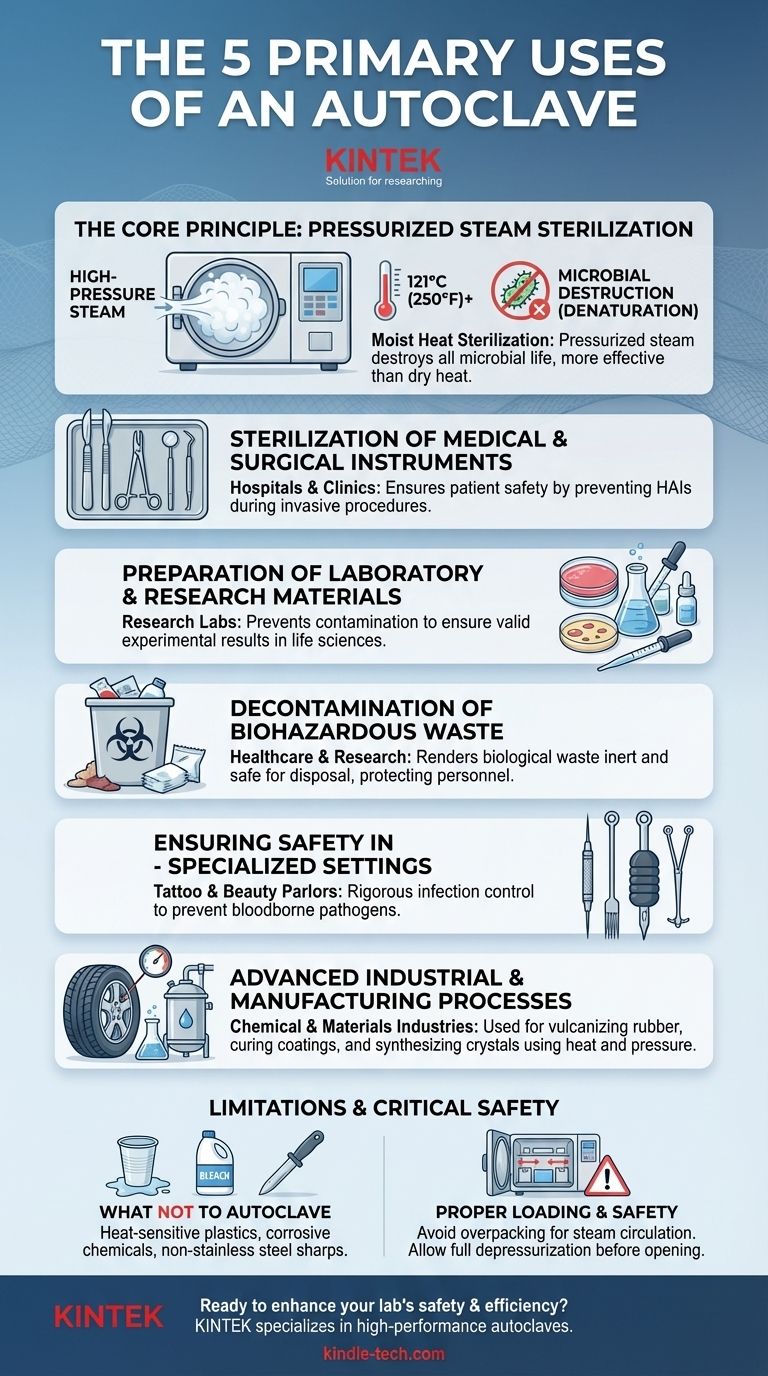
While often associated with hospitals, the autoclave's core function of using high-pressure steam for sterilization has five primary applications across various fields. These include the sterilization of medical and surgical instruments, the preparation of sterile laboratory materials like culture media, the safe decontamination of biohazardous waste, ensuring hygiene in specialized settings like tattoo parlors, and facilitating industrial processes like vulcanizing rubber.
An autoclave does more than just clean; it achieves complete sterilization by using pressurized steam to destroy all forms of microbial life. This capability makes it an indispensable tool in any environment where absolute sterility is non-negotiable, from operating rooms to advanced manufacturing facilities.

The Core Principle: How Autoclaves Achieve Sterilization
The Power of Pressurized Steam
An autoclave is essentially a sophisticated pressure chamber. It operates on the principle of moist heat sterilization.
Unlike simply boiling water, which reaches 100°C (212°F), an autoclave increases the pressure inside its chamber. This allows water vapor (steam) to reach much higher temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or more.
Why It's So Effective
This combination of intense heat and moisture is lethal to microorganisms. The high-temperature steam rapidly penetrates materials and denatures essential proteins and lipids within bacteria, viruses, and spores, effectively killing them.
This method is far more effective and reliable than dry heat or chemical disinfectants for items that can withstand the conditions.
Key Applications Across Industries
The autoclave's robust sterilization capability makes it essential in numerous sectors.
1. Sterilization of Medical and Surgical Instruments
This is the most recognized use. Hospitals, clinics, and dental offices rely on autoclaves to sterilize reusable surgical equipment, from scalpels and forceps to complex hollow instruments.
This process is critical for preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and ensuring patient safety during invasive procedures.
2. Preparation of Laboratory and Research Materials
In microbiology, genetics, and life science research, preventing contamination is paramount to achieving valid results.
Autoclaves are used daily to sterilize culture media, glassware, pipette tips, solutions, and other lab equipment before use. This ensures that experiments begin with a sterile, controlled environment.
3. Decontamination of Biohazardous Waste
Before disposal, any material contaminated with biological agents—such as used petri dishes, medical waste, or sharps containers—poses a significant safety risk.
Autoclaving is the gold-standard method for rendering this biohazardous waste inert and safe for final disposal, protecting healthcare workers, researchers, and the public.
4. Ensuring Safety in Specialized Professional Settings
The need for sterility extends beyond medicine and research. Fields where skin is punctured require rigorous infection control.
Tattoo studios, piercing parlors, and even high-end beauty salons use autoclaves to sterilize needles, grips, and other reusable tools to prevent the transmission of bloodborne pathogens.
5. Advanced Industrial and Manufacturing Processes
Beyond sterilization, the high-pressure, high-temperature environment of an autoclave is leveraged in manufacturing.
In the chemical and materials industries, autoclaves are used to cure coatings, vulcanize rubber, and synthesize crystals. In these applications, the pressure and heat catalyze chemical reactions and alter material properties, a process unrelated to killing microbes.
Understanding the Limitations and Critical Safety Practices
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution and requires proper handling to be effective and safe.
What Not to Autoclave
Certain materials cannot withstand the high heat and pressure. These include:
- Heat-sensitive plastics that can melt or warp.
- Corrosive chemicals like bleach, which can release toxic fumes and damage the autoclave chamber.
- Sharp instruments that are not made of stainless steel, as they can be dulled.
The Importance of Proper Loading
For sterilization to be successful, steam must circulate freely and contact all surfaces of the items inside.
Overpacking the chamber or using sealed containers can create air pockets where steam cannot penetrate, leading to incomplete sterilization. This is a critical point of failure that can compromise safety or research.
Ensuring User Safety
An autoclave is a high-pressure vessel and must be operated with caution. Modern units have multiple safety locks and valves, but users must always allow the chamber to cool and depressurize completely before opening the door to avoid severe steam burns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the autoclave's primary function helps you apply it correctly based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is healthcare and patient safety: Prioritize its use for the complete sterilization of surgical instruments and the safe decontamination of all medical waste.
- If your primary focus is research integrity: Use it diligently to prepare all media, solutions, and equipment to eliminate variables and prevent experimental contamination.
- If your primary focus is industrial production: Leverage its high-pressure environment for material curing and synthesis, recognizing it as a manufacturing tool beyond sterilization.
Ultimately, the autoclave is a cornerstone technology that enables the safety and progress of modern medicine, science, and industry.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Instrument Sterilization | Destroying microbes on surgical tools | Hospitals, Dental Clinics |
| Laboratory Material Preparation | Ensuring sterile culture media & equipment | Research Labs, Microbiology |
| Biohazardous Waste Decontamination | Rendering infectious waste safe | Healthcare, Research Facilities |
| Specialized Professional Safety | Sterilizing tattoo & piercing equipment | Tattoo Parlors, Beauty Salons |
| Industrial Manufacturing Processes | Vulcanizing rubber, curing coatings | Chemical, Materials Industries |
Ready to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed for healthcare, research, and industrial applications. Our solutions ensure reliable sterilization, contamination control, and precise process management. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















