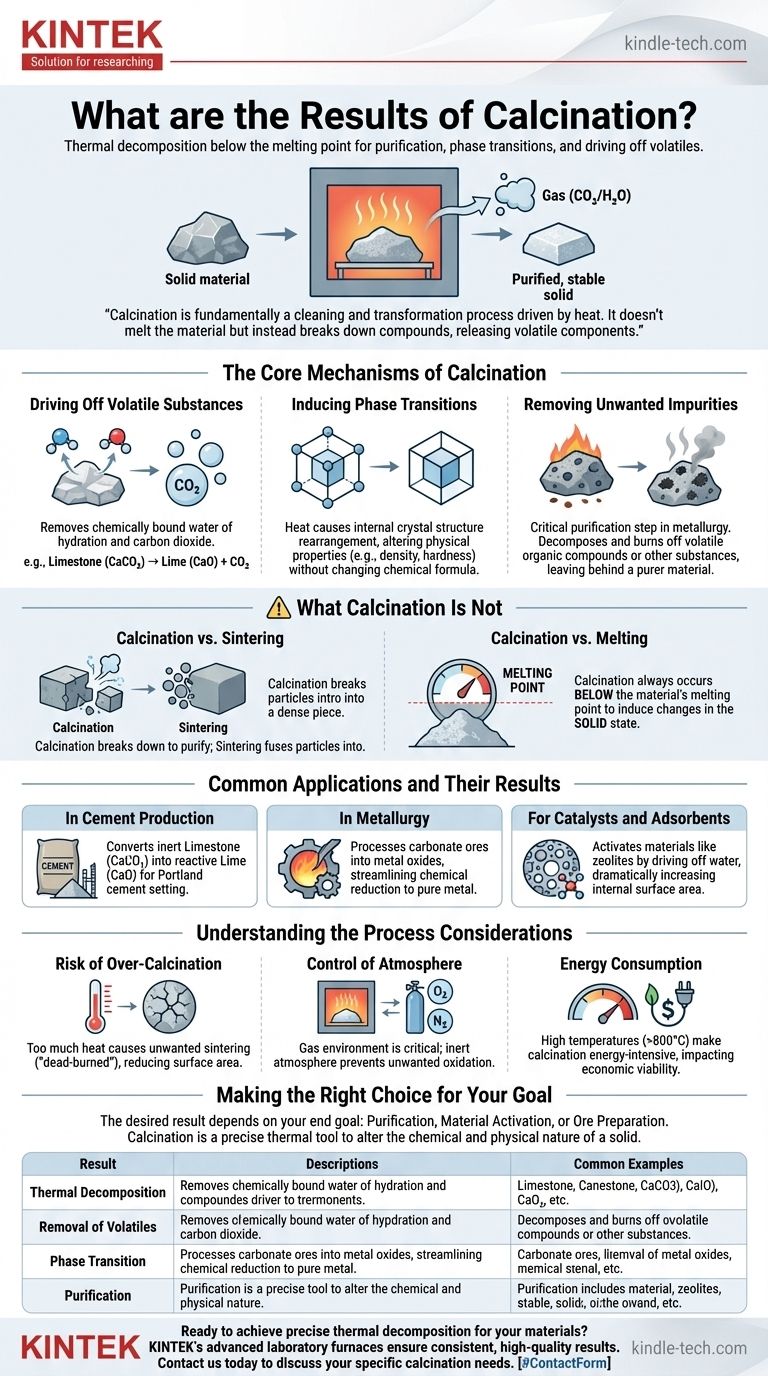
The primary result of calcination is the thermal decomposition of a solid material. This high-temperature heating process, conducted below the material's melting point, is designed to remove volatile substances, induce phase transitions, or purify the material by breaking down compounds and driving off components like water and carbon dioxide.
Calcination is fundamentally a cleaning and transformation process driven by heat. It doesn't melt the material but instead breaks down compounds within it, releasing volatile components to yield a purified, more stable, or more reactive solid product.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand the results, we must first understand what happens to a material at a chemical and physical level during this process.
Driving Off Volatile Substances
The most common result of calcination is the removal of volatile components that are chemically bound within the solid's structure. Heat provides the energy to break these bonds.
This includes removing water of hydration from hydrated minerals and driving carbon dioxide from carbonate materials. The classic example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO) for cement.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Heat can also cause a material's internal crystal structure to rearrange into a different, often more stable or useful, form.
This is a phase transition. While the chemical formula of the material remains the same, its physical properties—like density, hardness, and chemical reactivity—can change significantly.
Removing Unwanted Impurities
In metallurgy and materials processing, calcination is a critical purification step.
By carefully controlling the temperature, volatile organic compounds or other unwanted substances within an ore can be decomposed and burned off, leaving behind a more concentrated and purer desired material.
What Calcination Is Not: A Key Distinction
Understanding what calcination doesn't do is just as important as understanding what it does. Its purpose is often confused with other thermal processes.
Calcination vs. Sintering
These two processes have opposite goals. Calcination breaks a material down to purify it or drive off components.
Sintering, by contrast, uses heat to fuse small particles together, welding them into a single, dense, and stronger piece. Calcination prepares the powder; sintering consolidates it.
Calcination vs. Melting
A critical rule of calcination is that it always occurs below the material's melting point. The goal is to induce chemical and physical changes while the substance remains in a solid state.
Common Applications and Their Results
The specific outcome of calcination is directly tied to its industrial application.
In Cement Production
The calcination of limestone is the foundational step in manufacturing Portland cement. The result is the conversion of inert calcium carbonate into highly reactive calcium oxide (lime), which is the primary ingredient that enables cement to set and harden.
In Metallurgy
Calcination is used to process metal ores before the final smelting step. For example, carbonate ores are converted into their metal oxide forms, which are much easier to chemically reduce into a pure metal.
For Catalysts and Adsorbents
Materials like zeolites and alumina are activated through calcination. The process drives off water from their microscopic pores, dramatically increasing their internal surface area and making them highly effective as catalysts or chemical adsorbents.
Understanding the Process Considerations
Achieving the desired result requires careful control, as several factors can lead to unwanted outcomes.
Risk of Over-Calcination
Applying too much heat or for too long can be counterproductive. It can cause unwanted sintering, which reduces the material's surface area and reactivity. This is often referred to as producing a "dead-burned" material.
Control of Atmosphere
The gas environment inside the furnace is critical. Calcining in air can cause oxidation, which may be desirable for some processes but detrimental to others. Using an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen) prevents these unwanted reactions.
Energy Consumption
Heating materials to the high temperatures required for calcination (often >800°C) is an extremely energy-intensive process. The cost of energy is a major factor in the economic viability of any calcination operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "result" you want from calcination depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is purification and decomposition: Your key objective is precise temperature control to drive off volatiles without causing unwanted phase changes or sintering.
- If your primary focus is material activation (e.g., for catalysts): Your goal is to maximize surface area by removing adsorbed water, requiring careful temperature ramps and strict atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is preparing an ore for smelting: The main result is converting a complex carbonate or hydrate into a simpler oxide, which streamlines the subsequent chemical reduction to pure metal.
Ultimately, calcination is a precise thermal tool used to fundamentally alter the chemical and physical nature of a solid to prepare it for its final purpose.
Summary Table:
| Result of Calcination | Description | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Breaking down compounds using heat below the melting point. | CaCO₃ (limestone) → CaO (lime) + CO₂ |
| Removal of Volatiles | Driving off water (dehydration) or carbon dioxide (decarbonation). | Drying and activating catalysts like zeolites. |
| Phase Transition | Changing crystal structure to alter physical properties like hardness. | Converting a mineral to a more stable crystalline form. |
| Purification | Removing organic impurities or other contaminants from an ore. | Preparing metal ores for smelting. |
Ready to achieve precise thermal decomposition for your materials?
KINTEK's advanced laboratory furnaces are engineered for the exact temperature control and atmosphere management required for successful calcination processes. Whether you are purifying ores, activating catalysts, or producing cement, our equipment ensures consistent, high-quality results while optimizing energy efficiency.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific calcination needs. Our experts will help you select the perfect solution to transform your materials and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of melting process? Master the Foundation of Metal Production
- What controls melting point? The Hierarchy of Forces from Ionic Bonds to Intermolecular Attractions
- What is the burning temperature of a furnace? From 200°C to 3000°C, It Depends on Your Needs
- What temperature causes melting? Debinding vs. Melting in Metal Fabrication
- What temperature does molten steel melt? Understand the Melting Range, Not a Single Point



















