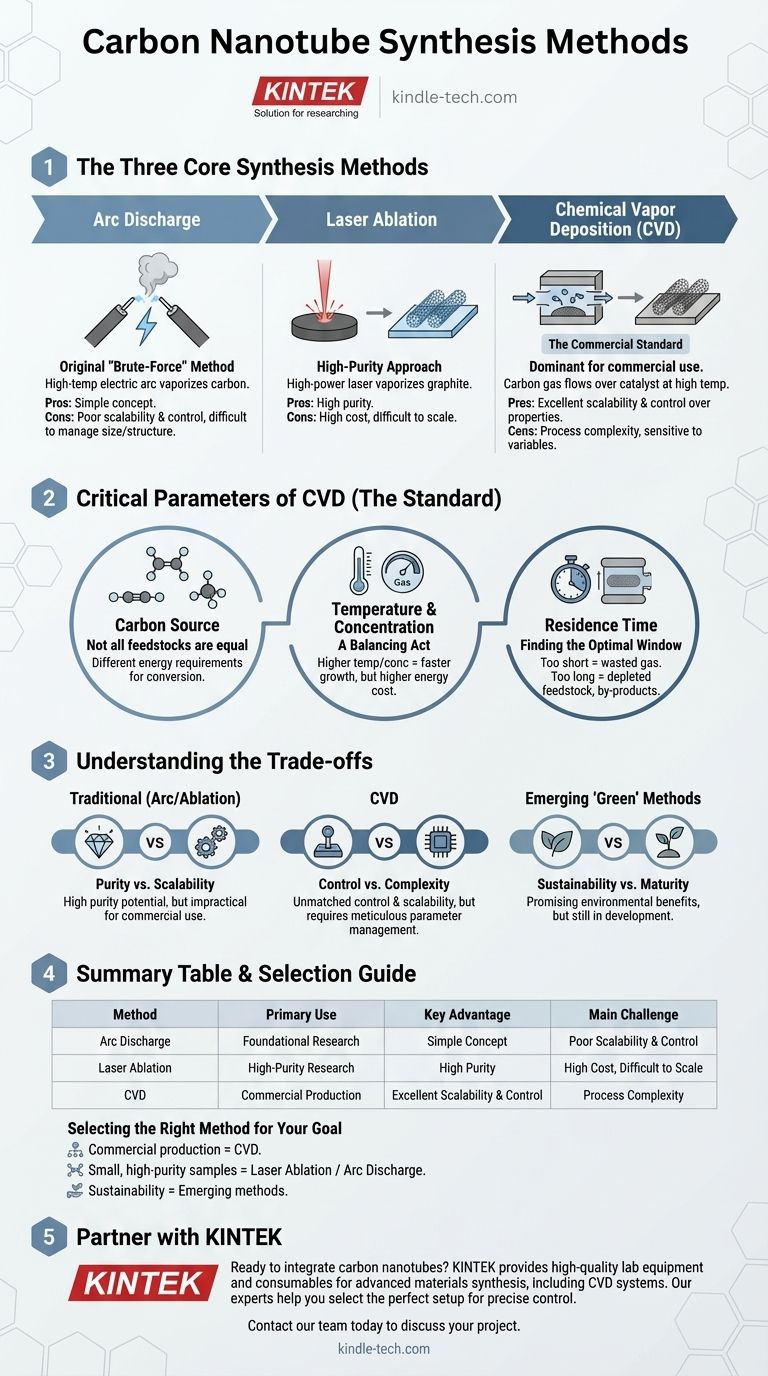
To synthesize carbon nanotubes, engineers and scientists primarily use three core techniques: arc discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While arc discharge and laser ablation were foundational methods, CVD has become the dominant commercial process due to its superior scalability and control over the final product.
While multiple methods exist, the industry has largely standardized on Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This is because it offers unparalleled control over nanotube properties and is the most viable path for large-scale, cost-effective production.

The Three Core Synthesis Methods
Understanding the fundamental differences between the main production techniques is key to appreciating why the industry has evolved. Each method operates on a different principle to transform a carbon source into a nanostructure.
Arc Discharge: The Original Method
The arc discharge technique was one of the first used to produce carbon nanotubes. It involves creating a high-temperature electric arc between two carbon electrodes, which vaporizes the carbon to form CNTs.
This method is effective but is considered a "brute-force" approach. The high temperatures and complex setup make it difficult to control the precise size and structure of the resulting nanotubes.
Laser Ablation: A High-Purity Approach
In laser ablation, a high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target in a high-temperature furnace. The laser vaporizes the carbon, which then condenses into nanotubes on a cooler surface.
This technique is known for producing high-purity carbon nanotubes. However, like arc discharge, it is an expensive process that is difficult to scale for mass production.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Commercial Standard
CVD is the most widely used method for commercial CNT synthesis. The process involves flowing a carbon-containing gas (a feedstock) over a substrate coated with a catalyst at high temperatures.
The catalyst breaks down the carbon gas, and the carbon atoms reassemble into nanotubes. The primary advantage of CVD is its high degree of control; by carefully managing the parameters, manufacturers can tune the diameter, length, and even the electronic properties of the nanotubes.
Critical Parameters That Define Success
The quality and efficiency of CNT synthesis, particularly with CVD, depend on a delicate balance of several operating parameters. Mastering these variables is the difference between a low-yield batch and a highly efficient production run.
The Carbon Source: Not All Feedstocks Are Equal
The choice of carbon-containing gas is critical. Common feedstocks include acetylene, ethylene, and methane.
These gasses have different energy requirements for conversion. Acetylene can be a direct precursor for CNTs, while ethylene and methane require more energy for thermal conversion to form the necessary carbon building blocks.
Temperature and Concentration: A Balancing Act
Higher synthesis temperatures and greater concentrations of the carbon source can lead to faster CNT growth rates. This is because more carbon precursors are available for assembly.
However, this comes at a cost. Increased temperature and concentration lead to significantly higher energy consumption, creating a crucial trade-off between production speed and operational cost.
Residence Time: Finding the Optimal Window
Residence time refers to how long the carbon source gas spends in the reaction chamber. This parameter must be precisely optimized.
If the residence time is too short, the carbon source is wasted as it doesn't have enough time to accumulate and react. If it is too long, the feedstock can become depleted, and unwanted by-products can accumulate, hindering growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No synthesis method is perfect; each involves a series of compromises. Acknowledging these trade-offs is essential for making an informed decision based on your specific goals.
Traditional Methods (Arc/Ablation): Purity vs. Scalability
The primary advantage of arc discharge and laser ablation is the potential for high-purity material, which is useful for certain research applications.
The overwhelming disadvantage is their lack of scalability, high energy cost, and the difficulty in controlling the final nanotube shape and size. This makes them impractical for most commercial uses.
CVD: Control vs. Complexity
CVD's strength is its unmatched control and scalability, making it the go-to for industrial production.
Its main challenge lies in its complexity. The process is highly sensitive to a multitude of variables—including temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and catalyst choice—that must be meticulously managed to achieve consistent results.
Emerging "Green" Methods: Sustainability vs. Maturity
Newer, more sustainable methods are being explored, such as using waste carbon dioxide or methane pyrolysis as a feedstock.
These approaches are promising for reducing the environmental impact of CNT production. However, they are not yet as mature or widely adopted as CVD and require further development to become commercially competitive.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Goal
Your choice of synthesis method should be driven by your end goal, whether it's commercial production, fundamental research, or sustainable innovation.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, cost-effective production with specific properties: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the undisputed industry standard due to its scalability and control.
- If your primary focus is small, high-purity samples for fundamental research: Laser ablation or arc discharge can be effective, though they offer poor control over structure.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and future-facing processes: Investigating emerging methods like methane pyrolysis or electrolysis from captured CO2 will be crucial.
Your choice of synthesis method is ultimately a strategic decision balancing production scale, desired nanotube characteristics, and operational cost.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | Foundational Research | Simple Concept | Poor Scalability & Control |
| Laser Ablation | High-Purity Research | High Purity | High Cost, Difficult to Scale |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Commercial Production | Excellent Scalability & Control | Process Complexity |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or production line? The right synthesis method is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced materials synthesis, including CVD systems. Our experts can help you select the perfect setup to achieve precise control over your CNT properties. Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's innovation goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems



















