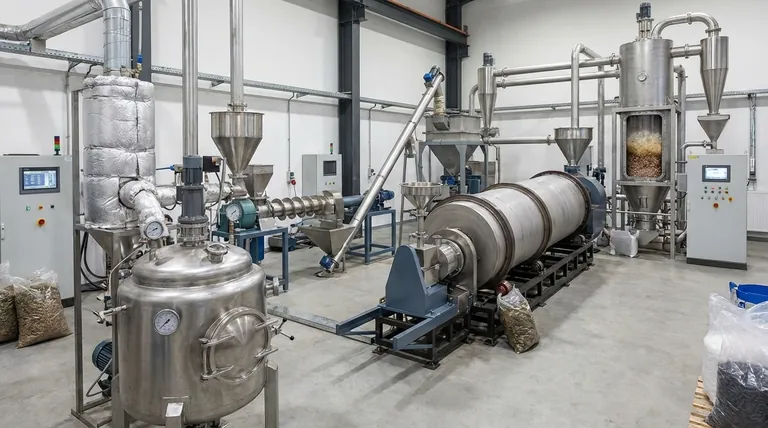
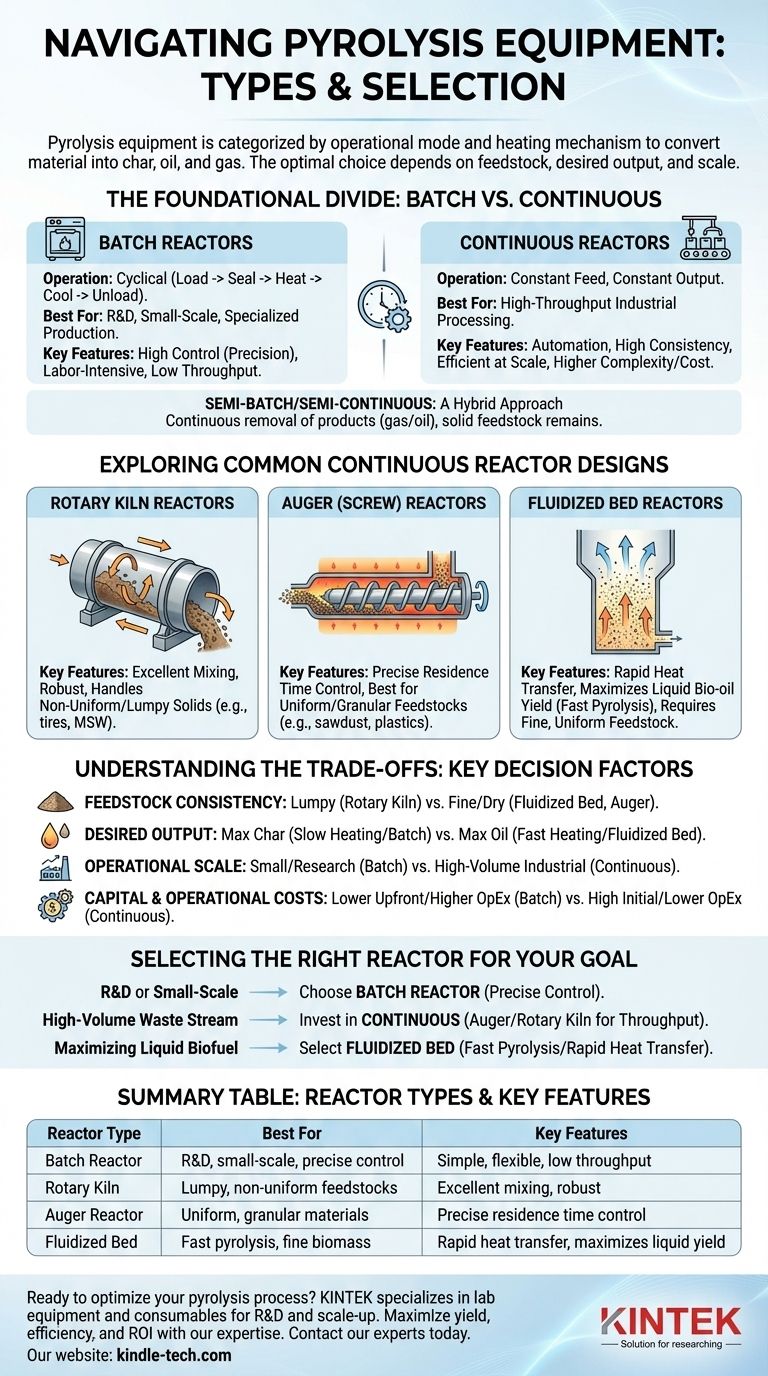
At its core, pyrolysis equipment is categorized by its operational mode and the specific mechanism used to heat and transport material. The main types are batch reactors, best for small-scale and research applications, and continuous reactors, which are designed for high-throughput industrial processing. Within continuous systems, designs like rotary kilns, auger reactors, and fluidized beds are chosen based on the specific feedstock and desired end-product.
The choice of pyrolysis equipment is not about finding the "best" type, but about matching the reactor's design to three critical factors: the physical form of your feedstock, your desired output products (char, oil, or gas), and your required operational scale.

The Foundational Divide: Batch vs. Continuous Operation
The most fundamental decision in pyrolysis technology is choosing between a batch or a continuous process. This choice dictates the project's scale, labor requirements, and overall workflow.
Batch Reactors: Precision and Flexibility
A batch reactor operates like an oven. Material is loaded in, the system is sealed, heated to the target temperature for a set time, and then cooled before the products are removed.
This design is the simplest and most common for laboratory research and small-scale, specialized production.
They offer excellent control over reaction time and temperature for a given batch. However, they are labor-intensive and have low throughput due to the cyclical loading, heating, cooling, and unloading process.
Continuous Reactors: Scale and Efficiency
A continuous reactor operates like an assembly line. Feedstock is constantly fed into one end of the system, and the resulting char, oil, and gas are continuously removed from the other.
These systems are the standard for industrial-scale applications where high throughput and automation are essential. They provide a highly consistent product because operating conditions remain stable.
While efficient at scale, continuous reactors are more complex, have a higher initial capital cost, and are often less tolerant of variations in feedstock size and composition compared to batch systems.
Semi-Batch/Semi-Continuous: A Hybrid Approach
This hybrid model involves the continuous removal of some products (like gas and oil) while the solid feedstock and char remain in the reactor for the duration of the "batch."
It offers a compromise, providing better efficiency than a pure batch system without the full mechanical complexity of a fully continuous design.
Exploring Common Continuous Reactor Designs
Once you decide on a continuous process, several proven designs exist, each optimized for different types of materials and heat transfer characteristics.
Rotary Kiln Reactors
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical drum that is slightly inclined. As the drum rotates, the feedstock tumbles and mixes, gradually moving from the higher feed end to the lower discharge end.
This tumbling action provides excellent mixing, ensuring uniform heating. Rotary kilns are robust and highly effective for processing non-uniform, lumpy solids like whole tires, municipal solid waste, and sludges.
Auger (Screw) Reactors
An auger reactor uses one or more large screws (Archimedes' screws) to push material through a heated horizontal or inclined tube.
This design offers precise control over how long the material stays in the reactor (residence time). It is best suited for more uniform and granular feedstocks like sawdust, shredded plastics, or agricultural powders.
Fluidized Bed Reactors
In a fluidized bed, an upward flow of hot gas is used to suspend the feedstock particles, causing them to behave like a fluid. This "fluidization" creates an environment of intense mixing and extremely rapid heat transfer.
These reactors are ideal for fast pyrolysis, a process designed to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil. They require small, uniform feedstock particles that can be easily suspended by the gas flow.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Decision Factors
Choosing the right equipment requires a clear-eyed assessment of the technical and economic trade-offs involved. Your decision should be guided by the following factors.
Feedstock Consistency and Form
The physical nature of your input material is paramount. Lumpy, heterogeneous materials (like construction debris) are handled well by a robust rotary kiln, while fine, dry powders (like biomass flour) are perfect for a fluidized bed or auger reactor.
Desired Output Products (Char, Oil, Gas)
Your primary product goal dictates the ideal process conditions, which in turn favors certain reactor types.
Slow heating with long residence times, typical of batch reactors, maximizes char production. Extremely rapid heating with short residence times, the specialty of fluidized bed reactors, maximizes liquid oil production.
Operational Scale and Throughput
Your required processing volume is a clear dividing line. If you are processing a few hundred kilograms per day or conducting research, a batch reactor is sufficient. If you need to process many tons per hour, a continuous system is the only viable option.
Capital and Operational Costs
Batch systems have a lower upfront capital cost but higher operational costs per ton due to labor and inefficiencies. Continuous systems have a very high initial investment but benefit from economies of scale and automation, leading to a lower cost per ton processed.
Selecting the Right Reactor for Your Goal
Ultimately, the optimal equipment is the one that aligns with the specific goals of your project.
- If your primary focus is R&D or small-scale specialized processing: Choose a batch reactor for its precise process control and operational flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of a consistent waste stream: Invest in a continuous reactor like an auger or rotary kiln to maximize throughput and automation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid biofuel yield from fine biomass: Select a fast pyrolysis system, such as a fluidized bed reactor, for its superior heat transfer rates.
Understanding the interplay between your material, your product goals, and your operational scale is the key to engineering a successful pyrolysis venture.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Reactor | R&D, small-scale, precise control | Simple, flexible, low throughput |
| Rotary Kiln | Lumpy, non-uniform feedstocks (e.g., tires, MSW) | Excellent mixing, robust, handles solids |
| Auger Reactor | Uniform, granular materials (e.g., sawdust, plastics) | Precise residence time control |
| Fluidized Bed | Fast pyrolysis, fine biomass for bio-oil | Rapid heat transfer, maximizes liquid yield |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis R&D and scale-up. Whether you're testing feedstocks in a batch reactor or scaling to continuous production, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific needs—maximizing yield, efficiency, and ROI. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















