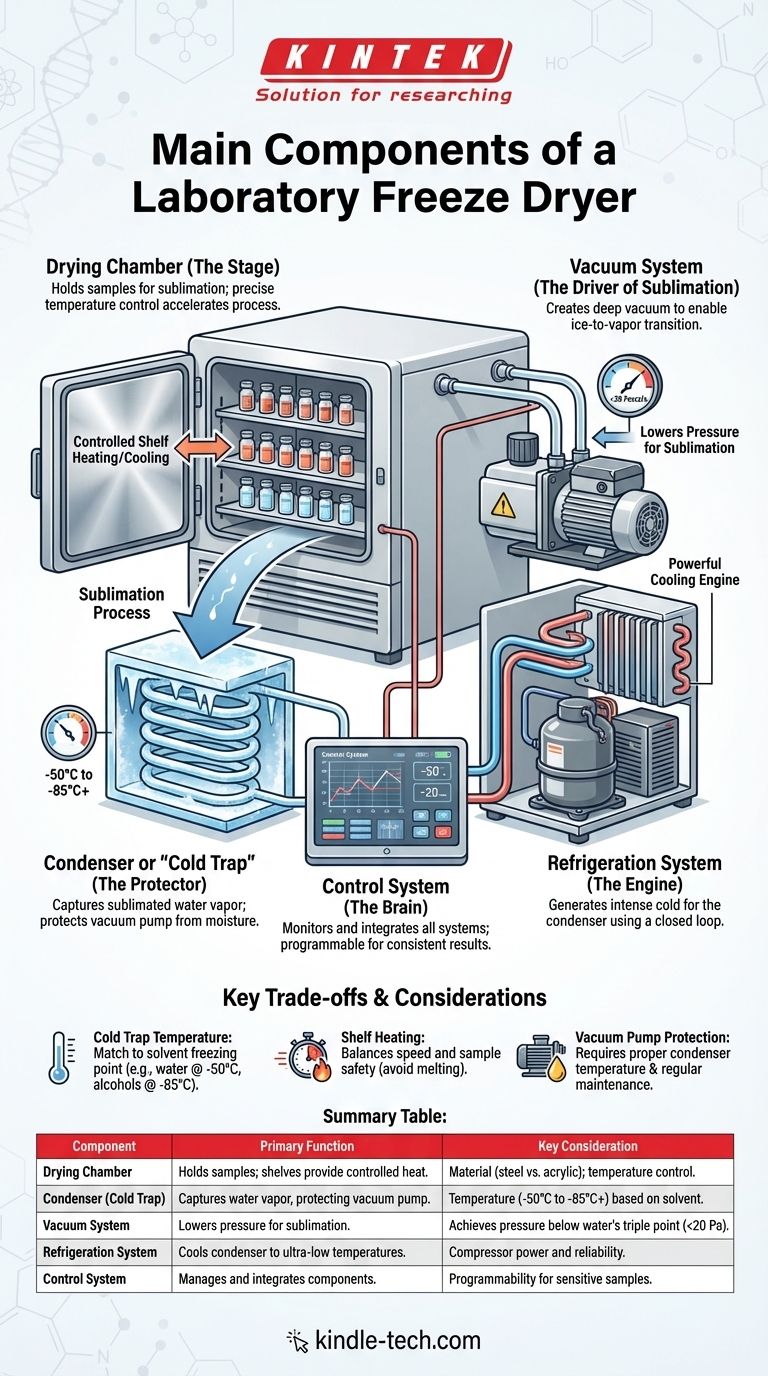
At its core, a laboratory freeze dryer is an integrated system built around five essential components: a drying chamber where samples are placed, a condenser or "cold trap" to capture moisture, a refrigeration system to cool the condenser, a vacuum system to lower the pressure, and a control system to manage the entire process. These parts work in concert to create the precise low-temperature, low-pressure environment required for lyophilization.
A freeze dryer functions by first freezing a sample, then creating a powerful vacuum that forces the frozen water to turn directly into vapor—a process called sublimation. Each component plays a critical, non-negotiable role in controlling this delicate physical transition to preserve the sample's structure.

The Core Systems of a Freeze Dryer
To truly understand a freeze dryer, it's best to think of it not as a list of parts, but as a set of interconnected systems, each with a specific job.
The Drying Chamber (The Stage)
This is the main enclosure where you place your samples. It can range from a simple acrylic bell jar that sits atop the unit to a more complex stainless steel chamber with multiple shelves.
In advanced models, these shelves can be heated or cooled. Precise temperature control of the shelves provides energy to the samples, which helps to speed up the sublimation process in a controlled manner.
The Condenser or "Cold Trap" (The Protector)
The condenser is arguably the most critical component for the health of the system. It is an extremely cold surface (often -50°C to -85°C or lower) located between the drying chamber and the vacuum pump.
Its sole purpose is to capture the water vapor that sublimates from your samples, turning it back into ice on the condenser coils. This "traps" the moisture, preventing it from entering and destroying the sensitive vacuum pump.
The Vacuum System (The Driver of Sublimation)
This system, centered on a vacuum pump, is responsible for lowering the atmospheric pressure inside the freeze dryer.
By creating a deep vacuum (often below 20 Pascals), the system reduces the pressure to a point below the triple point of water. This is the physical key that enables ice to turn directly into vapor without first melting into a liquid.
The Refrigeration System (The Engine)
The refrigeration system is the workhorse that generates the intense cold required by the condenser. It functions much like a home freezer but is significantly more powerful.
It consists of a compressor, heat exchanger, expansion valve, and evaporator coils. These components work together in a closed loop to extract heat and achieve the ultra-low temperatures needed to effectively trap water vapor.
The Control System (The Brain)
The control system integrates and manages all the other components. It monitors the temperature of the condenser and shelves, as well as the pressure level from the vacuum system.
For sensitive materials like vaccines or enzymes, a sophisticated control system that allows for programmable, multi-step drying "recipes" is essential for achieving consistent and successful results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Selecting or operating a freeze dryer involves balancing performance with the specific demands of your application. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial.
Cold Trap Temperature vs. Sample Type
The required temperature of your cold trap is dictated by the freezing point of your sample's solvent. While water can be trapped effectively at -50°C, samples containing alcohols or other solvents with lower freezing points require a much colder trap (-85°C or lower) to be captured efficiently.
Shelf Heating vs. Drying Time
While adding heat via shelves can significantly reduce drying time, too much heat can cause your sample to melt or collapse, destroying it. The trade-off is between speed and safety, requiring careful optimization for each type of sample.
Vacuum Pump Protection
The cold trap is the primary defense for the vacuum pump, but it's not foolproof. If the condenser is overloaded with ice or not cold enough, moisture can pass through to the pump. Regular oil changes (for oil-sealed pumps) and proper shutdown procedures are non-negotiable for ensuring a long operational life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the nature of your samples and the goals of your work.
- If your primary focus is routine sample preservation: A basic system with a reliable vacuum and a standard -50°C cold trap is likely sufficient.
- If your primary focus is sensitive biologics (enzymes, vaccines): Prioritize a system with precise, programmable shelf temperature control to ensure sample integrity.
- If your primary focus is samples with organic solvents: You must select a unit with a low-temperature (-85°C or colder) cold trap and potentially a chemically resistant hybrid vacuum pump.
By understanding how these core components unite to control temperature and pressure, you can effectively master the lyophilization process for your specific research goals.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Chamber | Holds samples; shelves can provide controlled heat. | Material (stainless steel vs. acrylic); shelf temperature control. |
| Condenser (Cold Trap) | Captures water vapor, protecting the vacuum pump. | Temperature (-50°C to -85°C+) based on sample solvent. |
| Vacuum System | Lowers pressure to enable sublimation. | Achieves pressure below water's triple point (<20 Pa). |
| Refrigeration System | Cools the condenser to ultra-low temperatures. | Compressor power and reliability for consistent performance. |
| Control System | Manages and integrates all other components. | Programmability for sensitive samples (e.g., vaccines, enzymes). |
Ready to Master Lyophilization in Your Lab?
Understanding the components is the first step. Selecting the right freeze dryer for your specific samples—whether they are sensitive biologics, materials with solvents, or routine preparations—is what ensures success.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose a freeze dryer with the precise condenser temperature, shelf control, and vacuum performance your application demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and ensure your lab is equipped for optimal sample preservation and research outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis



















