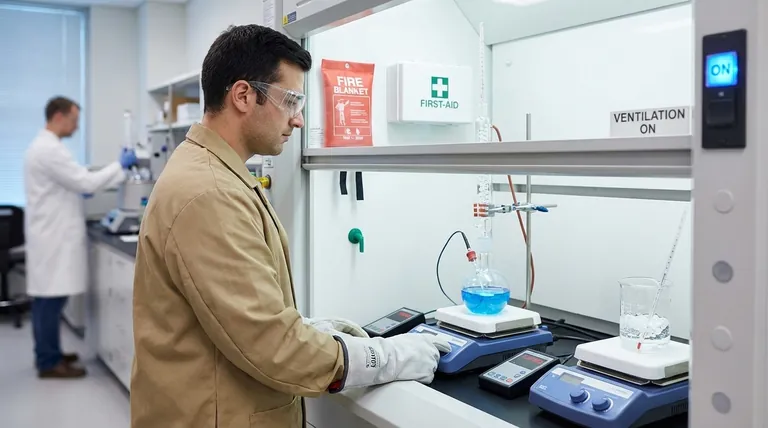
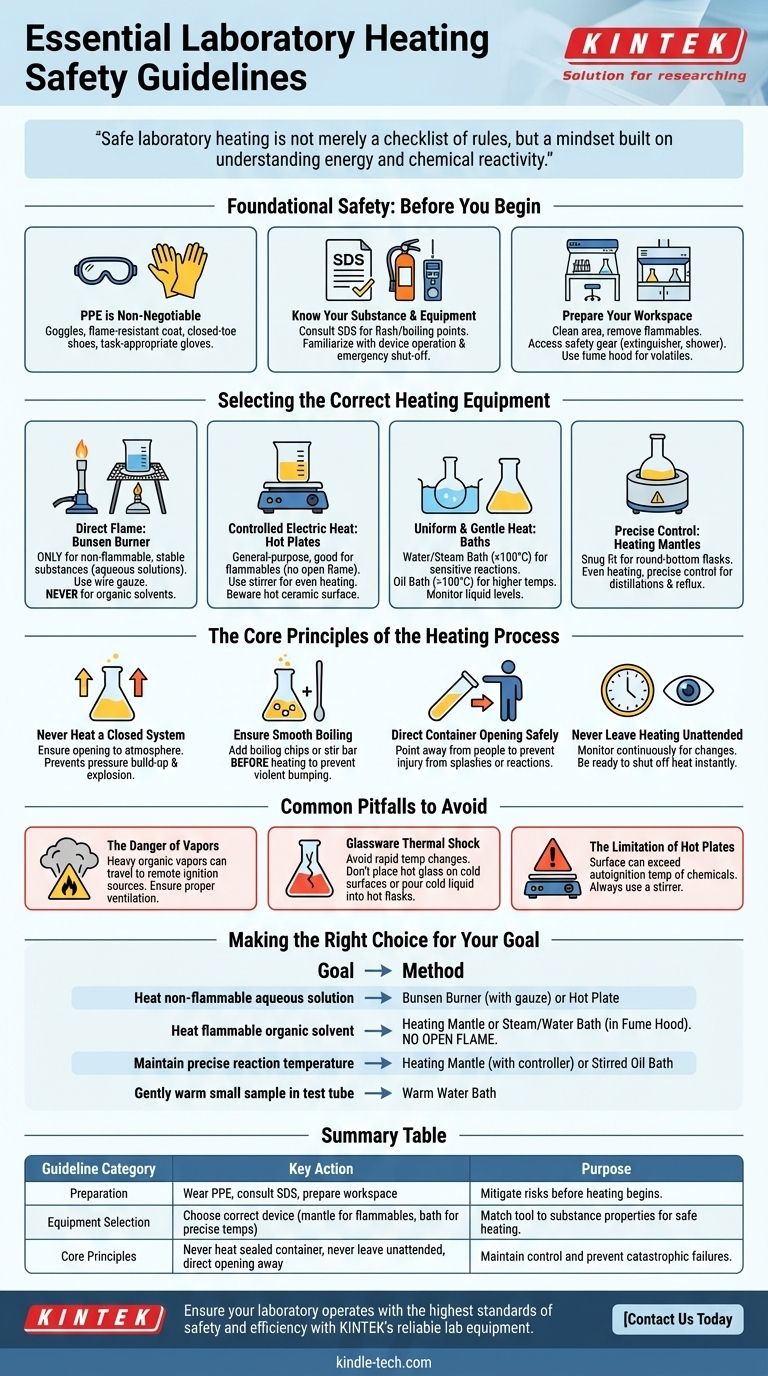
The fundamental guidelines for heating substances in the laboratory center on five critical actions: always wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), select the correct heating apparatus for the substance, never heat a sealed container, always point the vessel opening away from people, and never leave a heating process unattended. Adhering to these rules is the foundation of preventing burns, fires, and explosions.
Safe laboratory heating is not merely a checklist of rules, but a mindset built on understanding energy and chemical reactivity. Your primary responsibility is to maintain absolute control over the heating process at all times, anticipating risks to prevent accidents before they happen.

Foundational Safety: Before You Begin
Proper preparation is the most critical phase of any heating procedure. Rushing this step introduces unacceptable risks.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
Safety goggles, a flame-resistant lab coat, and closed-toe shoes are the bare minimum. Goggles protect your eyes from splashes and vessel failures.
Select gloves appropriate for the task. Use thermally insulated gloves for handling hot objects and chemically resistant gloves for handling the substances themselves.
Know Your Substance and Your Equipment
Before applying any heat, consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the substance. Pay close attention to its flash point, boiling point, and any notes on thermal decomposition or hazardous byproducts.
Familiarize yourself with the operation of your heating device, whether it's a Bunsen burner, hot plate, or heating mantle. Know how to shut it off quickly in an emergency.
Prepare Your Workspace
Ensure your work area is clean and uncluttered. Remove all flammable materials (like paper towels or solvent bottles) from the vicinity of the heating apparatus.
Confirm you have clear access to safety equipment, including a fire extinguisher, fire blanket, and safety shower. If heating a volatile or toxic substance, perform the entire procedure inside a certified fume hood.
Selecting the Correct Heating Equipment
The choice of heating device is dictated by the chemical properties of your substance and the precision required. Using the wrong tool is a common cause of lab accidents.
Direct Flame: The Bunsen Burner
A Bunsen burner provides intense, direct heat. It should only be used for heating non-flammable, stable substances, typically aqueous solutions in borosilicate glassware.
Never use a Bunsen burner to heat organic solvents or other flammable liquids. Vapors can easily travel and ignite in the open flame. Always place glassware on a wire gauze over the flame to diffuse the heat and reduce thermal stress.
Controlled Electric Heat: Hot Plates
Hot plates are the workhorses for general-purpose heating, especially for flammable liquids, as they eliminate the open flame.
Use a hot plate with a stirrer function to ensure even heating and prevent bumping. Be aware that the ceramic surface can remain dangerously hot long after the device is turned off.
Uniform & Gentle Heat: Water and Oil Baths
For sensitive reactions or when a temperature must not exceed a certain point (like 100°C), a water or steam bath is ideal. It provides exceptionally gentle and uniform heat.
For temperatures above 100°C, an oil bath is used. Always monitor the liquid level in the bath and use a non-volatile, stable oil.
Precise Control: Heating Mantles
Heating mantles are designed to fit snugly around round-bottom flasks. They provide extremely even heating across the glass surface, minimizing the risk of thermal shock and enabling precise temperature control, making them essential for distillations and refluxing.
The Core Principles of the Heating Process
Once heating begins, a strict set of principles must be followed to maintain control.
Never Heat a Closed System
This is the most important rule. Heating a liquid in a sealed container causes it to vaporize, creating an immense pressure build-up. This will inevitably lead to a violent explosion, turning the glassware into shrapnel.
Always ensure the system is open to the atmosphere, even if through a condenser or a drying tube.
Ensure Smooth Boiling
Superheated liquids can boil suddenly and violently in a phenomenon called bumping, which can eject hot contents from the vessel.
To prevent this, add one or two boiling chips or a magnetic stir bar to the liquid before you begin heating. Never add boiling chips to an already hot liquid, as this will trigger immediate, violent boiling.
Direct the Container Opening Safely
Always hold a heated test tube or position a flask so that its opening points away from you and everyone else in the lab. This ensures that in the event of bumping or an unexpected reaction, the hazardous contents are not ejected toward anyone.
Never Leave Heating Unattended
A situation can escalate from normal to critical in seconds. You must always be present to monitor the temperature, watch for signs of trouble (e.g., color change, pressure build-up), and be ready to shut off the heat source immediately.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding common mistakes helps build the intuition required for true safety.
The Danger of Vapors
Many organic solvent vapors are heavier than air. They can flow invisibly along a benchtop or floor and be ignited by a remote ignition source, such as a pilot light or another student's Bunsen burner. This is why proper ventilation in a fume hood is paramount when heating flammables.
Glassware Thermal Shock
Borosilicate glassware (e.g., Pyrex®, Kimax®) is resistant to heat but not invincible. Placing hot glassware on a cold stone benchtop or pouring cold liquid into a hot flask can cause it to shatter from thermal shock. Allow glassware to cool gradually.
The Limitation of Hot Plates
While safer than open flames, hot plates are still a significant ignition source. Do not assume a hot plate is safe if its surface temperature exceeds the autoignition temperature of the chemical you are working with. Always use a stirrer to distribute heat and prevent localized hot spots.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your heating method based on safety first, then on the needs of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is heating a non-flammable aqueous solution: A Bunsen burner on a ring stand with a wire gauze is efficient, but a hot plate offers simpler control.
- If your primary focus is heating a flammable organic solvent: Use an electrically-rated heating mantle or a steam/water bath inside a fume hood. Never use an open flame.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a precise reaction temperature: A heating mantle connected to a temperature controller or a stirred oil bath offers the best precision.
- If your primary focus is gently warming a small sample in a test tube: A warm water bath provides the safest and most controlled method.
Ultimately, laboratory safety is an active process, not a passive one; your constant vigilance is the most crucial safety device.
Summary Table:
| Guideline Category | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Wear appropriate PPE, consult SDS, prepare workspace | Mitigate risks before heating begins |
| Equipment Selection | Choose correct device (e.g., mantle for flammables, bath for precise temps) | Match tool to substance properties for safe heating |
| Core Principles | Never heat a sealed container, never leave unattended, direct opening away | Maintain control and prevent catastrophic failures |
Ensure your laboratory operates with the highest standards of safety and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including heating mantles, hot plates, and safety accessories, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories. Let our expertise help you create a safer, more productive workspace. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and find the perfect heating solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors that affect the quality of heat treatment? Mastering Temperature, Atmosphere, and Process Control
- Why is it necessary to encapsulate alloy samples? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Equilibrium Heat Treatment
- What is the purpose of sample preparation? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Analytical Results
- What device is used to test real diamonds? The Definitive Guide to Diamond Testers & Verification
- What is the process of slow heating and low temperature pyrolysis produces? Maximizing Biochar for Carbon Sequestration
- Why must cold traps and drying tubes be configured for WGS gas analysis? Protect Your Micro-GC from Moisture Damage.
- How are electron beams made? From Thermionic to Field Emission Explained
- What are the hazards in heat treatment operation? Mitigate Thermal, Chemical, and Mechanical Risks



















