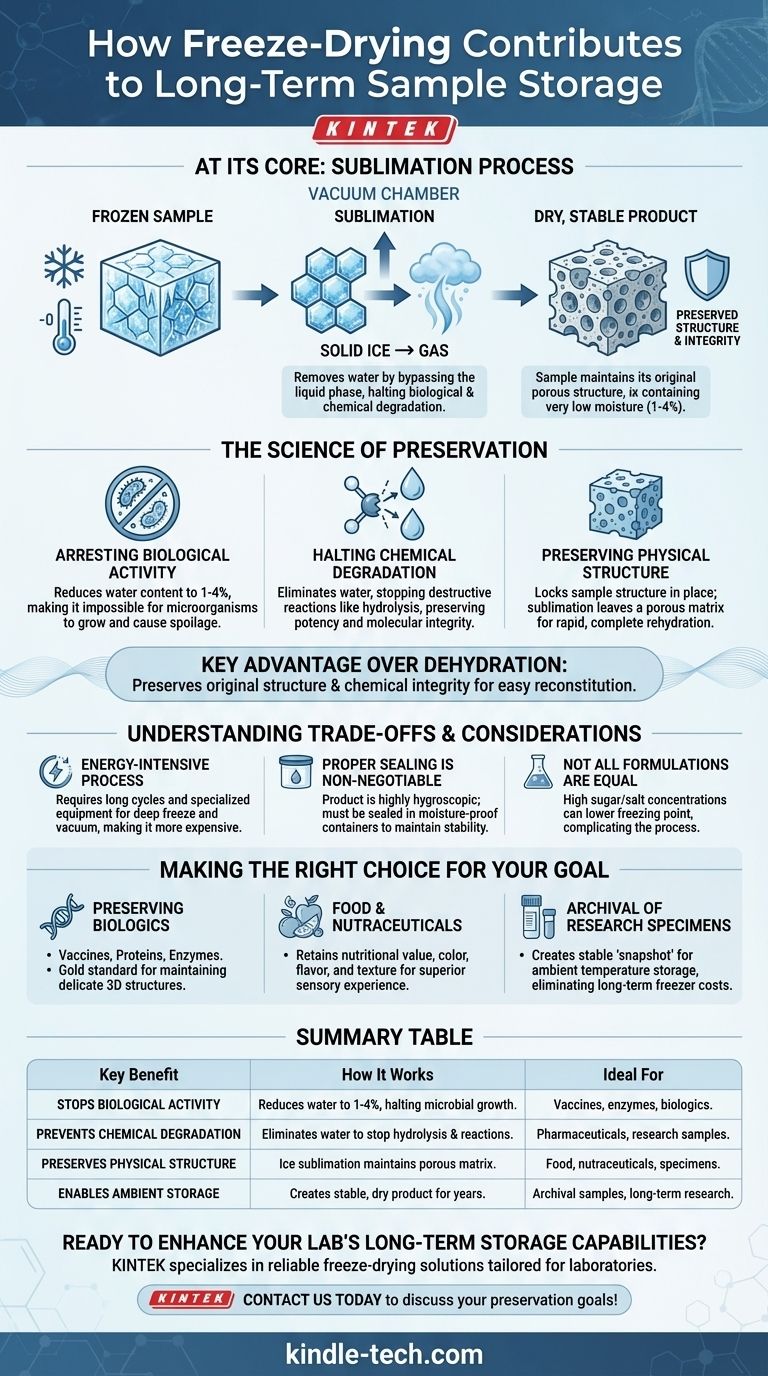
At its core, freeze-drying enables long-term storage by removing water from a sample while it is in a frozen state. This process, known as sublimation, transitions water directly from solid ice to a gas, bypassing the liquid phase. By eliminating water, you effectively halt nearly all biological and chemical degradation pathways, creating a stable product that can last for years without refrigeration.
The critical advantage of freeze-drying over simple dehydration is its ability to preserve the original physical structure and chemical integrity of the sample. By locking the product's form in a frozen state before gently removing the water, it ensures easy reconstitution and maintains the sample's original effectiveness.

The Science of Preservation: How Freeze-Drying Works
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is a multi-step process designed for maximum preservation. Understanding the principle behind it clarifies why it is so effective for sensitive materials.
The Principle of Sublimation
The process begins by freezing the sample solid. Then, under a strong vacuum, the temperature is carefully raised. This combination of low pressure and controlled heat gives the frozen water molecules enough energy to turn directly into a vapor, which is then collected, leaving a dry, structurally intact product behind.
Arresting Biological Activity
Microorganisms like bacteria, molds, and yeast require water to grow and metabolize. By reducing the water content to a minimal level (typically 1-4%), freeze-drying creates a state of suspended animation, making it impossible for these microbes to cause spoilage or degradation.
Halting Chemical Degradation
Water is a universal solvent and a key participant in many chemical reactions that break down complex molecules, such as hydrolysis. Removing water effectively stops these destructive reactions, preserving the potency of pharmaceuticals, the structure of proteins, and the integrity of research samples.
Preserving Physical Structure
Unlike heat-based drying that causes shrinkage and structural collapse, freeze-drying locks the sample's structure in place during the initial freezing step. The subsequent sublimation of ice leaves behind a porous, sponge-like matrix that retains the original volume and shape, which is crucial for rapid and complete rehydration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, freeze-drying is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its limitations is essential for proper application.
It's an Energy-Intensive Process
Lyophilization cycles are often long, lasting anywhere from hours to several days. The specialized equipment and energy required to maintain a deep freeze and a strong vacuum make it a more expensive preservation method compared to simple heating or air drying.
Proper Sealing is Non-Negotiable
The resulting freeze-dried product is highly hygroscopic, meaning it will readily absorb moisture from the atmosphere. To maintain its long-term stability, the product must be immediately sealed in a moisture-proof container, often under a dry, inert gas like nitrogen. Failure to do so will negate the benefits of the process.
Not All Formulations Are Equal
Samples containing high concentrations of sugars or salts can be challenging to freeze-dry. These components can lower the freezing point of the water, making it difficult to fully solidify the product before applying the vacuum, which can lead to processing failures and a poor-quality final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Freeze-drying is a strategic tool, and its application depends entirely on your preservation objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving biologics (vaccines, proteins, enzymes): Freeze-drying is the gold standard for maintaining the delicate three-dimensional structures essential for their biological activity.
- If your primary focus is food and nutraceuticals: This method excels at retaining nutritional value, color, flavor, and texture, providing a superior sensory experience compared to other drying techniques.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival of research specimens: Lyophilization creates an incredibly stable "snapshot" of a sample that can be stored at ambient temperature, eliminating the cost and risk associated with long-term freezer storage.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently leverage freeze-drying as a reliable tool in your long-term preservation strategy.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | How It Works | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Stops Biological Activity | Reduces water content to 1-4%, halting microbial growth. | Vaccines, enzymes, biologics. |
| Prevents Chemical Degradation | Eliminates water to stop hydrolysis and other reactions. | Pharmaceuticals, research samples. |
| Preserves Physical Structure | Ice sublimation maintains porous matrix for easy rehydration. | Food, nutraceuticals, specimens. |
| Enables Ambient Storage | Creates stable, dry product that lasts years without refrigeration. | Archival samples, long-term research. |
Ready to enhance your lab's long-term storage capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable freeze-drying solutions and consumables tailored for laboratories. Whether you're preserving sensitive biologics, research specimens, or nutraceuticals, our expertise ensures your samples remain stable and effective for years.
Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment can support your preservation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for drying nickel nanoparticle precursors? Prevent Hard Agglomeration Now
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure



















