In short, the product of sintering is a solid, densified body created from a starting material of metal or ceramic powder. This process transforms a loose or compacted powder into a coherent, strengthened mass by applying heat below the material's melting point, fundamentally altering its physical and mechanical properties.
The core purpose of sintering is not to create a new chemical substance, but to engineer the physical structure of a material. It turns a powder into a solid object with specific, desirable properties like high strength, controlled density, and complex shapes that are difficult to achieve through other means.

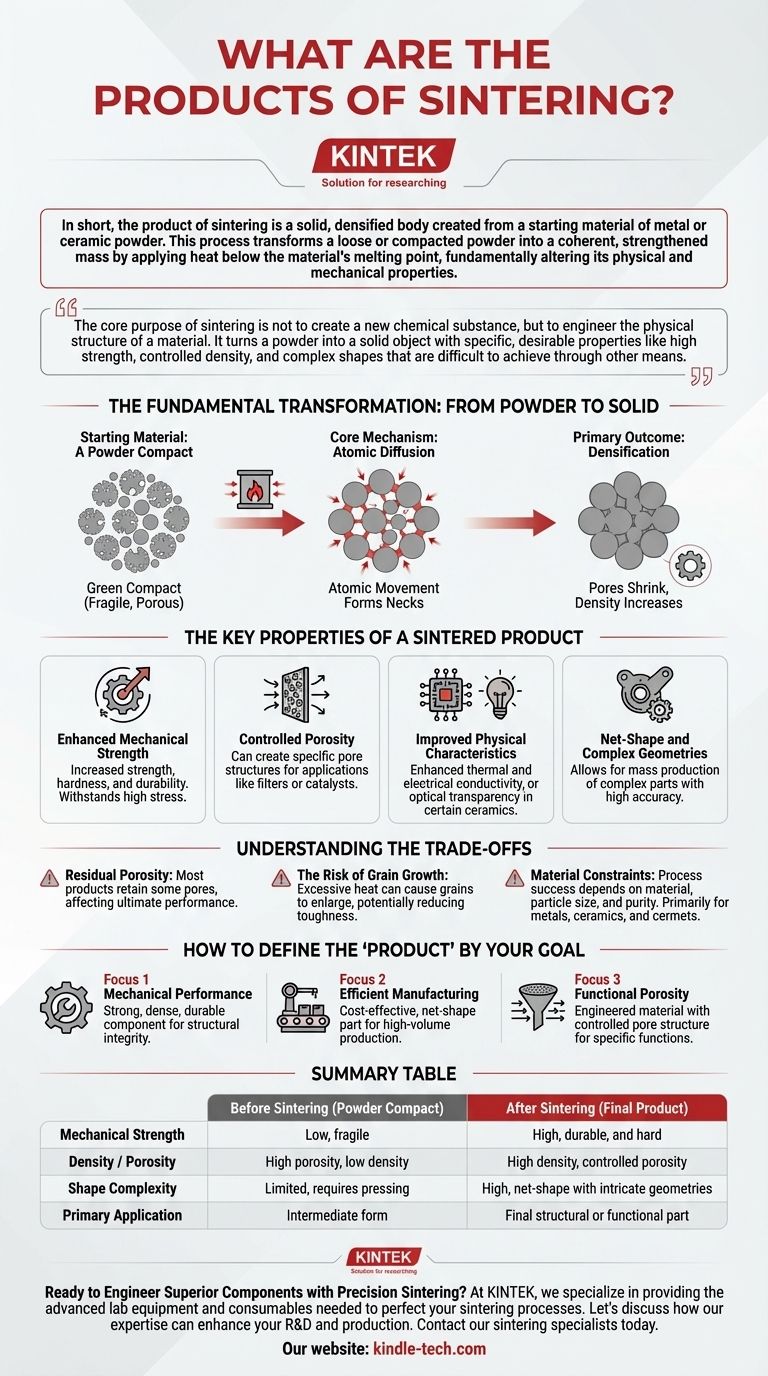
The Fundamental Transformation: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a thermal process that causes individual particles in a powder to bond together, creating a solid part. This transformation is driven by reducing the surface energy of the powder particles.
The Starting Material: A Powder Compact
The process begins with a powder, typically of a metal or ceramic. This powder is often first pressed into a desired shape, known as a "green compact," which is fragile and has significant porosity between particles.
The Core Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
When heated, the atoms at the contact points between particles become mobile and begin to diffuse across the particle boundaries. This atomic movement forms small bridges, or "necks," between adjacent particles, effectively welding them together without melting the bulk material.
The Primary Outcome: Densification
As these necks grow, the particles pull closer together. This action shrinks or eliminates the pores (empty spaces) that existed between the particles in the original compact. The result is a denser, more solid material.
The Key Properties of a Sintered Product
The "product" of sintering is best defined by the new and improved properties it possesses compared to the original powder.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
By bonding particles and reducing pores, sintering dramatically increases the material's strength, hardness, and overall durability. The resulting part can withstand mechanical stress far better than the initial powder compact.
Controlled Porosity
While sintering typically aims to reduce porosity, the process can also be controlled to create products with a specific, interconnected pore structure. This is essential for manufacturing products like porous metal filters or catalysts, where gas or liquid flow is required.
Improved Physical Characteristics
Densification improves more than just strength. For many materials, it also enhances thermal and electrical conductivity. In the case of certain ceramics, sintering is critical for achieving optical transparency.
Net-Shape and Complex Geometries
A major advantage of sintering is its ability to produce parts in their final or "net" shape with high accuracy and repeatability. This allows for the mass production of complex components, such as gears or intricate structural parts, that would be costly or impossible to create with traditional machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent limitations that define the characteristics of its products.
Residual Porosity
Achieving 100% theoretical density is extremely difficult and often not economical. Most sintered products will retain a small amount of residual porosity, which can influence their ultimate mechanical performance in highly demanding applications.
The Risk of Grain Growth
The same heat that drives densification can also cause the individual crystal grains within the material to grow larger. Excessive grain growth can sometimes be detrimental, potentially reducing the material's toughness or fracture resistance. Balancing densification while controlling grain size is a key challenge in process control.
Material Constraints
Sintering is primarily suited for metals, ceramics, and cermets. The success of the process is highly dependent on the material's characteristics, particle size, and purity. Not all materials can be effectively sintered.
How to Define the "Product" by Your Goal
The specific product of sintering depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance: The product is a strong, dense, and durable component designed for structural integrity and load-bearing applications.
- If your primary focus is efficient manufacturing: The product is a cost-effective, net-shape part that minimizes or eliminates the need for subsequent machining, ideal for high-volume production.
- If your primary focus is functional porosity: The product is an engineered material, like a filter or catalyst support, where the pore structure is precisely controlled to perform a specific function.
Ultimately, sintering produces materials with carefully engineered microstructures to meet a specific performance target.
Summary Table:
| Property | Before Sintering (Powder Compact) | After Sintering (Final Product) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Low, fragile | High, durable, and hard |
| Density / Porosity | High porosity, low density | High density, controlled porosity |
| Shape Complexity | Limited, requires pressing | High, net-shape with intricate geometries |
| Primary Application | Intermediate form | Final structural or functional part |
Ready to Engineer Superior Components with Precision Sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your sintering processes. Whether you are developing high-strength metal parts, intricate ceramic components, or porous filters, our solutions help you achieve the precise material properties and complex geometries your projects demand.
Let's discuss how our expertise can enhance your R&D and production. Contact our sintering specialists today to explore the right equipment for your specific material and application goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















