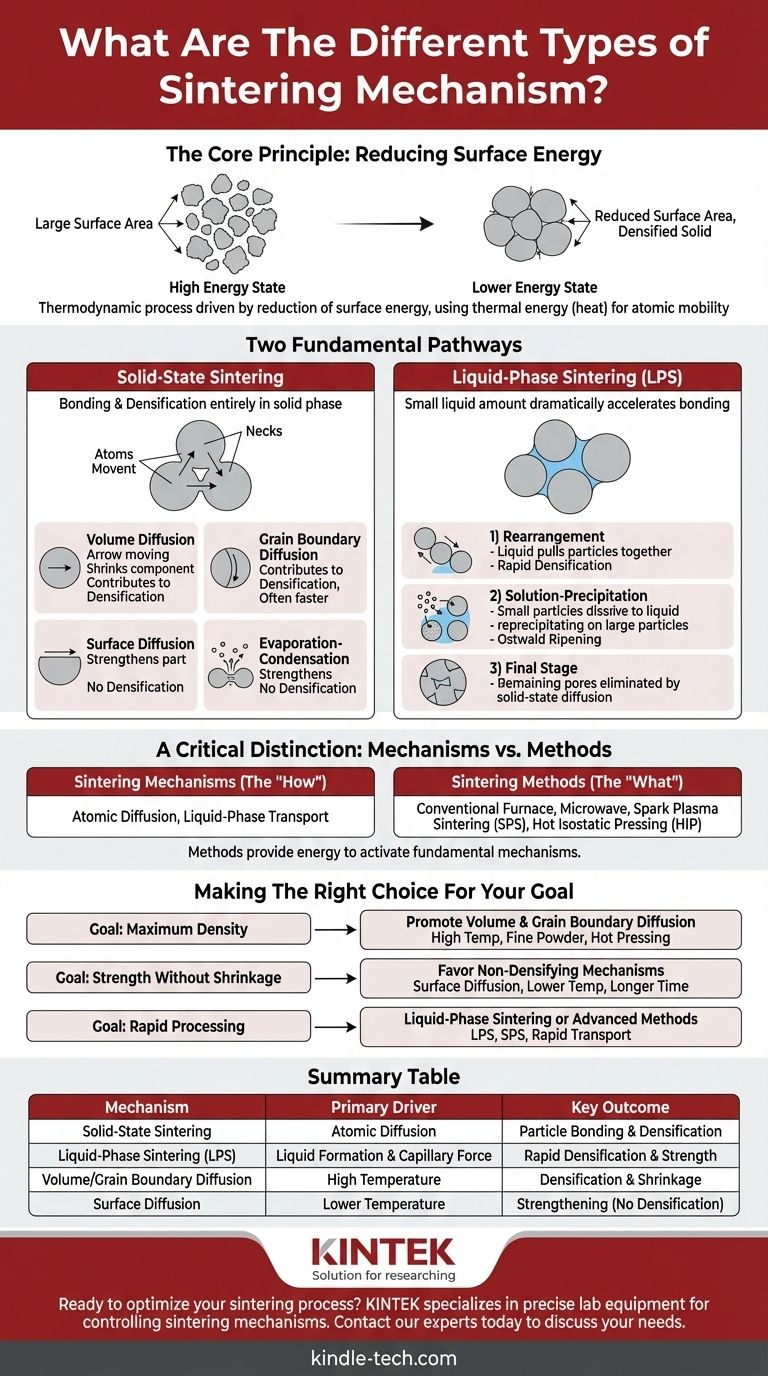
At its core, sintering is driven by two fundamental pathways. These are Solid-State Sintering, where particles bond and densify entirely in the solid phase, and Liquid-Phase Sintering (LPS), where a small amount of liquid forms to dramatically accelerate the bonding and densification process. The specific mechanisms within these pathways all relate to how atoms and material move to reduce the overall energy of the system.
The central concept to grasp is that sintering is not just about melting things together. It is a thermodynamic process driven by the reduction of surface energy, where individual material transport mechanisms—like atomic diffusion—work to eliminate the empty spaces between particles, creating a solid, dense object.
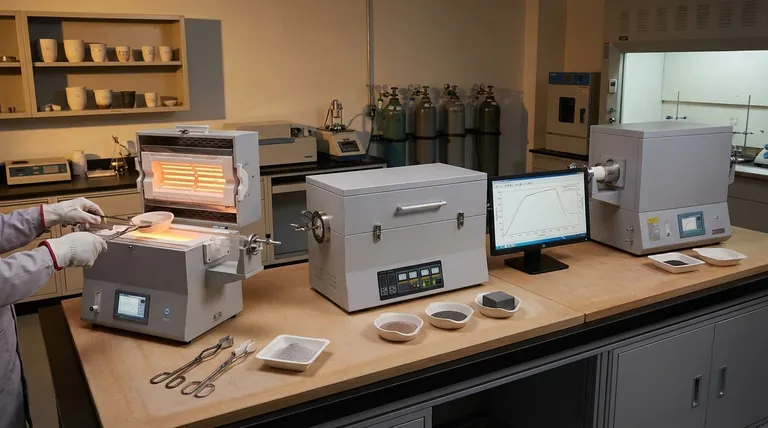

The Core Principle: Reducing Surface Energy
Before diving into the mechanisms, it's critical to understand why sintering happens at all. The driving force is thermodynamics.
The High Energy of Surfaces
A collection of fine powder has an enormous amount of surface area. Surfaces represent a state of high energy because the atoms there are not fully bonded like the atoms in the interior of a particle.
The Path to a Lower Energy State
The universe favors lower energy states. By bonding together and reducing the total surface area, the powder particles can achieve a more stable, lower-energy configuration. Sintering is simply the application of thermal energy (heat) to give the atoms the mobility they need to accomplish this.
Solid-State Sintering Mechanisms
In solid-state sintering, all material transport occurs without any melting. The primary mechanism is diffusion, the net movement of atoms from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion: The Engine of Densification
During the initial stage of sintering, particles touch, forming "necks." Diffusion causes atoms to move toward these necks, making them grow. The specific path the atoms take determines the outcome.
Key Diffusion Paths
- Volume Diffusion: Atoms move through the crystal lattice (the bulk) of the particles. This is a primary mechanism for densification, as it moves material from the particle centers to the necks, pulling the particles closer and shrinking the component.
- Grain Boundary Diffusion: Atoms move along the interface between the particles (the grain boundary). This is also a major contributor to densification and is often faster than volume diffusion.
- Surface Diffusion: Atoms move along the free surface of the particles. While this mechanism helps the necks grow and increases the strength of the part, it does not cause densification. It merely rearranges material on the surface without pulling the particle centers closer.
Evaporation-Condensation
In some materials with high vapor pressure, atoms can evaporate from the particle surface and condense at the neck region. Like surface diffusion, this mechanism strengthens the bonds between particles but does not contribute to densification or shrinkage.
Liquid-Phase Sintering (LPS) Mechanisms
Introducing a small amount of liquid into the system can dramatically increase the rate of sintering. This happens when a minor component of the powder mixture melts at the sintering temperature.
The Role of the Liquid
The liquid phase wets the solid particles, and the resulting surface tension pulls the particles together, causing rapid initial densification. The liquid also acts as a high-speed transport path for atoms.
Stages of Liquid-Phase Sintering
- Rearrangement: As the liquid forms, it allows the solid particles to slide past one another and repack into a denser arrangement.
- Solution-Precipitation: Smaller particles dissolve into the liquid phase and then precipitate onto larger particles. This process, known as Ostwald ripening, increases the average particle size and further densifies the material.
- Final Stage Sintering: Once a rigid solid skeleton has formed, any remaining pores are eliminated through slower solid-state diffusion mechanisms.
A Critical Distinction: Mechanisms vs. Methods
It is crucial not to confuse the underlying physical mechanisms with the industrial methods used to achieve sintering. The references often list methods as if they are mechanisms.
Sintering Mechanisms (The "How")
This refers to the atomic-level phenomena that cause bonding and densification. As we've discussed, the primary mechanisms are diffusion (volume, grain boundary, surface) and the stages of liquid-phase transport.
Sintering Methods (The "What")
This refers to the technology or equipment used to apply heat and/or pressure to drive the mechanisms. Examples include:
- Conventional Sintering: Heating parts in a furnace.
- Microwave Sintering: Using microwaves for rapid, volumetric heating.
- Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): Using a pulsed DC current and pressure to achieve extremely rapid heating and densification.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Applying high gas pressure at elevated temperatures to eliminate residual porosity.
Each of these methods simply provides the energy needed to activate the fundamental mechanisms of diffusion and material transport.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the difference between mechanisms allows you to control the final properties of a component, such as its density and strength.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density: You must promote mechanisms like volume and grain boundary diffusion, often by using higher temperatures, finer powders, or methods like hot pressing.
- If your primary focus is increasing strength without shrinkage: You need to favor non-densifying mechanisms like surface diffusion by sintering at lower temperatures for longer times.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing: Liquid-phase sintering or advanced methods like Spark Plasma Sintering are ideal, as they dramatically accelerate the underlying transport mechanisms.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively control the sintering process to engineer a material with the precise properties your application requires.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Primary Driver | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic Diffusion | Particle bonding & densification |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering (LPS) | Liquid Formation & Capillary Force | Rapid densification & strength |
| Volume/Grain Boundary Diffusion | High Temperature | Densification & Shrinkage |
| Surface Diffusion | Lower Temperature | Strengthening (No Densification) |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for superior material properties? KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to control sintering mechanisms—from furnaces for solid-state diffusion to systems enabling liquid-phase sintering. Our expertise helps you achieve the perfect density, strength, and microstructure for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right sintering solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- How do you clean an alumina tube furnace? Extend Tube Life with Proper Maintenance



















