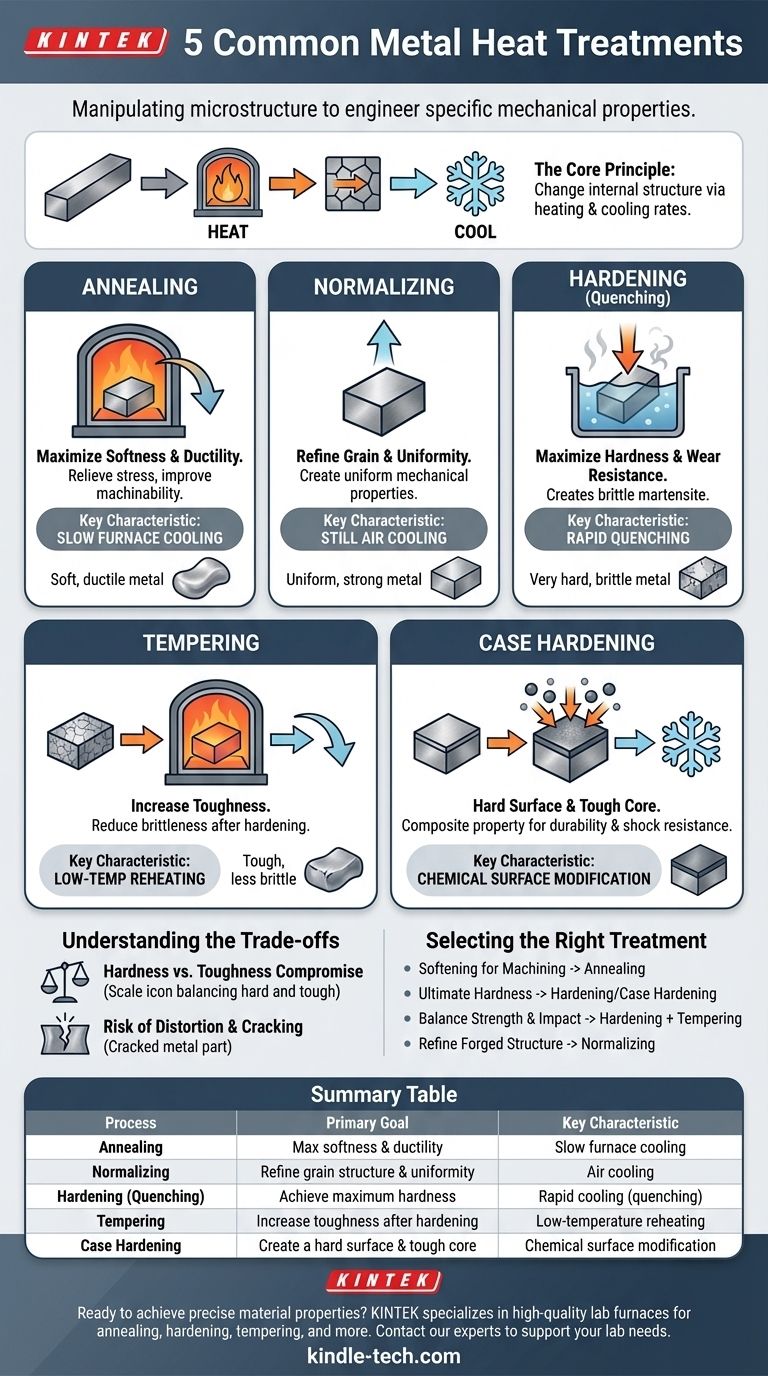
In essence, the five most common heat treatment processes are annealing, normalizing, hardening, tempering, and case hardening. Each process involves a specific, controlled cycle of heating and cooling designed to manipulate a metal's internal structure, thereby altering its physical properties like hardness, toughness, and ductility to fit a desired application.
Heat treatment is not about making a metal generically "better," but about precisely engineering its microscopic crystal structure (microstructure) to achieve a specific balance of properties required for its function.
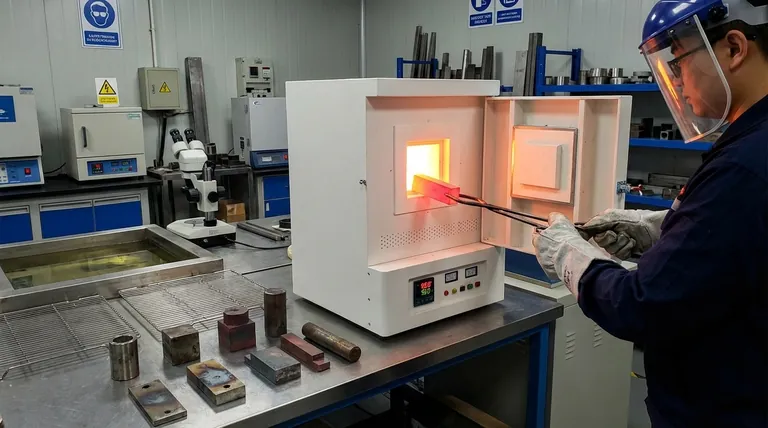

The Core Principle: Manipulating Microstructure
The properties of a metal are dictated by its internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure. Heat treatment works by changing this structure.
By heating a metal above a critical temperature, you dissolve its existing structure into a different, more uniform phase. The rate at which you cool it back down determines the final microstructure and, consequently, its mechanical properties.
Foundational "Through" Treatments
These processes affect the entire cross-section of the metal part.
Annealing: For Maximum Softness and Ductility
Annealing is a process used to make a metal as soft, ductile, and easy to work with as possible. It is often performed to relieve internal stresses from prior work, improve machinability, or prepare a metal for severe cold forming.
The process involves heating the metal to a specific temperature, holding it there for a period, and then cooling it very slowly, typically inside the furnace. This slow cooling allows the microstructure to form in the most stable, stress-free state.
Normalizing: For Uniformity and Strength
Normalizing is often used on steel after processes like forging or rolling to refine its grain structure and create more uniform mechanical properties.
Similar to annealing, the metal is heated to a specific temperature. However, it is then removed from the furnace and cooled in still air. This faster cooling rate results in a finer, stronger microstructure than annealing, offering a good balance of strength and ductility.
Hardening (Quenching): For Maximum Hardness
When the goal is to make a steel part as hard and wear-resistant as possible, hardening is the primary method.
The process involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then cooling it with extreme rapidity. This rapid cooling, called quenching, is done by plunging the hot part into a medium like water, oil, or brine. This "freezes" the microstructure in a very hard but brittle state called martensite.
Tempering: To Add Toughness
A part that has been hardened is often too brittle for practical use; a sharp impact could cause it to shatter. Tempering is a secondary process performed after hardening to reduce this brittleness.
The hardened part is re-heated to a much lower temperature and held for a set time. This process relieves internal stresses and trades a small amount of hardness for a significant increase in toughness, which is the ability to absorb impact without fracturing.
Surface-Specific Treatment: Case Hardening
Sometimes, you need a part with a very hard, wear-resistant surface but a softer, tougher interior or "core." This is achieved through case hardening.
How Case Hardening Works
Case hardening is a group of processes that chemically modifies the surface of a metal, typically low-carbon steel, to give it a "case" of higher hardness. This creates a composite part with excellent surface durability and a ductile core that resists shock and impact.
A common method is carburizing, where the part is heated in a carbon-rich atmosphere. Carbon atoms diffuse into the surface, which can then be hardened via quenching, leaving the low-carbon core unaffected and tough.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a game of balancing opposing properties. Understanding these trade-offs is critical to selecting the correct process.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Compromise
This is the most fundamental trade-off in metallurgy. As you increase a metal's hardness, you almost always decrease its toughness. A fully hardened, un-tempered steel is like glass: extremely hard but brittle. Tempering is the act of intentionally negotiating this trade-off.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid temperature changes involved in heat treatment, especially quenching, induce immense internal stress. If not properly controlled, this stress can cause parts to warp, distort, or even crack during or after the process.
Process Control is Everything
The final properties of a heat-treated part are highly sensitive to the exact temperatures, hold times, and cooling rates used. A slight deviation can produce a dramatically different and undesirable outcome. This is why heat treatment is considered a highly skilled and precise industrial process.
Selecting the Right Treatment for Your Goal
Base your choice on the primary requirement for the finished component.
- If your primary focus is to soften metal for easy machining or forming: Choose annealing for maximum stress relief and ductility.
- If your primary focus is ultimate hardness and wear resistance (e.g., for a cutting tool or bearing surface): Use hardening (quenching) or, for a dual-property part, case hardening.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high strength and impact resistance (e.g., for a hammer or axle): The required process is hardening followed immediately by tempering.
- If your primary focus is to refine the structure and strength of a forged or rolled part: Choose normalizing to create a uniform and reliable result.
By understanding these core processes, you can begin to specify the precise material properties needed for any engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Maximize softness & ductility | Slow furnace cooling |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure & uniformity | Air cooling |
| Hardening (Quenching) | Achieve maximum hardness | Rapid cooling (quenching) |
| Tempering | Increase toughness after hardening | Low-temperature reheating |
| Case Hardening | Create a hard surface & tough core | Chemical surface modification |
Ready to achieve precise material properties in your lab? The right heat treatment process is critical for your application's success. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab furnaces and equipment needed for precise annealing, hardening, tempering, and more. Our solutions help you control every variable to ensure consistent, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific metal heat treatment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What affects melting range? Understand the Critical Role of Purity and Structure
- What is the cooling rate of a muffle furnace? Understanding Its Slow, Passive Nature
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What is ramp rate and how does that affect a melting point measurement? Master the Key to Accurate Thermal Analysis
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating



















