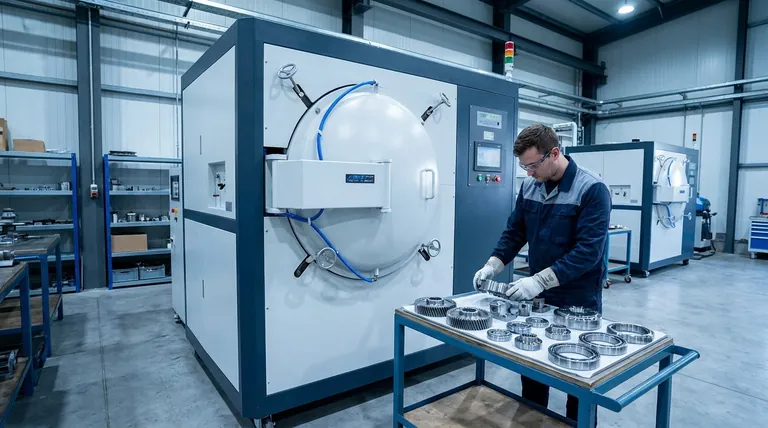
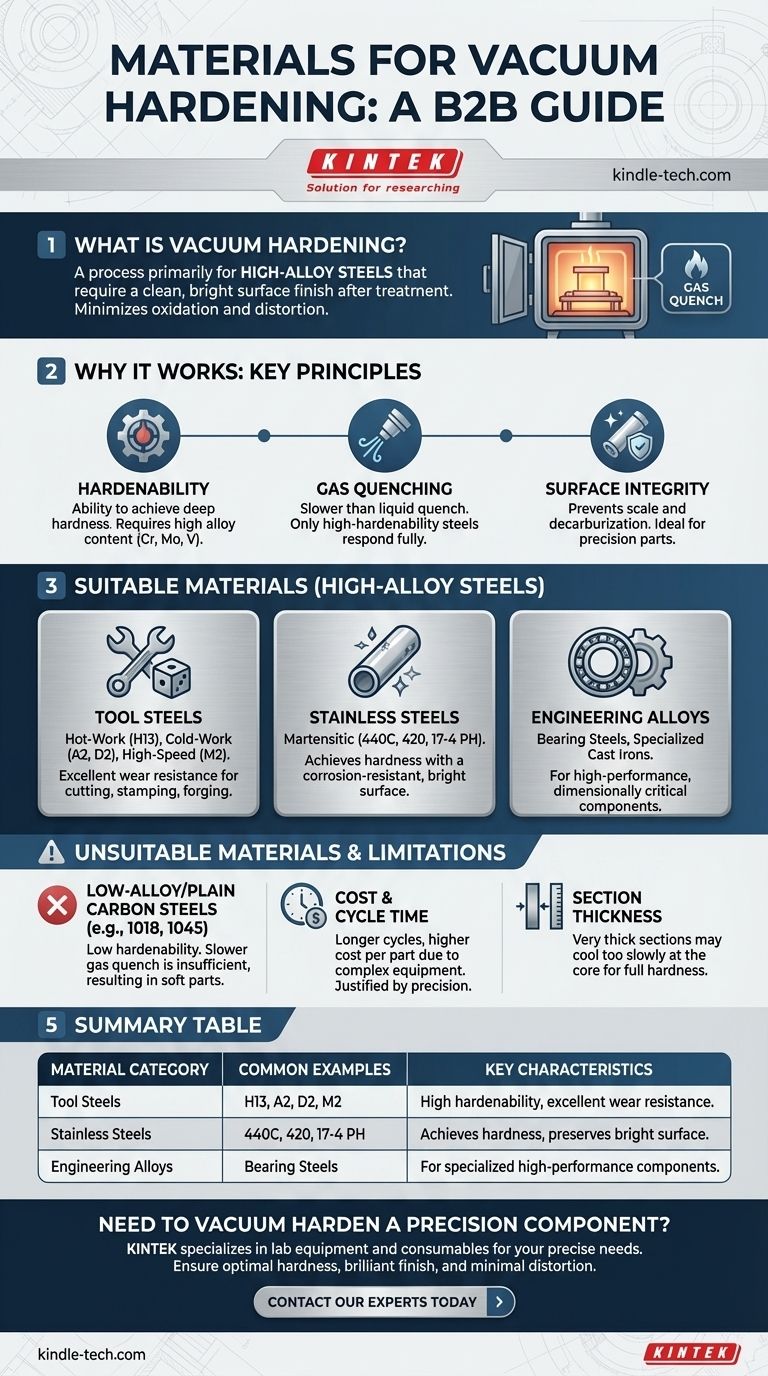
In short, vacuum hardening is primarily used for high-alloy steels that require a clean, bright surface finish after treatment. This includes a wide range of materials such as tool steels, high-speed steels, stainless steels, and certain specialty engineering alloys. The process is chosen when minimizing surface oxidation and distortion is as critical as achieving the desired hardness.
The suitability of a material for vacuum hardening is not just about whether it can be hardened, but whether its alloy content allows it to harden fully during the slower gas quenching process inherent to vacuum furnaces. This makes it a specialized method for high-performance, dimensionally critical components.

What Makes a Material Suitable for Vacuum Hardening?
The effectiveness of vacuum hardening is dictated by the interplay between the material's properties and the unique environment of a vacuum furnace. It is not a universal solution for all steels.
The Critical Role of "Hardenability"
Hardenability is a measure of a steel's ability to achieve hardness deep into its cross-section. It is not the same as maximum achievable hardness.
Steels with high alloy content—such as chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium—have high hardenability. These elements slow down the internal transformations during cooling, allowing the material to form a hard martensitic structure even with a less aggressive quench.
The Gas Quenching Process
Vacuum furnaces remove the air to prevent oxidation and then cool the heated part by backfilling the chamber with a high-pressure inert gas, such as nitrogen.
This gas quench is significantly slower than traditional liquid quenching in oil or water. Therefore, only materials with high hardenability will respond properly and harden through their entire thickness.
The Need for Superior Surface Integrity
The primary reason to choose vacuum hardening is to produce a part with a clean, bright, and unoxidized surface. The vacuum environment prevents the formation of scale and eliminates the risk of decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface).
This makes it ideal for finished parts, precision tools, and dies where post-treatment grinding or cleaning would be costly or compromise dimensional accuracy.
Key Material Categories for Vacuum Hardening
Based on the principles of hardenability and surface integrity, several families of steel are excellent candidates for this process.
Tool Steels (Hot and Cold Work)
These are the most common materials for vacuum hardening. Their high alloy content gives them the necessary hardenability and wear resistance.
Common examples include hot-work steels (H13), cold-work steels (A2, D2), and high-speed steels (M2, T1) used for cutting tools, stamping dies, and forging tools.
High-Alloy Stainless Steels
Martensitic stainless steels, which are designed to be hardened, are frequently processed in a vacuum. The process achieves the required hardness while preserving the bright, corrosion-resistant surface.
Materials like 440C, 420, and 17-4 PH are common candidates for applications ranging from industrial knives to aerospace components.
Specialized Engineering Steels
Other alloy steels can be vacuum hardened, provided they have sufficient alloy content. This includes:
- Bearing steels
- Quenched and tempered steels with high alloy additions
- Certain cast-iron alloys
The specific grade and its hardenability curve must always be reviewed to confirm its suitability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Vacuum hardening is a powerful tool, but it is not the right choice for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making a sound engineering decision.
Unsuitable for Low-Alloy and Plain Carbon Steels
Steels like 1018 or 1045 have very low hardenability. They require an extremely rapid quench (typically in water or brine) to harden.
The slower gas quench of a vacuum furnace is insufficient to harden these materials, resulting in soft parts with poor mechanical properties.
Cost and Cycle Time Considerations
Vacuum furnace equipment is complex and expensive to operate. The cycles, which involve pumping down to a deep vacuum and precise heating and cooling stages, are generally longer than conventional atmosphere furnace cycles.
This makes the process more costly on a per-part basis and is typically reserved for components where the benefits of cleanliness and low distortion justify the expense.
Section Thickness Limitations
Even for a high-hardenability steel, there is a limit to the thickness that can be fully hardened with a gas quench. Very thick cross-sections may cool too slowly at their core, even with high-pressure gas.
For extremely large components, a more aggressive liquid quench may still be necessary to achieve the required through-hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right hardening process depends entirely on your material and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is high-precision tools or dies: Vacuum hardening is ideal for maintaining dimensional stability and surface finish on materials like D2, A2, or H13 tool steels.
- If your primary focus is surface-critical stainless parts: This process is perfect for hardening martensitic stainless steels that must be both hard and cosmetically pristine without secondary finishing.
- If your primary focus is hardening low-cost, low-alloy steels: You must use conventional atmosphere furnace hardening with a liquid quench, as vacuum hardening is technically unsuitable for these materials.
Ultimately, you should choose vacuum hardening when the precision and integrity of the final component are as important as its hardness.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Steels | H13, A2, D2, M2 | High hardenability, excellent wear resistance for tools and dies. |
| Stainless Steels | 440C, 420, 17-4 PH | Achieves hardness while preserving corrosion-resistant, bright surface. |
| Engineering Alloys | Bearing steels, high-alloy cast irons | Used for specialized components requiring high performance. |
Need to vacuum harden a precision component?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and manufacturing facilities. Our expertise ensures your high-alloy steel parts achieve optimal hardness, a brilliant surface finish, and minimal distortion.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance the performance and longevity of your critical tools and components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Do you quench before tempering? Master the Essential Sequence for Strong, Durable Steel
- What happened during sintering? Unlock the Secrets of Powder-to-Solid Transformation
- What are the two types of quenching? Master Gas vs. Liquid for Superior Heat Treatment
- Which furnace removes most air to prevent decarburization? The Definitive Guide to Vacuum Furnaces
- What are the advantages of using high-temperature industrial furnaces for thermal regeneration of spent carbon?
- What is plasma pyrolysis waste treatment and disposal? Convert Waste into Clean Energy & Inert Materials
- What role does the crystallizer perform in magnesium recovery? Master Pure Sublimation and Yield
- What is the main disadvantage of quenching a part rapidly in water? High Risk of Cracking and Distortion



















