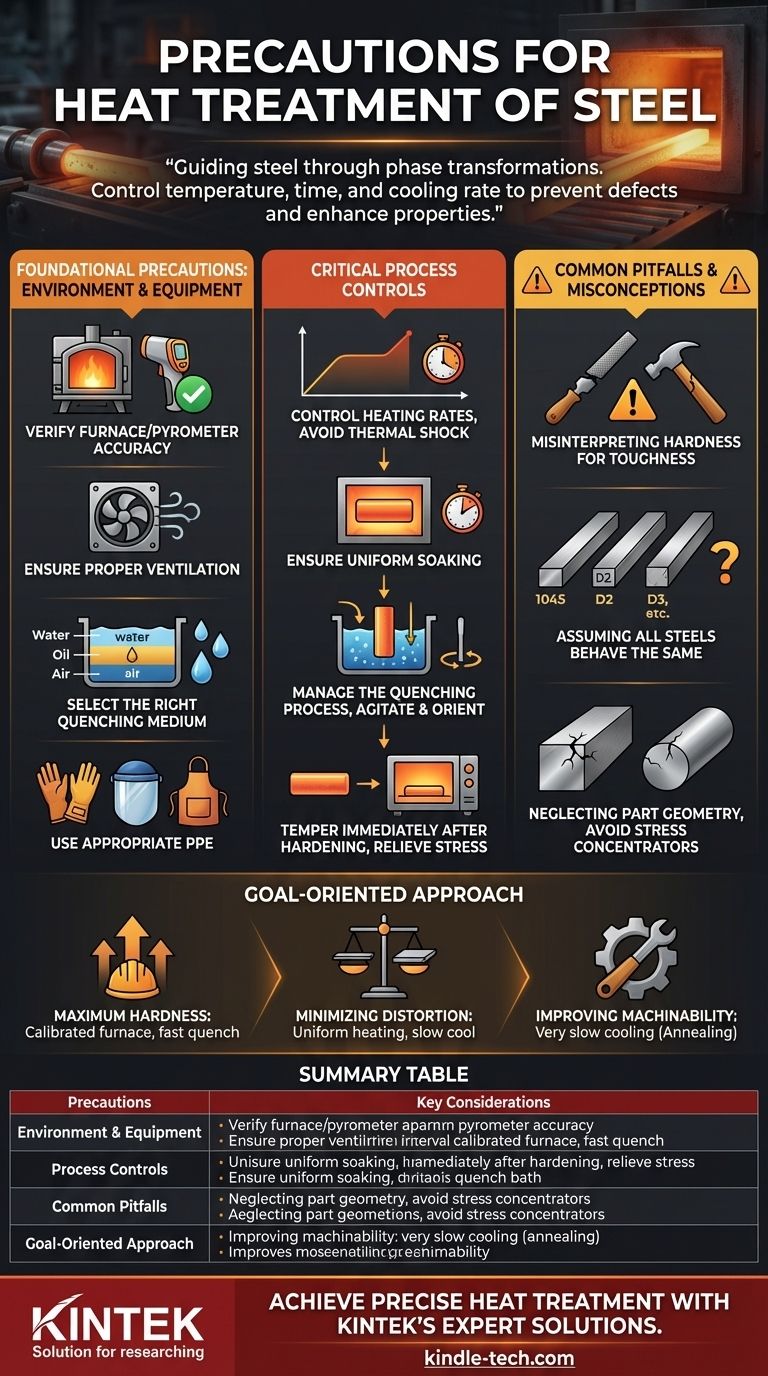
The most critical precautions for heat treating steel involve the meticulous control of three factors: temperature, time, and cooling rate. These variables must be precisely managed to achieve the desired metallurgical transformation without introducing defects like cracking or warping. Success depends on understanding your specific steel alloy and ensuring your equipment is calibrated and your environment is safe.
The core principle of heat treatment is not just about heating and cooling; it's about guiding steel through specific phase transformations. Every precaution is designed to control these transformations to enhance properties predictably while preventing the immense internal stresses that can destroy the component.

Foundational Precautions: Environment and Equipment
Before the process begins, the foundation for success is laid by preparing the workspace and verifying the equipment. Overlooking this stage is a common source of failure and safety incidents.
Verify Furnace and Pyrometer Accuracy
Your temperature readings are the single most important data point in heat treatment. An inaccurate pyrometer or a furnace with hot spots will render any procedure unreliable.
Regular calibration of temperature-measuring equipment against a known standard is not optional; it is essential for repeatable, accurate results.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Many heat treatment processes, especially oil quenching, produce smoke, fumes, and potentially flammable vapors. A well-ventilated workspace is a fundamental safety requirement to prevent inhalation hazards and fire risks.
Select the Right Quenching Medium
The quenching medium—typically water, brine, oil, or air—dictates the cooling rate. A faster quench increases hardness but also raises the risk of distortion and cracking.
The correct choice depends entirely on the hardenability of the steel alloy. Using an aggressive quenchant like water on a high-alloy steel designed for oil quenching is a primary cause of cracking.
Use Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Handling extremely hot materials requires specialized PPE. This includes high-temperature gloves, full-face shields, and non-flammable clothing like leather or aluminized coats.
Critical Process Controls
Once the environment is prepared, the focus shifts to the precise execution of the heating and cooling cycle. Each step presents a unique set of risks that must be actively managed.
Control Heating Rates
Heating steel too rapidly can cause thermal shock, especially in parts with complex geometries or varying cross-sections. This leads to internal stresses that cause warping before the part even reaches its target temperature.
A slower, pre-heating step is often used for high-alloy steels or intricate parts to allow the temperature to equalize throughout the component.
Ensure Uniform Soaking
"Soaking" is the period where the steel is held at the target temperature (e.g., its austenitizing temperature). The entire cross-section of the part must reach this temperature and be held long enough for the internal crystal structure to fully transform.
Insufficient soaking time results in incomplete hardening and inconsistent properties across the part.
Manage the Quenching Process
The quench is the most dynamic and high-risk stage. Agitating the part or the quenchant is crucial to break up vapor barriers (the "vapor jacket") that can form on the surface and cause soft spots.
The orientation of the part as it enters the quench bath also matters. Long, thin parts should enter vertically to minimize warping.
Temper Immediately After Hardening
For many carbon and alloy steels, the as-quenched state is extremely hard but also highly brittle and full of internal stress. This condition is unstable, and the part is at high risk of cracking on its own.
Tempering, which is a lower-temperature heating process, must be performed as soon as possible after the part has cooled from the quench to relieve stress and increase toughness.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
True expertise comes from not only knowing the procedure but also understanding the common ways it can fail. Avoiding these pitfalls is as important as following the steps correctly.
Misinterpreting Hardness for Toughness
The goal is rarely to achieve maximum possible hardness. A file-hard piece of steel is often too brittle for practical use. The purpose of tempering is to trade some of that peak hardness for a significant gain in toughness—the ability to resist fracture.
Assuming All Steels Behave the Same
A procedure that works for a simple 1045 carbon steel will destroy a D2 tool steel. You must know the specific alloy you are working with. Its chemical composition dictates its critical temperatures, required soak times, and appropriate quench medium.
Neglecting Part Geometry
Sharp internal corners are natural stress concentrators. During the rapid temperature change of a quench, these areas are overwhelmingly the most likely points for a crack to initiate.
Whenever possible, designing parts with generous radii and uniform thicknesses makes successful heat treatment far more likely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your precautions should be tailored to your specific objective. The ideal process for one outcome is often incorrect for another.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: Use a calibrated furnace to reach the correct austenitizing temperature for your specific alloy and quench in the fastest appropriate medium without causing cracks.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion: Prioritize slower, uniform heating, proper support for the workpiece in the furnace, and quenching symmetrically to ensure even cooling.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Your goal is likely annealing, which requires very slow, controlled cooling—often by leaving the part to cool down inside the furnace overnight.
Ultimately, successful heat treatment is a discipline of precision, where careful control and a deep understanding of the material lead to predictable and powerful results.
Summary Table:
| Precautions | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Environment & Equipment | Verify furnace/pyrometer accuracy, ensure proper ventilation, select correct quenching medium, use appropriate PPE. |
| Process Controls | Control heating rates to prevent thermal shock, ensure uniform soaking, manage quenching process, temper immediately after hardening. |
| Common Pitfalls | Avoid misinterpreting hardness for toughness, know your specific steel alloy, consider part geometry to prevent stress concentrations. |
| Goal-Oriented Approach | Tailor precautions for maximum hardness, minimal distortion, or improved machinability based on your specific objective. |
Achieve precise and reliable steel heat treatment with KINTEK's expert solutions.
Navigating the complexities of temperature control, quenching, and material-specific requirements is critical for successful heat treatment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, temperature calibration equipment, and consumables designed for accuracy and repeatability. Whether you're working with carbon steels, alloy steels, or tool steels, our products help you maintain the precise control needed to prevent defects and achieve optimal material properties.
Let us support your laboratory's success:
- Precise Temperature Control: Our calibrated furnaces ensure uniform heating and accurate soaking times.
- Tailored Quenching Solutions: Access the right quenching media and agitation tools for your specific steel alloy.
- Safety and Compliance: Equipment designed with ventilation and safety features to protect your team.
Ready to enhance your heat treatment process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions



















