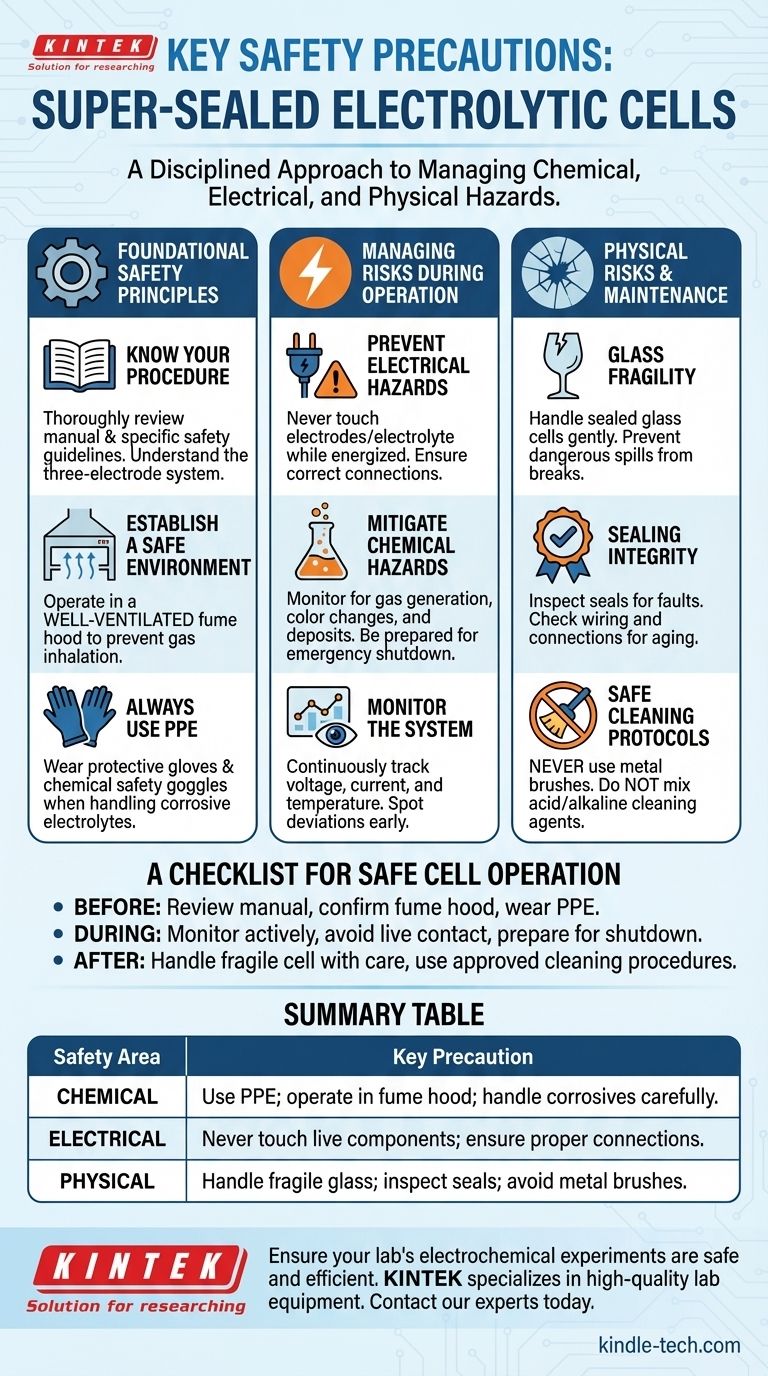
The key safety precautions for operating a super-sealed electrolytic cell involve a disciplined approach to managing chemical, electrical, and physical hazards. You must use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and goggles, operate within a well-ventilated area such as a fume hood, and strictly follow established procedures for setup, monitoring, and cleaning.
Safe operation of a sealed electrolytic cell is not merely a checklist; it's a systematic process. The core principle is to anticipate and mitigate the distinct risks associated with corrosive chemicals, electrical current, and the physical constraints of a sealed glass vessel.

Foundational Safety Principles
Before any experiment begins, establishing a safe baseline is critical. This involves understanding your equipment, environment, and personal protection.
Know Your Procedure and Manual
You must be thoroughly familiar with the operation manual and all safety guidelines specific to your cell. These documents contain critical parameters and warnings.
This cell typically operates as part of a three-electrode system (working, counter, and reference electrodes), where applied voltage drives specific electrochemical reactions. Understanding this process helps you anticipate outcomes.
Establish a Safe Environment
All operations should be conducted in a well-ventilated environment, preferably a fume hood. This is non-negotiable when the process may produce harmful or toxic gases.
Proper ventilation protects you from inhaling dangerous substances that can be released from the electrolyte or generated at the electrodes.
Always Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
When handling corrosive electrolytes or assembling the cell, always wear protective gloves and chemical safety goggles.
Direct contact with electrolytes can cause chemical burns, while splashes can result in serious eye injury. PPE is your first and most important line of defense.
Managing Risks During Operation
Once the experiment is running, your focus shifts to active monitoring to prevent accidents and ensure the integrity of the experiment.
Prevent Electrical Hazards
Ensure the cell is correctly connected to the power supply and any detection instruments before activating the power.
Never make direct contact with the electrodes or the electrolyte while the system is energized. This is essential to prevent electric shock, which can be severe.
Mitigate Chemical Hazards
Pay close attention to the reaction. Note any gas generation, changes in solution color, or deposits forming on the electrodes.
Sealed cells can build pressure if gas is produced unexpectedly. Be prepared to address any abnormalities immediately by following your lab's emergency shutdown procedure.
Monitor the System Continuously
Control reaction conditions like voltage, current, and temperature according to your experimental plan.
Consistent monitoring and data recording are not just for good results; they are also safety measures that help you spot dangerous deviations from expected behavior.
Understanding the Physical Risks
The physical nature of a sealed glass electrolytic cell presents unique hazards that demand careful handling and maintenance.
The Fragility of Glass Components
The cell body is made of glass and is inherently fragile. It must be handled gently at all times to prevent cracks or breakage.
A sudden break can lead to a dangerous spill of corrosive and electrically live material. Always support the cell securely.
The Importance of Sealing Integrity
Part of your routine safety check should be inspecting the cell's sealing integrity. A faulty seal can lead to leaks of hazardous materials.
Additionally, check for signs of aging or degradation in the wiring and connections to prevent electrical faults.
Follow Safe Cleaning Protocols
When cleaning the cell, never use metal brushes, as they can scratch the glass surfaces, creating weak points that may fail under pressure or thermal stress.
It is strictly forbidden to mix acid and alkaline cleaning agents, such as nitric acid and sodium hydroxide. This can cause a violent exothermic reaction.
A Checklist for Safe Cell Operation
Use these points to guide your actions during each phase of the experimental process.
- Before beginning any experiment: Review the operating manual, confirm your fume hood is operational, and put on your required PPE (gloves and goggles).
- During the electrolysis process: Actively monitor for abnormalities, never touch live components, and be prepared to execute a safe shutdown.
- After the experiment is complete: Handle the fragile glass cell with extreme care and use only approved, non-reactive cleaning procedures.
Ultimately, disciplined adherence to safety protocols is inseparable from conducting sound and successful science.
Summary Table:
| Safety Area | Key Precaution |
|---|---|
| Chemical | Use PPE; operate in a fume hood; handle corrosive electrolytes with care. |
| Electrical | Never touch live components; ensure proper connections before powering on. |
| Physical | Handle fragile glass carefully; inspect seals; avoid metal brushes during cleaning. |
Ensure your lab's electrochemical experiments are safe and efficient. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable electrolytic cells and safety gear designed for demanding laboratory environments. Our products help you mitigate risks and achieve precise results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What role do nickel-plated bipolar plates play in an electrolyzer stack? Enhance Efficiency and Durability
- What technical advantages are gained by coupling ion exchange resin regeneration with electrochemical oxidation systems?
- What are the advantages of a flat electrochemical cell for corrosion? Achieve Precise Pitting & Crevice Analysis
- How should an all-PTFE electrolytic cell be stored after use? Expert Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Performance
- What are the necessary preparation steps before using a side-window optical electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate Spectroelectrochemical Data
- What are the advantages of using a three-electrode electrolytic cell with a quartz window for photoelectric testing?
- What role does an electrochemical workstation play in TiNO coating evaluation? Quantify Biological Corrosion Protection
- What is the purpose of using a frit glass tube in a three-electrode cell? Enhance Vanadium Redox Testing Accuracy