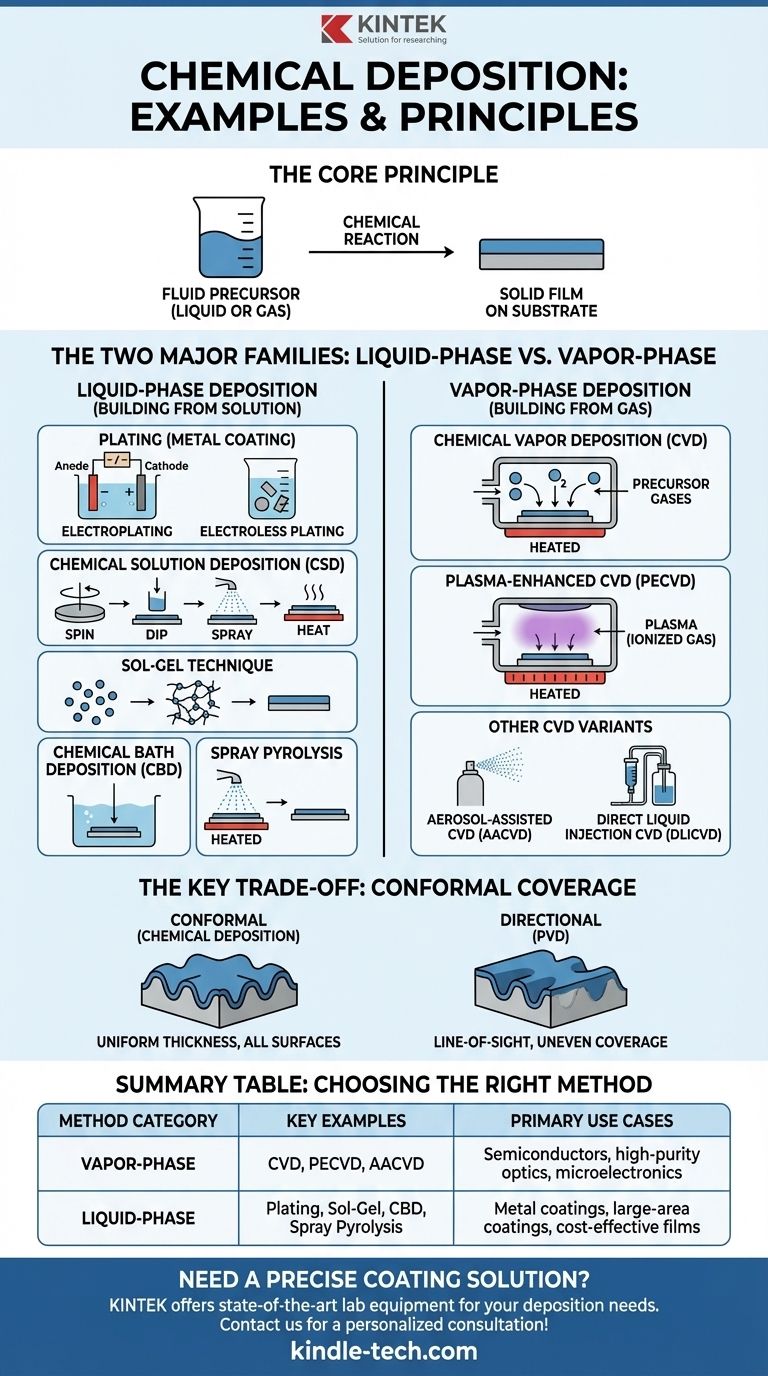
The primary examples of chemical deposition are broadly categorized by whether the material precursor is a liquid or a gas. Major techniques include Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and its variants from the gas phase, and methods like Plating, Sol-Gel, and Chemical Bath Deposition from the liquid phase. Each method uses a chemical reaction to create a solid film on a substrate.
The core principle uniting all chemical deposition techniques is the transformation of a fluid precursor—either a gas or a liquid—into a solid film on a surface through a controlled chemical reaction. This process is fundamentally different from physical deposition, where a material is simply moved from a source to a substrate without chemical change.

The Two Major Families: Liquid-Phase vs. Vapor-Phase
Chemical deposition methods are best understood by dividing them into two main categories based on the state of the starting material, or "precursor."
Liquid-Phase Deposition: Building from a Solution
These techniques use a liquid solution containing the necessary chemical precursors to form a solid film.
Plating
Plating involves depositing a metal coating onto a conductive surface. It is one of the oldest and most common forms of chemical deposition.
- Electroplating: An external electric current is used to drive the chemical reaction, reducing metal ions from the solution onto the object's surface.
- Electroless Plating: This process uses an autocatalytic chemical reaction to deposit the metal layer without the need for an external electrical power source.
Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD)
This is a general term for processes that use a chemical solution to deposit a film, often by spinning, dipping, or spraying the solution onto a substrate, followed by heating to solidify the film.
Sol-Gel Technique
The sol-gel process creates a solid material from small molecules in a solution (the "sol"). This "sol" evolves towards the formation of a gel-like network, which can be applied to a surface and heated to create a dense, solid film.
Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD)
In CBD, the substrate is simply immersed in a chemical bath where a slow, controlled reaction causes the desired material to precipitate and form a thin film on its surface.
Spray Pyrolysis
This method involves spraying a precursor solution onto a heated substrate. The droplets undergo a thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) upon contact, leaving behind a solid film.
Vapor-Phase Deposition: Building from a Gas
These advanced techniques are critical in manufacturing high-performance electronics and materials, delivering highly pure and uniform films.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. In this process, the substrate is placed in a reaction chamber and exposed to one or more volatile precursor gases, which react and decompose on the substrate's surface to produce the desired solid deposit.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD is a variation of CVD that uses a plasma (an ionized gas) to energize the precursor gases. This allows the deposition to occur at much lower temperatures, which is crucial for temperature-sensitive substrates.
Other CVD Variants
To handle different types of precursors, several specialized CVD methods exist.
- Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD): A liquid precursor is first atomized to form an aerosol (a fine mist), which is then transported into the reaction chamber.
- Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD): A liquid precursor is precisely injected into a heated vaporization zone before entering the reaction chamber as a gas.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Conformal Coverage
A defining characteristic of chemical deposition is its ability to produce highly conformal films.
The Advantage of Conformal Films
A conformal film coats every exposed surface of a substrate with a layer of uniform thickness. Imagine painting a complex, 3D object by dipping it in paint—the paint covers the top, bottom, and all crevices equally.
This is the nature of chemical deposition. Because the chemical reaction happens everywhere the precursor fluid touches, it perfectly coats even intricate and complex surface geometries.
The Contrast: Directional Deposition
This is distinct from "line-of-sight" or directional processes like physical vapor deposition (PVD). In PVD, the material travels in a straight line from source to substrate, creating thicker deposits on surfaces directly facing the source and thinner "shadowed" areas in trenches or on sidewalls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best method depends entirely on your material requirements, budget, and the geometry of the part you are coating.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform films for semiconductors or optics: Your best options are CVD or PECVD due to their exceptional control and film quality.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating of large areas: Methods like Spray Pyrolysis or Chemical Bath Deposition offer a scalable solution for applications like solar cells or window coatings.
- If your primary focus is applying a durable metal coating to a complex part: Electroplating or Electroless Plating are the established, reliable choices for corrosion resistance and conductivity.
Ultimately, selecting the right chemical deposition method is a matter of matching the technique's strengths to your specific engineering objective.
Summary Table:
| Method Category | Key Examples | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Vapor-Phase | CVD, PECVD, AACVD | Semiconductors, high-purity optics, microelectronics |
| Liquid-Phase | Electroplating, Electroless Plating, Sol-Gel, Chemical Bath Deposition | Metal coatings, large-area coatings, cost-effective films |
Need a precise coating solution for your lab? The right chemical deposition method is critical for achieving uniform, high-performance films on your substrates. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific deposition needs—whether you're working with semiconductors, complex metal parts, or large-scale coatings.
Let our experts help you select the ideal system to enhance your research or production. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















