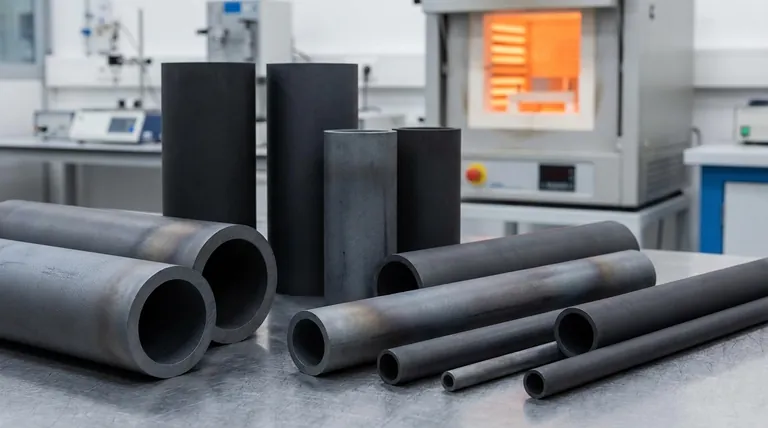
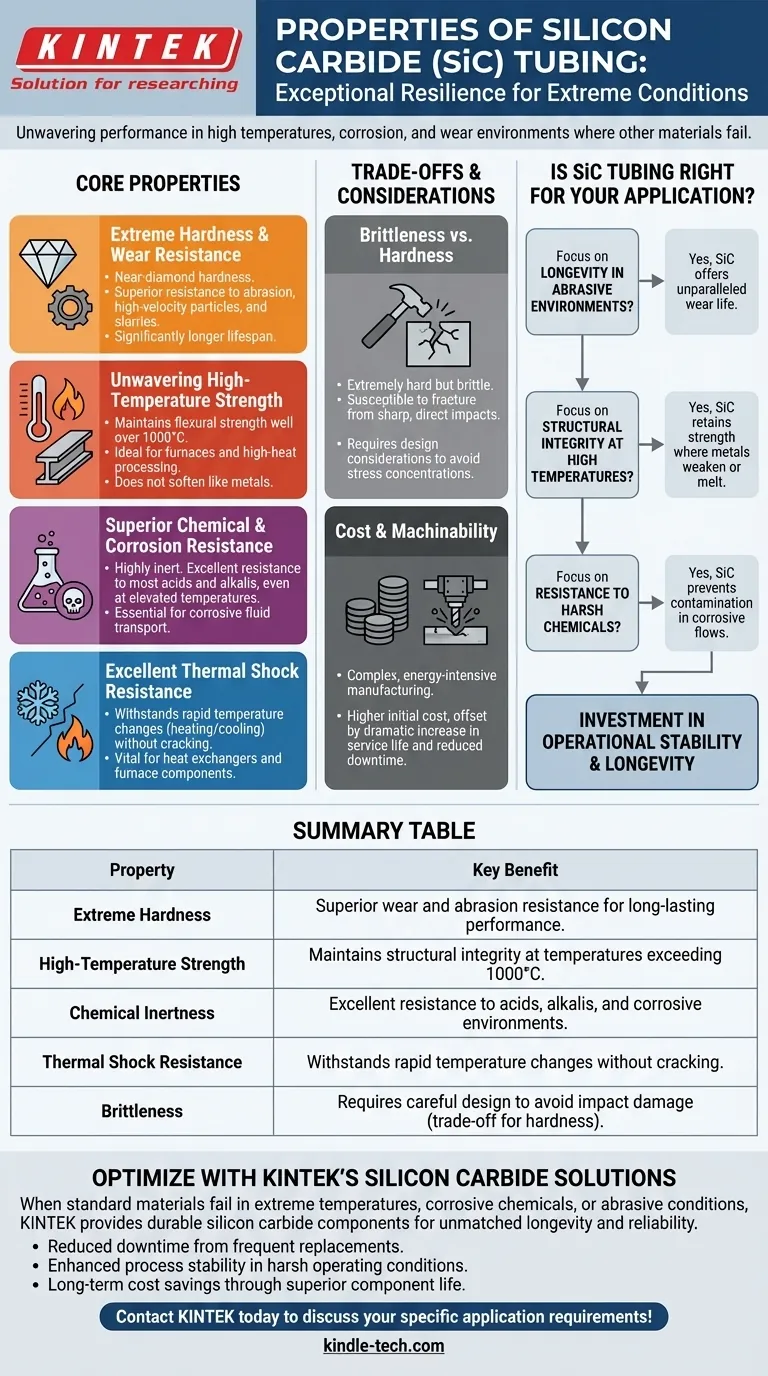
Silicon carbide (SiC) tubing is defined by its exceptional resilience in extreme conditions. It possesses a unique combination of high density and hardness, excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal shock, and maintains its structural strength and integrity at very high temperatures. These characteristics make it a critical material for severe-service industrial applications where conventional materials would fail.
The primary reason to select silicon carbide tubing is for its unwavering performance where other materials fail. Its ability to maintain mechanical strength and resist chemical and thermal degradation at extreme temperatures makes it a definitive solution for the most demanding industrial environments.

Core Properties Explained
Silicon carbide's value comes from a combination of physical properties that work together. Understanding how they interact is key to understanding its role in advanced applications.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Silicon carbide is one of the hardest commercially available materials, approaching the hardness of diamond.
This extreme hardness translates directly into superior resistance to abrasion and wear. Components made from SiC last significantly longer in environments with abrasive slurries, high-velocity particles, or mechanical friction.
Unwavering High-Temperature Strength
This is arguably the most critical property of SiC. Unlike metals that soften and lose strength dramatically as they are heated, silicon carbide maintains its high flexural strength at temperatures well over 1000°C.
This allows it to be used for structural components, such as beams, rollers, and thermocouple protection tubes, inside furnaces and other high-temperature processing equipment where metals would deform or melt.
Superior Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Silicon carbide is a highly inert ceramic material. It exhibits excellent resistance to nearly all acids and alkalis, even at elevated temperatures.
This property makes it indispensable in the chemical processing, oil drilling, and paper industries, where equipment must transport or be exposed to highly corrosive fluids that would rapidly destroy metals and other materials.
Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance
The material has high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion. This combination gives it outstanding resistance to thermal shock.
This means SiC tubing can withstand rapid changes in temperature—for example, being heated or cooled very quickly—without cracking or failing. This is vital for applications like heat exchangers and furnace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While silicon carbide's properties are exceptional, it is an advanced material with specific engineering considerations. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its trade-offs.
Brittleness vs. Hardness
Like most advanced ceramics, silicon carbide is extremely hard but also brittle. While it can withstand immense compressive force and surface wear, it is susceptible to fracture from sharp, direct impacts.
Designs must account for this by avoiding stress concentrations and protecting against impact, a key difference from designing with ductile metals that bend before they break.
Cost and Machinability
Manufacturing and machining silicon carbide is a complex, energy-intensive process due to its extreme hardness.
This results in a higher initial component cost compared to stainless steels or other alloys. However, this cost is often justified by a dramatic increase in service life and a reduction in operational downtime for maintenance and replacement.
Is SiC Tubing Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right material depends entirely on the operational demands of your system. Silicon carbide excels where conditions are most severe.
- If your primary focus is longevity in abrasive environments: The unparalleled hardness of SiC provides a wear life far exceeding that of hardened metals or other ceramics.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity at high temperatures: SiC's ability to retain its strength where metals weaken or melt is its most significant advantage.
- If your primary focus is resistance to harsh chemicals: The chemical inertness of SiC tubing ensures reliability and prevents contamination in corrosive process flows.
Ultimately, choosing silicon carbide is an investment in operational stability and longevity for your most critical processes.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness | Superior wear and abrasion resistance for long-lasting performance. |
| High-Temperature Strength | Maintains structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000°C. |
| Chemical Inertness | Excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and corrosive environments. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking. |
| Brittleness | Requires careful design to avoid impact damage (trade-off for hardness). |
Optimize your most demanding processes with KINTEK's silicon carbide solutions.
When your application involves extreme temperatures, corrosive chemicals, or abrasive conditions, standard materials simply can't compete. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable silicon carbide components designed to provide unmatched longevity and reliability in severe-service environments.
By choosing KINTEK, you invest in:
- Reduced downtime from frequent replacements.
- Enhanced process stability in harsh operating conditions.
- Long-term cost savings through superior component life.
Let our experts help you determine if silicon carbide tubing is the right solution for your needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures



















