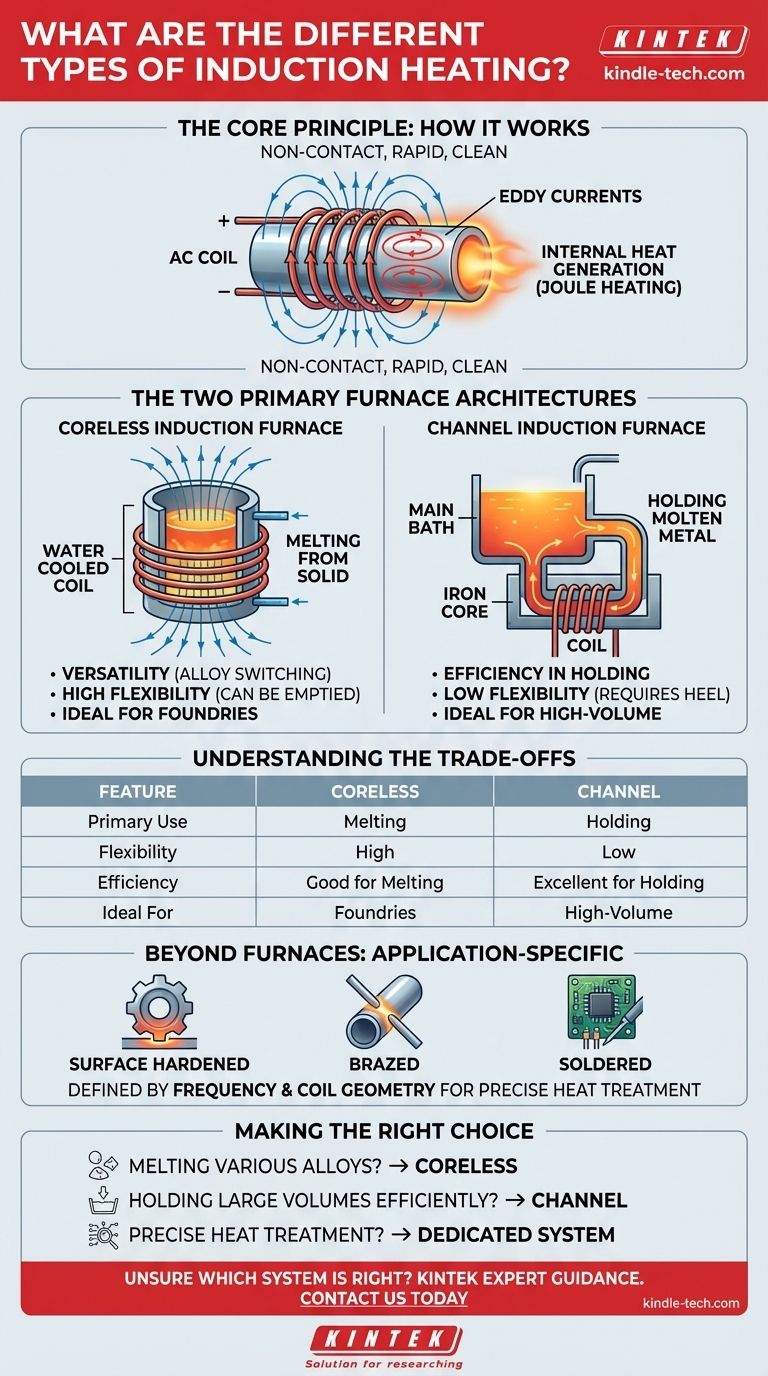
The Core Principle: How Induction Heating Works
To understand the different types, you must first understand the single principle that unites them. Induction heating is a non-contact method for heating conductive materials.
Electromagnetic Fields and Eddy Currents
An alternating current (AC) is passed through a coil of copper wire. According to Maxwell's equations, this creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
When a conductive material (like steel) is placed within this field, the magnetic field induces small, circulating electric currents within the material itself. These are known as eddy currents.
Internal Heat Generation
The material's natural electrical resistance opposes the flow of these eddy currents. This opposition generates immense heat directly inside the part through a process called Joule heating. The heat is generated from within, not applied from without.
Clean and Rapid Heating
Because the heat is generated internally and there is no direct contact with a flame or heating element, the process is extremely fast, precise, and clean. This prevents contamination and allows for tight control over the heating process.
The Two Primary Furnace Architectures
While the principle is the same, the engineering approach differs significantly between the two main types of induction furnaces.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
In a coreless furnace, the material to be heated is placed inside a refractory crucible. This entire crucible is surrounded by a water-cooled copper coil.
When energized, the magnetic field from the coil penetrates the crucible and induces eddy currents directly into the entire mass of the metal charge. This makes it highly effective for melting metal from a solid state.
The Channel Induction Furnace
A channel furnace operates more like a traditional transformer. It has an iron core with a primary coil wrapped around it.
A separate, looping channel connected to the main bath holds a "heel" of molten metal. This loop passes through the iron core, acting as a single-turn secondary winding. The current induced in this molten loop generates heat, which circulates into the main bath.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior; they are engineered for different purposes and present clear trade-offs.
Coreless Furnace: Versatility
The primary advantage of a coreless furnace is its flexibility. It can be started from cold (with a solid charge) and can be completely emptied between melts. This makes it ideal for foundries that switch between different alloys frequently.
Channel Furnace: Efficiency in Holding
The channel furnace is significantly more energy-efficient for holding large volumes of metal at a constant temperature. However, it must maintain a continuous heel of molten metal in the channel to operate, making it difficult to shut down or switch alloys. It is best suited for high-volume, continuous operations with a single metal type.
Beyond Furnaces: Application-Specific Heating
It's crucial to recognize that induction heating extends far beyond melting furnaces. For applications like surface hardening, brazing, or soldering, the "type" of induction heating is defined by the frequency of the power supply and the custom geometry of the induction coil, which is designed to heat a very specific area of a part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on your operational goal.
- If your primary focus is melting various alloys from a solid state: The versatility of a coreless furnace is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of a single molten metal efficiently: The high efficiency of a channel furnace is superior for continuous, large-scale production.
- If your primary focus is precise heat treatment on a finished part: Neither furnace type applies; you need a dedicated system with a custom-designed coil and a specific power supply frequency.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental principle of internal heat generation empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Melting from solid; alloy switching | Holding molten metal; continuous operation |
| Flexibility | High (can be emptied) | Low (requires a molten heel) |
| Efficiency for Melting | Good | Excellent for holding |
| Ideal For | Foundries, job shops | High-volume, single-alloy production |
Unsure which induction heating system is right for your laboratory or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance on induction heating solutions for melting, brazing, and heat treatment. Our team can help you select the ideal system to maximize efficiency, precision, and cleanliness in your operations. Contact us today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting



















