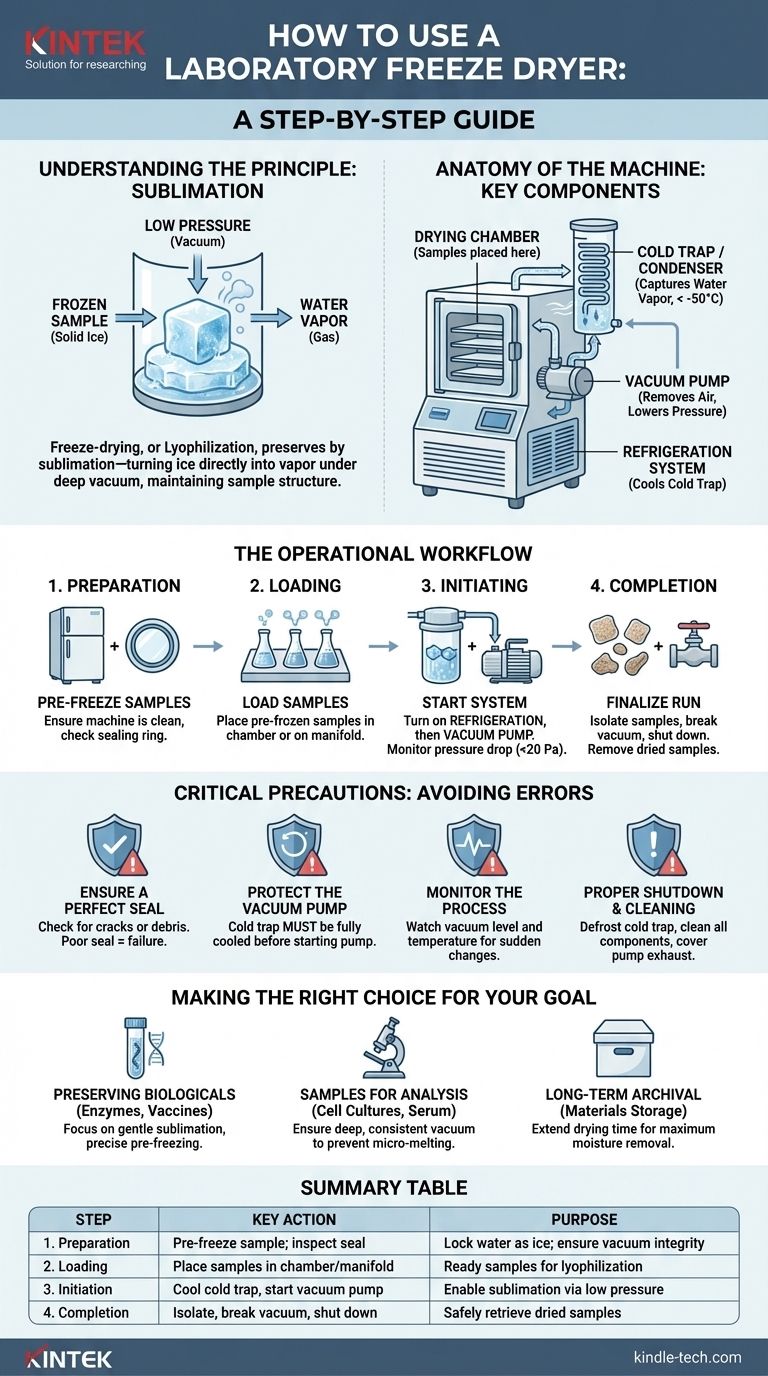
To properly use a laboratory freeze dryer, you must load pre-frozen materials, seal the chamber, and apply a strong vacuum. This process, known as lyophilization, carefully removes water by turning ice directly into vapor, preserving the sample's structure and integrity for long-term storage or analysis.
The core principle is not just drying, but preserving. Freeze-drying is a controlled process of freezing a sample, lowering the pressure, and adding just enough heat to sublimate the frozen water directly from a solid to a gas, bypassing the damaging liquid phase.

Understanding the "Why": The Principle of Sublimation
What is Freeze-Drying?
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is a dehydration process used to preserve perishable materials or make them more convenient for transport. It works by freezing the material and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water in the material to sublimate.
The Science of Sublimation
Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state.
By first freezing your sample, you lock the water molecules in place as solid ice. Then, by creating a deep vacuum, you lower the pressure to a point where ice can turn directly into water vapor, which is then collected by the machine.
This process is exceptionally gentle, as it avoids the surface tension and chemical changes that occur when water is removed as a liquid, thereby preserving the physical and biological structure of your sample.
Anatomy of the Machine: Key Components
The Drying Chamber or Manifold
This is where you place your samples. It can be a chamber with shelves or a manifold with multiple ports for attaching individual flasks. It must be sealed to hold a deep vacuum.
The Cold Trap (Condenser)
The cold trap is the most critical part of the system. It is an extremely cold surface (often below -50°C) that sits between the drying chamber and the vacuum pump. Its sole purpose is to capture the water vapor sublimating from your sample, turning it back into ice on its surface.
The Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump removes air from the system to reduce the pressure inside the drying chamber. This low-pressure environment is what enables sublimation to occur at a low temperature.
The Refrigeration System
This system, which includes a compressor and condenser coils, is the engine that cools the cold trap to its operational temperature, ensuring it is cold enough to effectively trap water vapor.
The Operational Workflow: A Step-by-Step Guide
Phase 1: Preparation
Before you begin, ensure your sample is properly pre-frozen. The freeze dryer is designed to sublimate ice, not to freeze the initial sample. Using a standard lab freezer is often sufficient.
Check that the machine is clean, particularly the sealing ring on the chamber lid, which must be free of debris to ensure a proper seal.
Phase 2: Loading the Samples
Place your pre-frozen samples onto the drying rack or attach flasks to the manifold.
Position the drying rack on the cold trap and place the plexiglass cover over the chamber, ensuring the sealing ring is seated correctly.
Phase 3: Initiating the Drying Process
Close the drain or water intake valve tightly. This is critical for achieving a vacuum.
Turn on the refrigeration system first and allow the cold trap to reach its target temperature.
Once the cold trap is cold, turn on the vacuum pump. Monitor the vacuum gauge; the pressure should drop significantly, often to below 20 Pascals (Pa), indicating the system is properly sealed and sublimation can begin.
Phase 4: Finalizing the Run and Shutdown
Once the sample appears completely dry (a process that can take hours or days), you can shut down the system.
First, close the valves connecting your samples (if using a manifold) to isolate them from the vacuum. Then, open the water intake valve to gently break the vacuum in the chamber.
Turn off the vacuum pump and then the refrigeration unit. You can now remove your dried samples.
Critical Precautions: Avoiding Common Errors
Ensure a Perfect Seal
The entire process depends on maintaining a deep vacuum. Before starting, always inspect the rubber sealing ring for cracks, debris, or dryness. A poor seal is the most common cause of failure.
Protect the Vacuum Pump
The cold trap's job is to protect the vacuum pump from water vapor, which can damage the pump's oil and internal components. Never start the vacuum pump before the cold trap is fully cooled.
Monitor the Process
Keep an eye on the vacuum level and cold trap temperature throughout the run. A sudden rise in pressure could indicate a leak or that the cold trap is overloaded and can no longer trap moisture effectively.
Proper Shutdown and Cleaning
After a run is complete, the ice on the cold trap must be melted and drained. This is the defrosting step.
Thoroughly clean and dry all components. When not in use, it's good practice to cover the vacuum pump's exhaust port to prevent dust from entering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive biologicals (enzymes, vaccines, antibodies): The gentleness of sublimation is paramount. Pay extra attention to pre-freezing methods to ensure sample viability before it even enters the machine.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for analysis (e.g., cell cultures, serum): Your goal is removing water without altering the remaining components. Ensure the vacuum is deep and consistent to prevent any micro-melting that could compromise the sample.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival of materials: The key is removing as much residual moisture as possible. This may require extending the drying time to ensure complete sublimation from deep within the sample.
Following these steps transforms the freeze dryer from a complex machine into a powerful tool for preservation.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Pre-freeze sample; inspect machine seal | Lock water as ice; ensure vacuum integrity |
| 2. Loading | Place pre-frozen samples in chamber/manifold | Ready samples for the lyophilization process |
| 3. Initiation | Cool cold trap first, then start vacuum pump | Enable sublimation by creating low-pressure environment |
| 4. Completion | Isolate samples, break vacuum, shut down systems | Safely retrieve dried, preserved samples |
Ready to achieve perfect sample preservation with a freeze dryer? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory freeze dryers and consumables designed for researchers focused on preserving sensitive biologicals, preparing samples for analysis, and long-term archival. Our equipment ensures precise temperature control and deep vacuum for reliable lyophilization results. Contact our experts today to find the ideal freeze-drying solution for your laboratory's specific needs and ensure your samples are protected with every run.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does freeze-drying contribute to long-term sample storage? Achieve Maximum Preservation Without Refrigeration
- How does cooling rate affect freeze dryer performance? Unlock Faster, More Reliable Lyophilization
- What makes freeze-dried products advantageous for transport? Drastically Reduce Shipping Costs & Simplify Logistics
- What role do laboratory freeze dryers play in the food industry? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- What happens during the freezing phase of lyophilization? Master the Critical First Step for Product Integrity



















