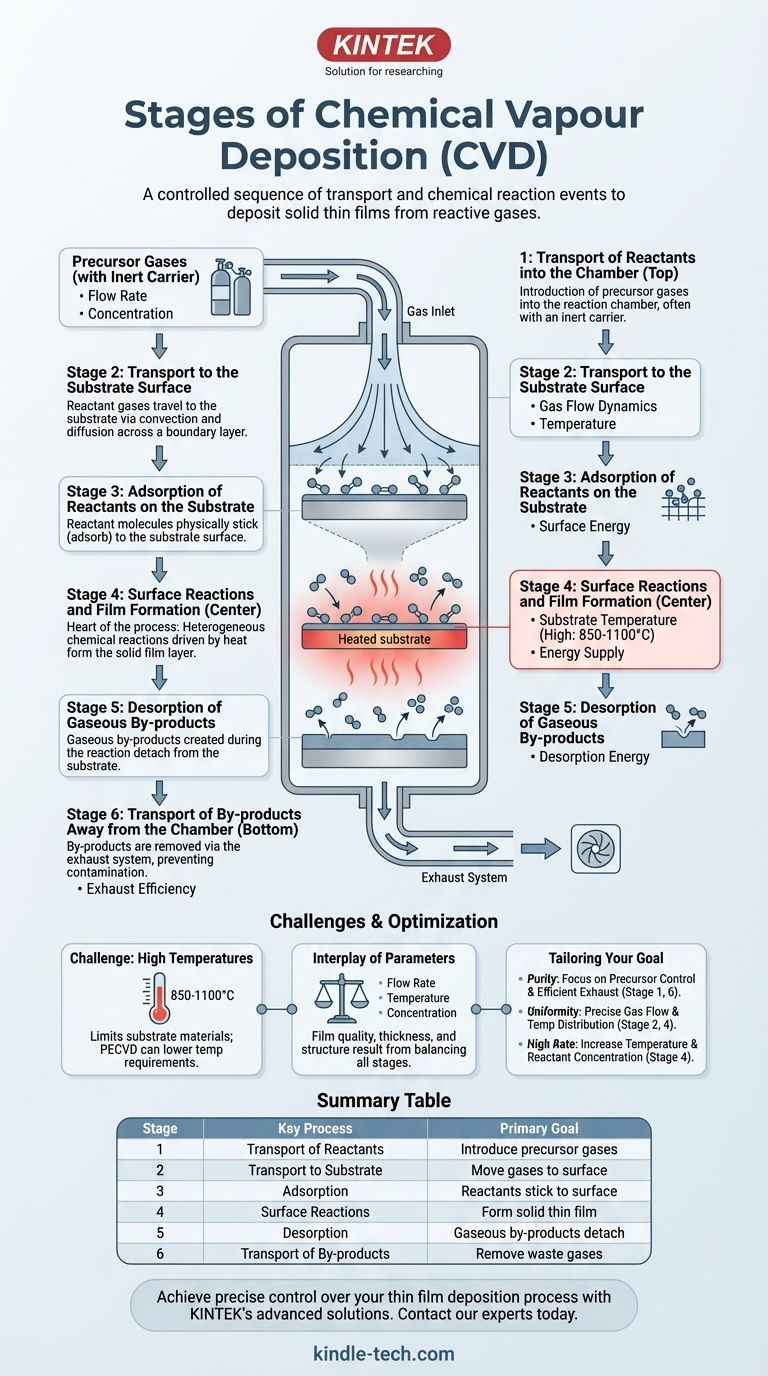
In essence, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is a sequence of events where reactive gases are transported into a chamber, diffuse to a heated substrate, and undergo chemical reactions on the surface to form a solid thin film. Throughout this process, gaseous by-products created during the reaction are adsorbed from the surface and removed from the chamber.
The core concept to grasp is that CVD is not a single event, but a carefully controlled chain of physical transport phenomena and chemical reactions. Mastering the final film quality requires understanding and controlling each distinct stage, from gas inlet to exhaust.
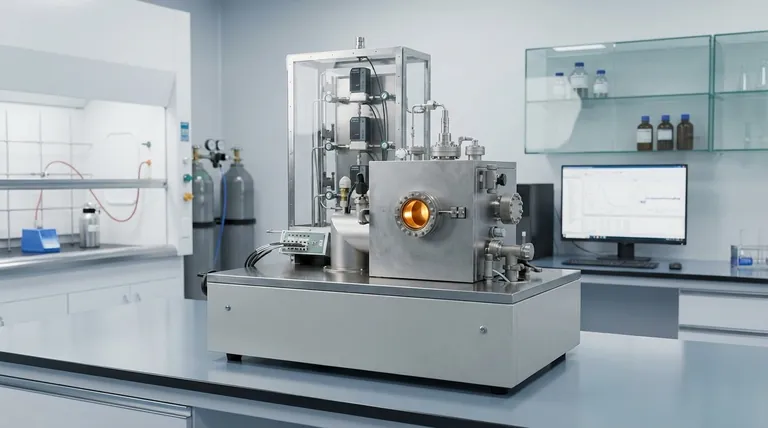

A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the CVD Process
To truly understand how a gas transforms into a high-purity solid layer, we must break the process down into its fundamental stages. Each stage presents an opportunity to control the final properties of the deposited material.
Stage 1: Transport of Reactants into the Chamber
This is the initial step where the precursor gases, often carried by an inert gas, are introduced into the reaction chamber. The flow rate and concentration of these reactants are critical parameters that are set and controlled externally.
Stage 2: Transport to the Substrate Surface
Once inside the chamber, the reactant gases must travel from the main gas stream to the substrate surface. This transport occurs primarily through convection (the bulk movement of the gas) and diffusion across a stationary boundary layer that forms just above the substrate. The properties of this layer significantly impact deposition uniformity.
Stage 3: Adsorption of Reactants on the Substrate
When the reactant molecules reach the substrate, they physically stick to the surface in a process called adsorption. This is a necessary precursor to any chemical reaction. The surface is now populated with the raw ingredients for film growth.
Stage 4: Surface Reactions and Film Formation
This is the heart of the CVD process. The adsorbed molecules may diffuse across the surface to find active sites. With energy provided by the heated substrate, they undergo heterogeneous chemical reactions. These reactions break down the precursor molecules, depositing the desired solid material and creating the film layer by layer.
Stage 5: Desorption of Gaseous By-products
The chemical reactions that form the solid film almost always produce unwanted gaseous by-products. These by-products must detach, or desorb, from the substrate surface to make room for new reactants to arrive and continue the film growth.
Stage 6: Transport of By-products Away from the Chamber
Finally, these desorbed by-products diffuse away from the substrate, back into the main gas stream. They are then carried out of the reaction chamber by the gas flow, effectively being removed through the exhaust system. Inefficient removal can lead to film contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the CVD process is governed by a sensitive interplay of factors, and a lack of control can lead to undesirable results.
The Challenge of High Temperatures
The single most significant limitation of traditional CVD is its reliance on high temperatures, often between 850-1100°C. This thermal energy is required to drive the surface reactions (Stage 4).
Many substrate materials cannot withstand such heat without deforming or melting, which limits the applicability of the technique. Modern variations like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) can lower this temperature requirement.
The Interplay of Control Parameters
The final film's characteristics—its purity, thickness, and structure—are not determined by a single setting. They are an outcome of the balance between all stages.
For example, a gas flow that is too high might not give reactants enough time to diffuse to the surface (Stage 2), resulting in a low deposition rate. Conversely, a temperature that is too low will slow the surface reactions (Stage 4), also reducing the growth rate and potentially affecting film quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the distinct stages of the CVD process allows you to tailor the final film to your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is film purity: Your control over the precursor gases (Stage 1) and the efficient removal of by-products (Stage 6) is paramount.
- If your primary focus is film uniformity: Precise management of gas flow dynamics and temperature distribution across the substrate is crucial for controlling Stage 2 and Stage 4 consistently.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate: Increasing substrate temperature and reactant concentration will be your key levers, as they directly accelerate the surface reactions in Stage 4.
Ultimately, mastering CVD is about understanding that you are not just depositing a film; you are orchestrating a sequence of transport and reaction events.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport of Reactants | Introduce precursor gases into the chamber |
| 2 | Transport to Substrate | Move gases to the substrate surface via diffusion |
| 3 | Adsorption | Reactant molecules stick to the substrate surface |
| 4 | Surface Reactions | Chemical reactions form the solid thin film |
| 5 | Desorption | Gaseous by-products detach from the surface |
| 6 | Transport of By-products | Remove waste gases from the chamber via exhaust |
Ready to achieve precise control over your thin film deposition process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables tailored for sophisticated processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether your goal is superior film purity, uniformity, or a high deposition rate, our expertise and solutions can help you optimize every stage of your workflow.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and enhance your research outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the apparatus of chemical vapor deposition? The Essential Components for Thin Film Deposition
- What are some of the different methods of chemical vapour deposition? Choose the Best CVD Process for Your Application
- What are the advantages of using a Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) system? Master BN Nanocoatings on LATP
- How is carbon coating done? Enhance Material Performance with Precision Coating
- What are the methods to synthesize carbon nanotubes? A Guide to Arc Discharge, Laser Ablation & CVD
- What is the dual function of the substrate heater in MW-SWP CVD hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Thin Film Growth
- How do you make diamonds with CVD? Grow High-Purity Diamonds Atom by Atom
- Why is a high-precision MFC essential for CVD systems? Ensure Superior Membrane Separation Performance



















