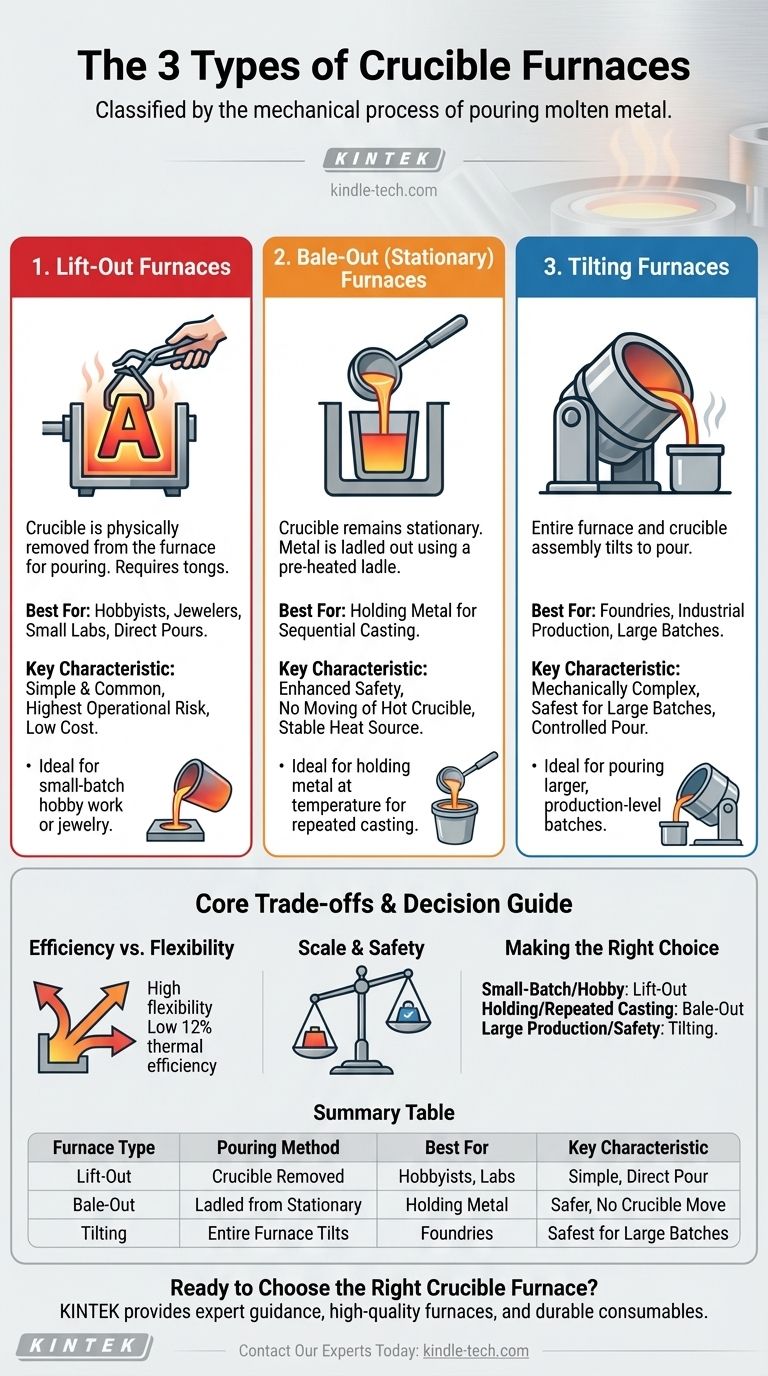
Crucible furnaces are defined by one key action: how you get the molten metal out. The three primary types are lift-out, bale-out, and tilting furnaces. This classification is not about how they generate heat, but rather the mechanical process used for pouring, which dictates their scale, safety, and ideal application.
The choice between a lift-out, bale-out, or tilting furnace is a strategic decision that balances batch size, safety, and operational workflow. Understanding this distinction is the first step in selecting the right tool for melting and casting metal.

How Crucible Furnaces Are Classified
The core difference between the three furnace types lies in the relationship between the crucible (the ceramic pot holding the metal) and the furnace (the heat source). One design moves the crucible, one moves the metal, and one moves the entire apparatus.
1. Lift-Out Furnaces
In a lift-out furnace, the crucible is heated inside the furnace chamber and then physically removed from the heat source for pouring.
This is the simplest and most common design for small-scale operations. It requires specialized tongs to securely grip the hot crucible, which is often bilge-shaped or A-shaped to facilitate a secure grip.
These are ideal for hobbyists, jewelers, and laboratories where small, direct pours into molds are required.
2. Bale-Out (Stationary) Furnaces
In a bale-out furnace, the crucible remains stationary inside the furnace at all times.
To extract the molten metal, an operator uses a smaller, pre-heated ladle to scoop, or "bale," the liquid from the crucible.
This design is often used as a holding furnace to keep a reservoir of metal at a consistent temperature for sequential, smaller casting jobs. It enhances safety by not requiring the operator to move a large, glowing-hot crucible.
3. Tilting Furnaces
A tilting furnace is the most mechanically complex design. The crucible and furnace chamber are built into a single assembly that pivots or tilts on an axis to pour the molten metal.
The pour is controlled by a gear mechanism, either manual or hydraulic, allowing for a very controlled and steady stream of metal.
This type is used in foundries and industrial settings for pouring large batches where lifting the crucible manually would be impractical and extremely dangerous.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
While simple in concept, crucible furnaces present a clear set of advantages and disadvantages. Your choice of type is a negotiation between these factors.
Efficiency vs. Flexibility
Crucible furnaces are prized for their flexibility. You can melt a batch of aluminum, and in the next run, easily switch to bronze with minimal cross-contamination.
However, this flexibility comes at the cost of low energy efficiency. With heat escaping each time a furnace is opened or a crucible is removed, their thermal efficiency can be as low as 12%, making them less economical for continuous, large-scale production.
Scale and Safety
The lift-out design is cost-effective and simple but carries the highest operational risk. Manually carrying a crucible filled with molten metal requires skill, proper safety gear, and a controlled environment.
Bale-out and tilting furnaces are inherently safer for the operator. They keep a greater distance between the person and the primary heat source, minimizing the risk of catastrophic spills.
Maintenance and Material Costs
A key advantage across all types is their low maintenance cost and simple construction, often consisting of a refractory-lined chamber and a heat source.
However, the crucibles themselves are consumables. They are subject to intense thermal shock and chemical attack from molten metal and fluxes, requiring periodic replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is small-batch hobby work or jewelry: A lift-out furnace offers the lowest cost of entry and simplest operation for direct pouring into small molds.
- If your primary focus is holding metal at temperature for repeated casting: A bale-out furnace provides a stable heat source and avoids the risks associated with moving the crucible.
- If your primary focus is pouring larger, production-level batches: A tilting furnace is the safest and most controlled method for handling significant volumes of molten metal.
By understanding this fundamental distinction, you can align your equipment precisely with your operational needs and safety requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Pouring Method | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lift-Out | Crucible is removed for pouring | Hobbyists, jewelers, small labs | Simple, direct pour into molds |
| Bale-Out | Metal is ladled from a stationary crucible | Holding metal for sequential casting | Safer, no moving of hot crucible |
| Tilting | Entire furnace assembly tilts to pour | Foundries, industrial production | Safest for large, controlled batches |
Ready to Choose the Right Crucible Furnace for Your Lab?
Selecting the correct furnace type is critical for the safety and efficiency of your metal melting and casting processes. Whether you need a compact lift-out furnace for R&D or a robust tilting furnace for production, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
We provide:
- High-quality crucible furnaces for all applications.
- Expert guidance to match the furnace type to your workflow.
- Durable consumables, including crucibles designed to withstand thermal shock.
Don't leave your lab's safety and performance to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment solutions can enhance your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What reaction conditions do high-temperature tube furnaces provide for biochar reduction? Optimize Ore Processing



















