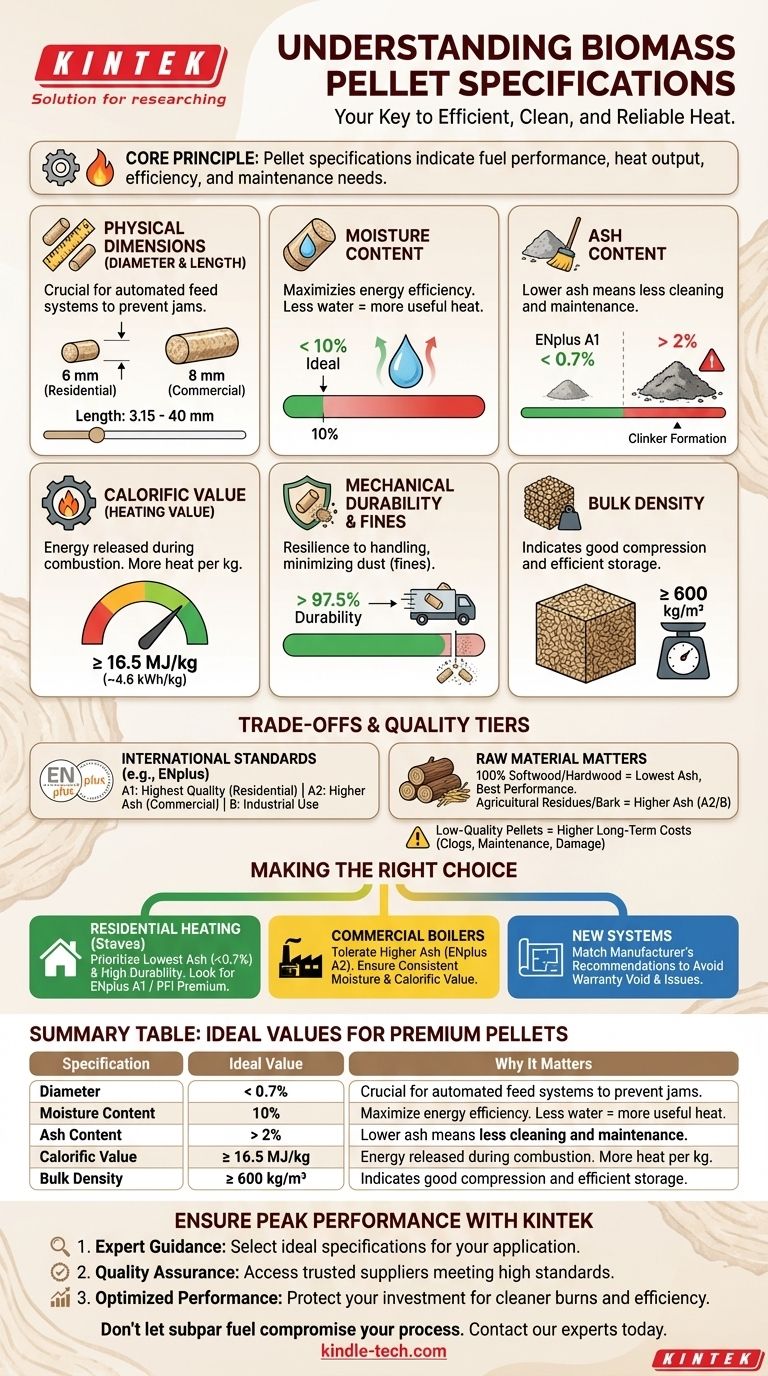
Understanding the specifications for biomass pellets is the key to ensuring efficient, clean, and reliable heat. The most critical specifications define a pellet's physical dimensions, moisture content, ash content, and energy value, which are governed by established international standards to guarantee quality and consistency.
The core principle is that pellet specifications are not just numbers on a bag; they are direct indicators of a fuel's performance, dictating everything from heat output and combustion efficiency to the amount of maintenance your equipment will require.

The Anatomy of a Quality Pellet: Key Specifications Explained
To truly assess biomass pellets, you must understand the individual metrics that define their quality. Each specification plays a distinct role in the pellet's overall performance.
Physical Dimensions (Diameter and Length)
A pellet's size is crucial for the proper functioning of automated feed systems in stoves and boilers. Inconsistency can lead to jams and feeding errors.
The most common diameters are 6 mm (primarily for residential use) and 8 mm (for larger commercial systems). Length is also controlled, typically within a range of 3.15 to 40 mm, to ensure smooth transport through an auger.
Moisture Content
This is one of the most important factors for energy efficiency. Moisture content measures the amount of water within the pellet, expressed as a percentage of its total weight.
Energy used to evaporate this water is wasted and cannot be converted into useful heat. High-quality pellets have a moisture content of less than 10%.
Ash Content
Ash is the non-combustible material left over after the pellet is burned. A lower ash content is always better, as it means less cleaning and maintenance.
High ash levels can lead to the formation of hard deposits called "clinkers" that can block the burner and reduce efficiency. Premium residential pellets (like ENplus A1 grade) target an ash content below 0.7%.
Calorific Value (Heating Value)
This specification measures the amount of energy released when the pellet is burned, typically expressed in megajoules per kilogram (MJ/kg) or kilowatt-hours per kilogram (kWh/kg).
A higher calorific value means more heat from the same amount of fuel. For quality wood pellets, you should look for a net calorific value of at least 16.5 MJ/kg (or ~4.6 kWh/kg).
Mechanical Durability & Fines
Durability measures a pellet's ability to withstand handling and transportation without crumbling. Low durability creates excessive dust, or "fines."
These fines can clog feed systems, reduce combustion efficiency, and pose a safety risk. A high durability rating (typically over 97.5%) ensures the pellet remains intact from the bag to the burner.
Bulk Density
Bulk density measures how much a given volume of pellets weighs (e.g., kg/m³). Higher density is preferable as it means more energy can be stored in the same amount of space.
It also indicates a well-compressed, high-quality pellet. A typical value for good wood pellets is 600 kg/m³ or higher.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Quality Tiers
Not all pellets are created equal. Understanding the certification systems and the impact of raw materials is essential to avoid common pitfalls.
The Role of International Standards
To simplify quality control, the industry relies on certification standards. The most prominent is ENplus, which categorizes pellets into three main classes for non-industrial use:
- A1: The highest quality, with very low ash and nitrogen content, intended for residential stoves and boilers.
- A2: Has slightly higher ash content and is suitable for larger boilers that can handle it.
- B: Allows for higher ash content and is generally used in dedicated industrial applications.
Another common standard, particularly in North America, is from the Pellet Fuels Institute (PFI), which has similar "Premium" and "Standard" grades.
Raw Material Matters
The type of biomass used to make the pellet directly impacts its specifications. Pellets made from 100% softwood or hardwood generally have the lowest ash content and perform most reliably.
Pellets incorporating agricultural residues or bark will have a higher ash content, placing them in lower quality tiers (e.g., ENplus A2 or B).
The Hidden Cost of Low-Quality Pellets
Opting for cheaper, non-certified pellets often leads to higher long-term costs. Poor specifications result in clogged augers, frequent and difficult cleaning, lower heat output, and even permanent damage to your heating system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your ideal pellet specification depends directly on your equipment and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is residential heating with a pellet stove: Prioritize pellets with the lowest possible ash content (<0.7%) and highest mechanical durability, and always look for an ENplus A1 or PFI Premium certification to ensure clean burning and minimal maintenance.
- If you are operating a larger commercial or industrial boiler: You may have more tolerance for higher ash pellets (like ENplus A2), but ensuring consistent moisture content and calorific value is critical for predictable heat output and operational efficiency.
- If you are evaluating fuel for a new system: Match the pellet specification directly to the manufacturer's recommendation, as using an incorrect grade can void the warranty and lead to performance issues.
Ultimately, selecting pellets based on certified specifications is the most reliable way to protect your investment and achieve consistent, efficient heating.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Ideal Value for Premium Pellets | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | < 10% | Maximizes heat output and combustion efficiency. |
| Ash Content | < 0.7% (ENplus A1) | Reduces maintenance and prevents clinker formation. |
| Calorific Value | ≥ 16.5 MJ/kg | Higher energy density for more heat per kg of fuel. |
| Mechanical Durability | > 97.5% | Minimizes dust (fines) and prevents feeding issues. |
| Diameter | 6mm (residential) / 8mm (commercial) | Ensures compatibility with automated feed systems. |
| Bulk Density | ≥ 600 kg/m³ | Indicates good compression and efficient storage. |
Ensure Peak Performance for Your Laboratory or Facility
Choosing the right biomass pellets is critical for efficient operation, whether you're running a lab furnace, an industrial boiler, or a residential heating system. The wrong specifications can lead to clogged feed systems, inconsistent heat, and increased maintenance costs.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. We understand that reliable heat sources are the backbone of consistent results and efficient operations. By partnering with us, you gain access to:
- Expert Guidance: Our team can help you select the ideal pellet specifications (like ENplus A1 or PFI Premium) tailored to your specific equipment and application.
- Quality Assurance: We connect you with trusted suppliers to ensure the pellets you use meet the highest standards for moisture, ash content, and durability.
- Optimized Performance: The right fuel protects your investment in heating systems, leading to cleaner burns, higher efficiency, and lower long-term costs.
Don't let subpar fuel compromise your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your biomass pellet needs and ensure your equipment runs at its best.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- FS Electrochemical Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Diverse Applications
- Customizable Fuel Cell Stack Components for Diverse Applications
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using ceramic materials as membranes in MFC stacks? Boost Scalability and Durability
- What are the dimensions for thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cells? Optimize Your Lab's Optical Path Length
- What system-level maintenance is important for a proton exchange membrane? Ensure Longevity with Proactive System Care
- What is the significance of using high-purity, corrosion-resistant electrolytic cells? Ensure Quality PEO Coatings
- What is the function of an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Master Precise Reaction Control





