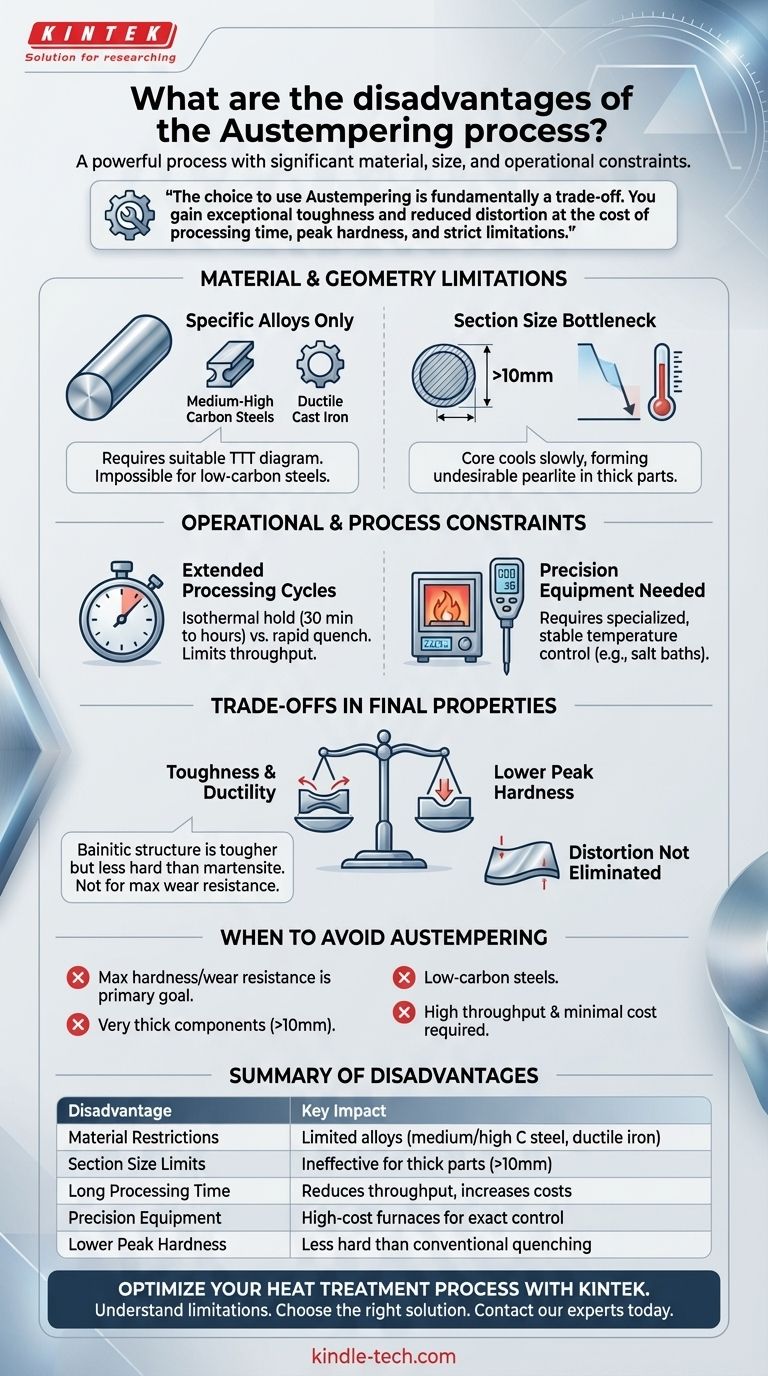
While a powerful heat treatment, the primary disadvantages of Austempering are its material and section size limitations, longer processing times, and the need for highly precise temperature control. This process is not a universal solution and is only suitable for a select range of ferrous alloys where its unique benefits of high toughness and ductility outweigh its significant operational constraints.
The choice to use Austempering is fundamentally a trade-off. You gain exceptional toughness and reduced distortion at the cost of processing time, peak hardness, and strict limitations on the type and size of the material you can treat.

The Challenge of Material and Geometry
Austempering's effectiveness is dictated by the fundamental metallurgical properties of the alloy and the physical dimensions of the component. Ignoring these factors is the most common source of failure.
Restricted to Specific Alloys
The process is only viable for materials with a suitable Time-Temperature-Transformation (TTT) diagram. This includes medium-to-high carbon steels and, most notably, ductile cast irons (to produce Austempered Ductile Iron or ADI).
These materials possess a "bainite bay"—a window of time at a specific temperature where the desired bainitic microstructure can form without transforming into undesirable pearlite or martensite.
Low-carbon steels lack this distinct processing window, making it impossible to perform a successful Austempering cycle.
The Section Size Bottleneck
The success of Austempering hinges on cooling the entire part quickly enough to avoid pearlite formation, then holding it at a stable temperature.
For thick or large components, the core cools much slower than the surface. This disparity means the core may begin transforming into soft, undesirable pearlite before it ever reaches the target Austempering temperature, resulting in inconsistent and inferior mechanical properties.
Operational and Process Constraints
Beyond material selection, Austempering presents unique operational challenges that can increase complexity and cost compared to conventional heat treatments.
Extended Processing Cycles
The isothermal hold required to transform austenite into bainite can take a significant amount of time, often lasting from 30 minutes to several hours.
This is substantially longer than the rapid quench of a conventional hardening process. These extended cycle times can limit furnace throughput, increase energy consumption, and ultimately raise the cost per part.
The Need for Precision Equipment
Maintaining a precise and uniform temperature during the isothermal hold is absolutely critical. This typically requires specialized equipment like agitated salt baths or sealed atmosphere furnaces with excellent thermal regulation.
Any significant temperature fluctuation can lead to the formation of unwanted microstructures, compromising the final part's integrity and performance. This requirement for precision adds to both capital equipment and operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Final Properties
Even when performed correctly, the resulting properties of an Austempered component involve specific compromises that may make it unsuitable for certain applications.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Balance
The bainitic structure produced by Austempering is renowned for its excellent toughness, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
However, it does not achieve the same peak hardness or wear resistance as a fully martensitic structure created by a conventional quench and temper process. If maximum surface hardness is the primary design goal, Austempering is often the inferior choice.
Distortion Isn't Completely Eliminated
Austempering is famous for producing less distortion than conventional quenching because the transformation to bainite is slower and more uniform.
However, it is not immune to distortion. Significant thermal stresses can still arise during the initial cooling to the Austempering temperature, especially in parts with complex geometries or drastic changes in thickness, leading to warping.
When to Avoid Austempering
Based on these limitations, you can make a clear decision about whether Austempering is the right process for your goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A conventional quench and temper process to achieve a fully martensitic structure is the superior choice.
- If you are working with very thick components (typically over 10mm): The risk of non-uniform microstructure and properties in the core makes Austempering a less reliable option.
- If your project involves low-carbon steels: The alloy's transformation kinetics make Austempering metallurgically impractical or impossible to perform correctly.
- If you require high throughput and minimal processing cost: The long cycle times and specialized equipment required for Austempering may not be economically viable.
Understanding these limitations is the key to leveraging Austempering for its intended purpose: creating exceptionally tough components where other methods fall short.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Material Restrictions | Limited to specific alloys (e.g., medium/high carbon steels, ductile iron) with a suitable TTT diagram. |
| Section Size Limits | Ineffective for thick parts (>10mm) due to non-uniform cooling and microstructure. |
| Long Processing Time | Isothermal hold can take hours, reducing throughput and increasing costs. |
| Precision Equipment Needed | Requires specialized, high-cost furnaces (e.g., salt baths) for exact temperature control. |
| Lower Peak Hardness | Bainitic structure offers superior toughness but less hardness than martensite from conventional quenching. |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Understanding the limitations of processes like Austempering is crucial for selecting the right solution for your laboratory or production needs. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific heat treatment challenges.
Whether you're working with specialized alloys or require precise temperature control, our range of furnaces and auxiliary equipment can help you achieve consistent, reliable results. Let our experts assist you in finding the perfect setup to enhance your efficiency and outcomes.
Ready to improve your heat treatment capabilities? Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















