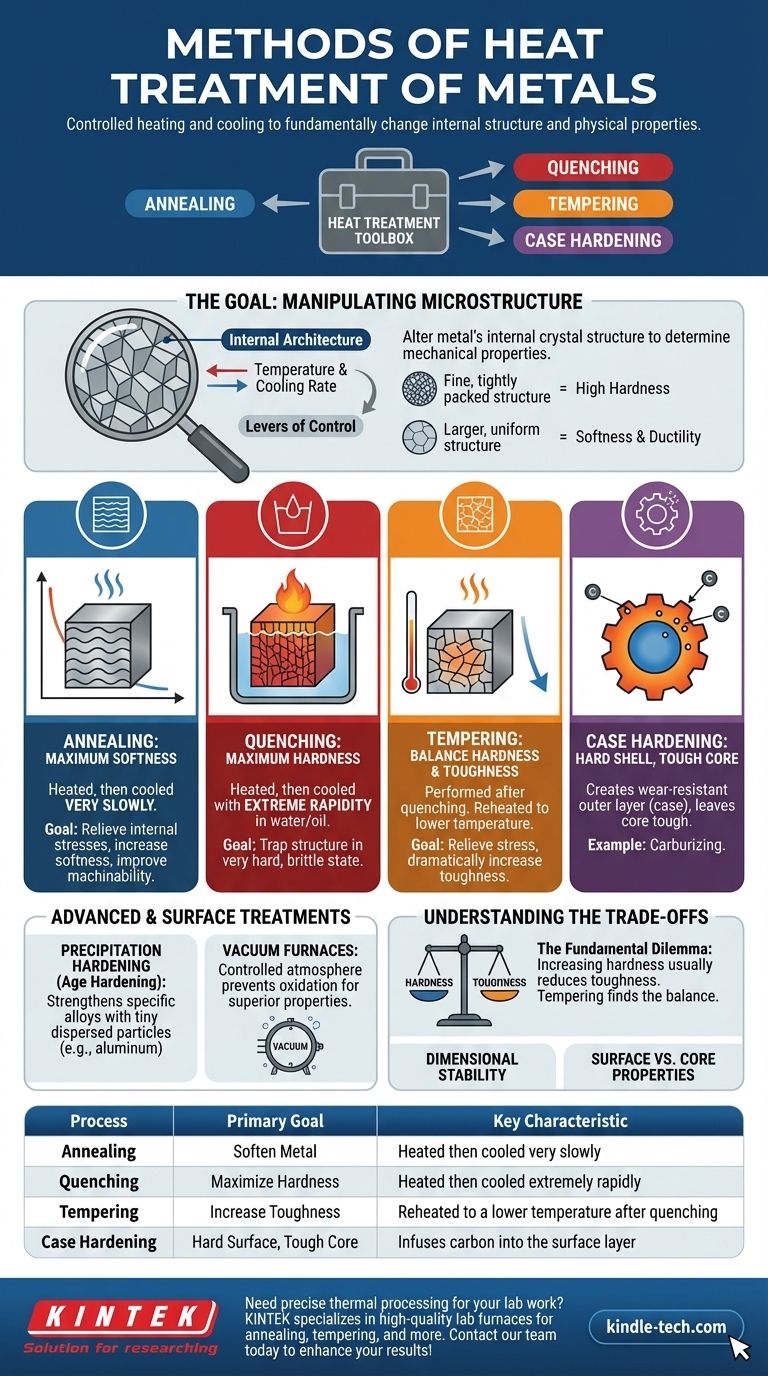
At its core, heat treatment is the controlled heating and cooling of metals to fundamentally change their internal structure and, therefore, their physical properties. The most common methods include annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening. Each process uses a unique cycle of temperature and cooling rates to achieve a specific outcome, such as making a metal softer and more formable or making it harder and more wear-resistant.
The essential takeaway is that heat treatment is not a single action but a toolbox of processes. The choice of method is dictated entirely by the desired end-state of the metal—whether you need it to be soft, hard, tough, or a specific combination of these properties.

The Goal of Heat Treatment: Manipulating Microstructure
Heat treatment works by altering a metal’s internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure. Think of this structure as the metal's internal architecture, which dictates its overall behavior.
Why Microstructure Matters
The size, shape, and composition of the crystals within a metal determine its mechanical properties. A fine, tightly packed structure often results in high hardness, while a larger, more uniform structure typically yields greater softness and ductility.
The Levers of Control: Temperature and Cooling Rate
The two primary variables in any heat treatment process are temperature and cooling rate. By precisely controlling how hot a metal gets, how long it's held at that temperature, and how quickly it cools, you can force its internal structure to rearrange into a more desirable configuration.
Core Heat Treatment Processes
While there are many variations, most heat treatments fall into a few fundamental categories aimed at either softening or hardening the material.
Annealing: For Maximum Softness and Ductility
Annealing is a process used to make a metal as soft as possible. It involves heating the metal to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it very slowly.
This slow cooling allows the internal crystals to grow and reform in a uniform, low-stress state. The primary goals of annealing are to relieve internal stresses from prior work, increase softness, and improve a metal's machinability.
Quenching: For Maximum Hardness
Quenching is the opposite of annealing. It involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then cooling it with extreme rapidity by submerging it in a medium like water, oil, or brine.
This rapid cooling traps the metal's crystal structure in a very hard, brittle state called martensite. While the resulting part is exceptionally hard, it is often too brittle for practical use without a subsequent treatment.
Tempering: Finding the Balance of Hardness and Toughness
Tempering is almost always performed immediately after quenching. The hardened, brittle part is reheated to a much lower temperature and held for a specific time before being allowed to cool in air.
This process relieves some of the internal stresses from quenching, reduces hardness slightly, but dramatically increases the metal's toughness (its ability to absorb impact without fracturing). The final balance of hardness and toughness is controlled by the tempering temperature.
Advanced & Surface-Specific Treatments
Beyond the core processes, specialized treatments can create unique property combinations or target only the surface of a part.
Case Hardening: A Hard Shell with a Tough Core
Case hardening, also known as surface hardening, creates a highly wear-resistant outer layer while leaving the inner core tough and ductile. One common method is carburizing, where a steel part is heated in a carbon-rich environment.
Carbon diffuses into the surface, allowing the outer "case" to become much harder than the interior after a final heat treatment. This is ideal for components like gears and bearings that need to resist surface wear but also withstand impact loads.
Precipitation Hardening: Strengthening Specific Alloys
Also known as age hardening, this process is used on non-ferrous alloys like aluminum, magnesium, and nickel. It involves heating the material to dissolve alloying elements into the base metal, followed by rapid cooling.
A second, lower-temperature heating cycle (the "aging" step) then causes these elements to form tiny, uniformly dispersed particles—or precipitates—that strengthen the material significantly.
The Environment Matters: Vacuum Furnaces
Modern heat treatments are often performed in a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum furnace. This prevents oxidation and surface contamination during heating, resulting in a cleaner part with superior mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties. Equipment like muffle furnaces provides the precise temperature control required for these processes, whether for large-scale production or smaller test batches.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process always involves balancing competing properties. There is no single "best" method, only the most appropriate one for a given application.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
This is the most fundamental trade-off in metallurgy. Increasing a metal's hardness almost always reduces its toughness, making it more brittle. Tempering is the primary method for navigating this compromise, but it's a balancing act: more toughness means less hardness, and vice versa.
Dimensional Stability and Distortion
The rapid temperature changes involved in processes like quenching can introduce significant internal stress. This stress can cause parts to warp, distort, or even crack if not managed carefully. The geometry of the part and the control of the cooling rate are critical factors.
Surface vs. Core Properties
Processes like case hardening are a deliberate trade-off. You gain exceptional surface hardness at the expense of a uniform material. This is a powerful design choice for components that experience high surface wear but must also resist bulk failure from impact.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
Your final selection should be guided by the primary performance requirement of the component.
- If your primary focus is machinability or formability: You need to soften the metal and relieve internal stress, making annealing your primary choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance: You need a hard surface, pointing directly to case hardening or a quench-and-temper process with minimal tempering.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength and impact resistance: Your goal is toughness, which is achieved by quenching to harden the material followed by a carefully controlled tempering cycle.
Understanding these principles allows you to select the precise heat treatment to engineer the exact material performance your project requires.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften Metal | Heated then cooled very slowly |
| Quenching | Maximize Hardness | Heated then cooled extremely rapidly |
| Tempering | Increase Toughness | Reheated to a lower temperature after quenching |
| Case Hardening | Hard Surface, Tough Core | Infuses carbon into the surface layer |
Need precise thermal processing for your lab work? The right heat treatment is critical for achieving the material properties your research or quality control demands. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, including vacuum and muffle furnaces, that provide the exact temperature control and atmosphere required for processes like annealing, tempering, and more. Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment to enhance your results.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum furnace with flexible pressure control essential for titanium alloy laminates? Achieve Atomic-Level Fusion
- What is the maximum temperature of an electric furnace? Choose the Right Tech for Your Process
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What are the disadvantages of nitriding? Key Limitations of Each Process Method
- What is physical Vapour deposition in crystal growth? Master Atomic-Level Thin Film Fabrication
- Why is post-treatment in a furnace required after hydrothermal synthesis of Magnéli phase? Ensure Material Stability
- What is the difference between a batch furnace and a continuous casting furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Production Line
- What role do industrial-grade high-temperature sintering furnaces play in the final formation of Lanthanum Zirconate?



















