In short, sintering temperature is the primary control variable that dictates the final density, strength, and microstructure of a part. It provides the thermal energy necessary to bond powder particles together, transforming a fragile "green" component into a solid, functional object. The correct temperature is not a single value but a carefully chosen point within a specific range for each material.
The core challenge of sintering is that temperature simultaneously drives desirable densification and potentially undesirable effects like grain growth and part distortion. Therefore, selecting the right temperature is a critical balancing act to achieve the required final properties without introducing defects.

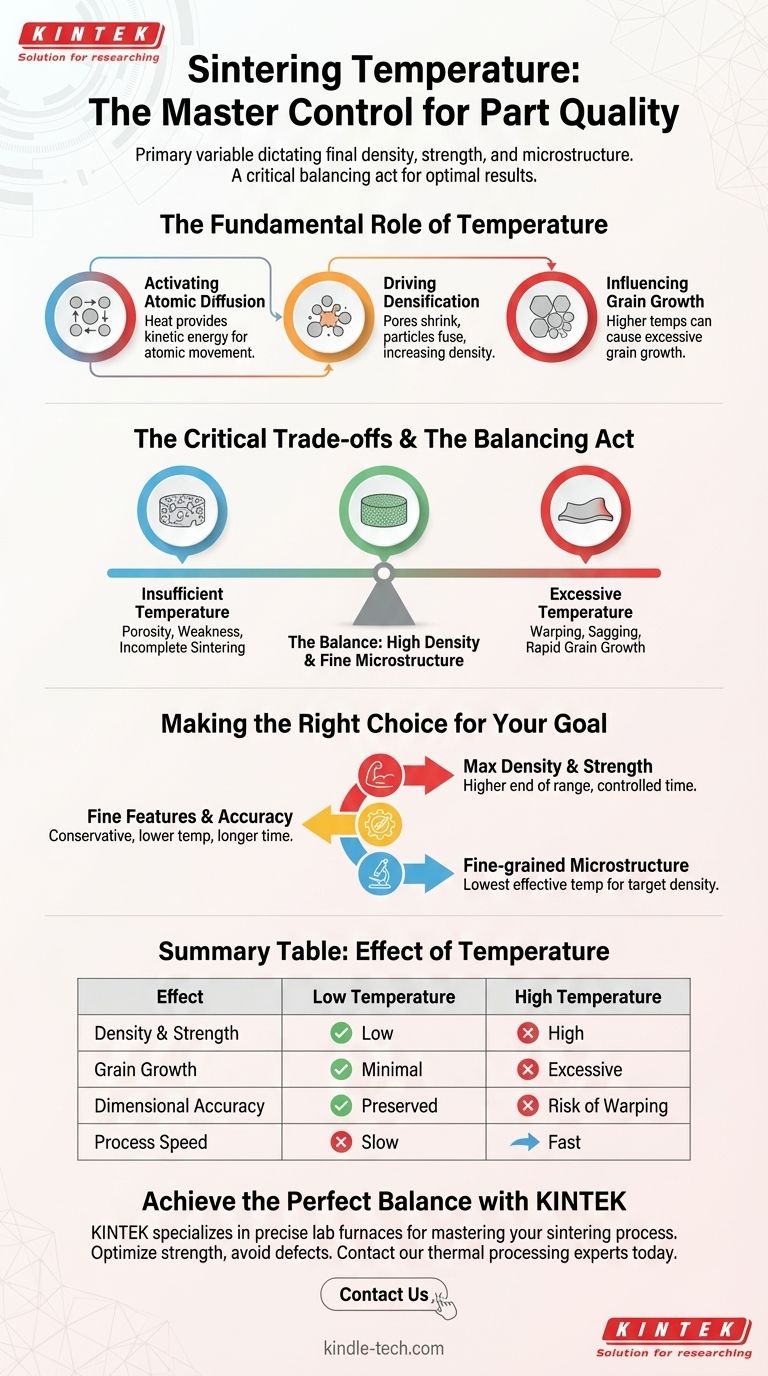
The Fundamental Role of Temperature in Sintering
Temperature is the engine of the entire sintering process. Without sufficient thermal energy, the atomic-level changes required to create a solid part simply cannot occur.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by diffusion, the process where atoms move and rearrange themselves to reduce energy. Heat provides the kinetic energy that allows atoms to move from one particle to another across their boundaries.
This process, known as grain boundary diffusion and bulk diffusion, is highly dependent on temperature. A small increase in temperature can cause an exponential increase in the diffusion rate.
Driving Densification
The primary goal of sintering is densification—the elimination of pores between the initial powder particles. As atoms diffuse, the particles fuse together, necks form and grow between them, and the empty spaces (pores) shrink and are eliminated.
Higher temperatures accelerate this process, leading to a denser, stronger part in less time.
Influencing Grain Growth
As particles bond, the original particle boundaries are consumed and replaced by grain boundaries in the new solid material. At high temperatures, these boundaries can migrate, causing larger grains to grow at the expense of smaller ones.
While some grain growth is inevitable, excessive growth can negatively impact mechanical properties like toughness, making the material more brittle.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering temperature is not simply about getting the material as hot as possible. It involves navigating critical trade-offs between achieving density and avoiding defects.
The Risk of Insufficient Temperature
An overly low temperature results in slow diffusion and incomplete sintering. This leaves behind significant porosity, creating a part that is mechanically weak, brittle, and has poor overall performance.
The Danger of Excessive Temperature
Conversely, too much heat can be disastrous. As the temperature approaches the material's melting point, the part can lose its structural integrity.
This can lead to severe defects mentioned in processing reports, such as warping under its own weight, sagging, or a complete loss of dimensional accuracy. It also promotes rapid and undesirable grain growth.
The Balance Between Density and Microstructure
The central trade-off is between achieving high density and maintaining a fine-grained microstructure. The ideal temperature is often the lowest possible temperature that can achieve the target density within an acceptable time frame, thereby minimizing excessive grain growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering temperature is always tied to the material being processed and the desired outcome. The typical range of 750°C to 1300°C covers a wide variety of metals and ceramics, but the specific target within that range is what matters.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: You will likely operate at the higher end of the material's recommended sintering range, carefully controlling time to prevent part distortion.
- If your primary focus is preserving fine features and dimensional accuracy: A more conservative, lower temperature with a potentially longer hold time is often the best approach to minimize any risk of warping or sagging.
- If your primary focus is achieving a fine-grained microstructure for specific properties like toughness: The goal is to use the lowest temperature that achieves the necessary density, thereby restricting grain boundary migration.
Ultimately, mastering sintering temperature is about using it as a precise tool to engineer the final material properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Effect of Temperature | Low Temperature | High Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Density & Strength | Low (Incomplete sintering) | High (Accelerated densification) |
| Grain Growth | Minimal | Excessive (Can cause brittleness) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Preserved | Risk of Warping and Sagging |
| Process Speed | Slow | Fast |
Achieve the perfect balance of density, strength, and dimensional accuracy in your sintered parts.
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab furnaces and expert consultation needed to master your sintering process. Whether you are working with metals or ceramics, our equipment ensures the exact temperature control required to achieve your target material properties—maximizing strength while avoiding defects like warping and excessive grain growth.
Let's optimize your sintering process together. Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does grain size affect the properties of ceramics? Master Hardness vs. Toughness for Your Application
- What are the useful applications of ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Your Industry
- What is the density of ceramic properties? A Guide to Material Selection for High-Performance Applications
- What temperature does clay sinter? Mastering the Range for Perfect Ceramic Results
- Why is silicon carbide more efficient? Unlock Higher Power Density with SiC's Superior Material Properties
- What are the advantages of silicon carbide? A Super-Material for Extreme Environments
- What is special about ceramic? Unmatched Durability Against Heat, Wear, and Chemicals
- What is the material used in high temperature furnace? Selecting the Right Ceramic for Extreme Heat



















