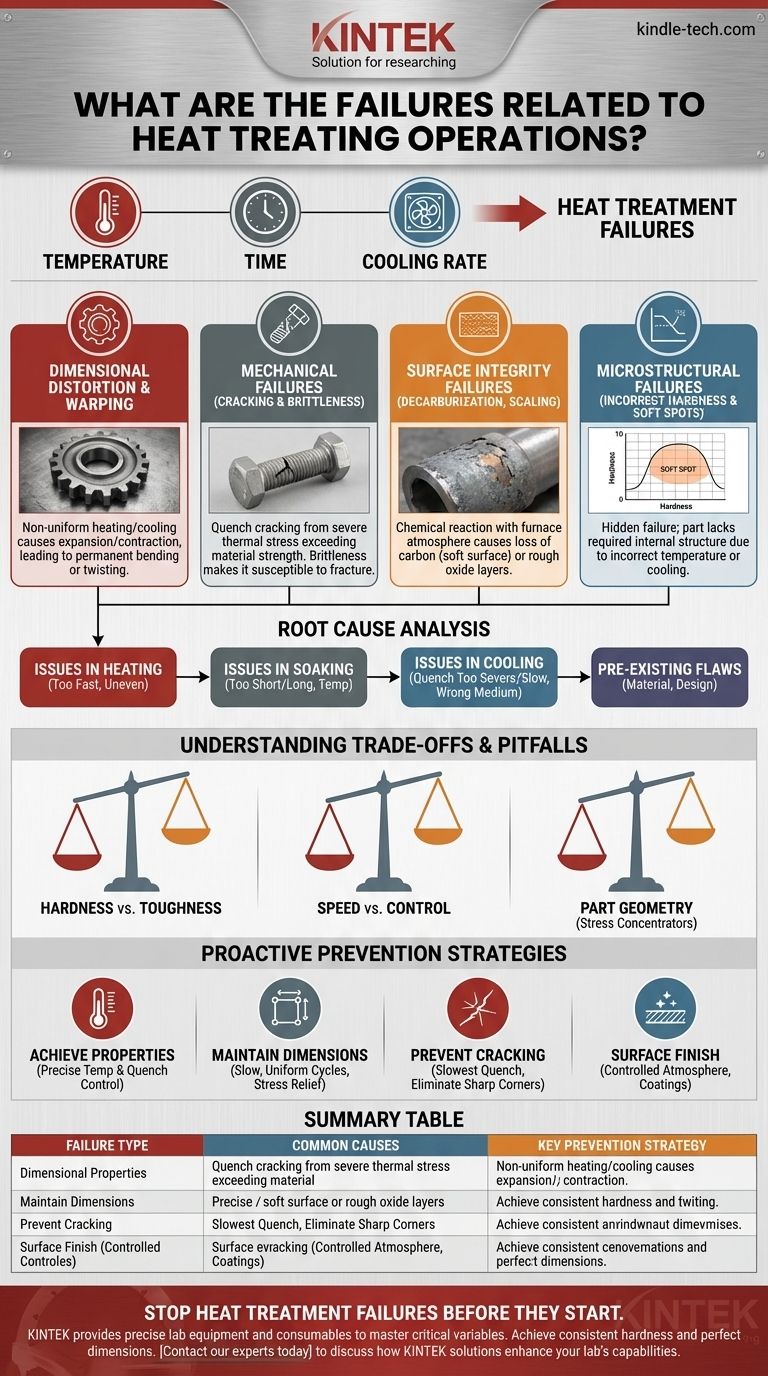
The most common failures in heat treating are dimensional distortion, surface cracking, incorrect hardness, and surface degradation. These issues almost always stem from a loss of control over three critical variables: temperature, time, and the rate of cooling.
Heat treatment failures are not random events. They are predictable outcomes resulting from a mismatch between the chosen process parameters, the material's properties, and the part's physical design. Understanding the root cause is the key to prevention.

The Anatomy of Heat Treatment Failures
Failures can be broadly categorized into four main types. Each points to a different problem in the process, material, or design.
Dimensional and Shape Failures (Distortion & Warping)
Distortion is a change in the size or shape of a part compared to its original dimensions. This occurs because of non-uniform heating or cooling.
As steel is heated and cooled, it expands and contracts. If one part of a component heats or cools faster than another, these volume changes create internal stresses that can bend, twist, or warp the part permanently.
Mechanical Failures (Cracking & Brittleness)
Cracking is the most catastrophic failure. Quench cracking is the most common form, happening when thermal stress from rapid cooling exceeds the material's strength.
This is especially common in high-hardenability steels or parts with complex geometries. Brittleness, while less visible, is equally dangerous and occurs when a part achieves high hardness but has no toughness, making it susceptible to fracture under impact.
Surface Integrity Failures (Decarburization, Scaling & Pitting)
These failures relate to the chemical reaction between the hot part and the furnace atmosphere.
Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface, resulting in a soft outer layer that has poor wear resistance and fatigue strength. Scaling, or oxidation, creates a rough, flaky layer on the surface that can interfere with final dimensions and performance.
Microstructural and Property Failures (Incorrect Hardness & Soft Spots)
This is a hidden but critical failure. The part may look perfect, but it lacks the required internal structure and mechanical properties.
This can manifest as soft spots (areas that failed to harden), or the entire part may be too soft or too hard. It's a direct result of failing to achieve the correct temperature or cooling the part too slowly to form the desired microstructure, such as martensite.
Root Cause Analysis: Tracing the Source of the Failure
Pinpointing the cause requires looking at the entire process, not just the final quenching step.
Issues in Heating
Heating a part too quickly is a primary cause of distortion. The surface heats up and expands much faster than the core, building up internal stresses before the part even reaches its target temperature.
Issues in Soaking (Holding)
The "soaking" phase, where the part is held at temperature, is critical for metallurgical transformation. If the time is too short, the transformation is incomplete, leading to soft spots. If it's too long, grains can grow too large, reducing toughness.
Issues in Cooling (Quenching)
The cooling stage is where most cracking failures occur. A quench that is too severe (too fast) for the material or geometry will cause massive thermal stress. Conversely, a quench that is too slow will fail to achieve the necessary hardness.
The choice of quenching medium—water, oil, polymer, or air—is one of the most important decisions in the entire process.
Pre-existing Material & Design Flaws
Often, the heat treatment process is blamed for failures that were initiated much earlier. Poor quality steel with inclusions, residual stresses from heavy machining, or poor part design can all lead to failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Achieving perfect results involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for success.
Hardness vs. Toughness
The fundamental trade-off in heat treating is that as hardness increases, toughness (and ductility) generally decreases. Pushing for maximum hardness often increases the risk of brittleness and cracking. The goal is always to find the optimal balance for the application.
Speed vs. Control
Attempting to accelerate a heat treatment cycle by heating or cooling too rapidly is a false economy. It is one of the leading causes of distortion and quench cracking. A successful process prioritizes uniformity and control over raw speed.
Ignoring Part Geometry
Design is a critical, and often overlooked, factor. Sharp internal corners, drilled holes near edges, and abrupt changes from thick to thin sections are stress concentrators. These areas cool at different rates and become prime locations for cracks to form during quenching.
A Proactive Approach to Preventing Failures
By understanding the principles behind the failures, you can design a robust and repeatable heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific mechanical properties (e.g., hardness): Your control over the soaking temperature and the quench rate must be absolutely precise.
- If your primary focus is maintaining dimensional accuracy: Prioritize slow, uniform heating and cooling, and consider adding stress-relieving steps before and after the main process.
- If your primary focus is preventing cracking: Select the slowest possible quench that still achieves the required hardness, and work with designers to eliminate sharp internal corners in the part.
- If your primary focus is surface finish: You must use a controlled furnace atmosphere or protective coating to prevent decarburization and oxidation.
Mastering these variables transforms heat treatment from a source of risk into a powerful tool for creating high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Failure Type | Common Causes | Key Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Distortion | Non-uniform heating/cooling | Prioritize slow, uniform heating and cooling cycles |
| Cracking & Brittleness | Severe quench, material flaws | Use a slower quench medium; eliminate stress concentrators in design |
| Surface Decarburization | Uncontrolled furnace atmosphere | Use protective atmosphere or coatings during heating |
| Incorrect Hardness/Soft Spots | Inaccurate temperature or soak time | Ensure precise temperature control and complete transformation |
Stop Heat Treatment Failures Before They Start
Don't let unpredictable failures like distortion, cracking, or soft spots compromise your components and impact your bottom line. The root cause often lies in a mismatch between your process and your materials.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need to master the critical variables of temperature, atmosphere, and cooling. Whether you require a reliable furnace with exact temperature control, the right quenching mediums, or expert advice, we are your partner in developing a robust and repeatable heat treatment process.
Achieve consistent hardness, perfect dimensions, and superior surface integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure your heat treatment success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between cannabis extract and distillate? A Guide to Potency vs. Full-Spectrum Effects
- What is the density of synthetic graphite? Understanding the Range from 1.5 to 2.26 g/cm³
- How does heat treatment affect metal properties? Engineer Strength, Hardness, and Toughness
- How does a DC magnetron sputtering work? A Guide to High-Speed, Uniform Thin Films
- Why should glass-ceramic green bodies be placed in a precision drying oven? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Yield
- Is sintering the same as welding? Key Differences in Material Bonding and Fusion Explained
- At what temperature does THC distillate degrade? A Guide to Preserving Potency and Purity
- Why is a high-performance laboratory magnetic stirrer necessary? Optimize Photocatalytic Degradation Results



















