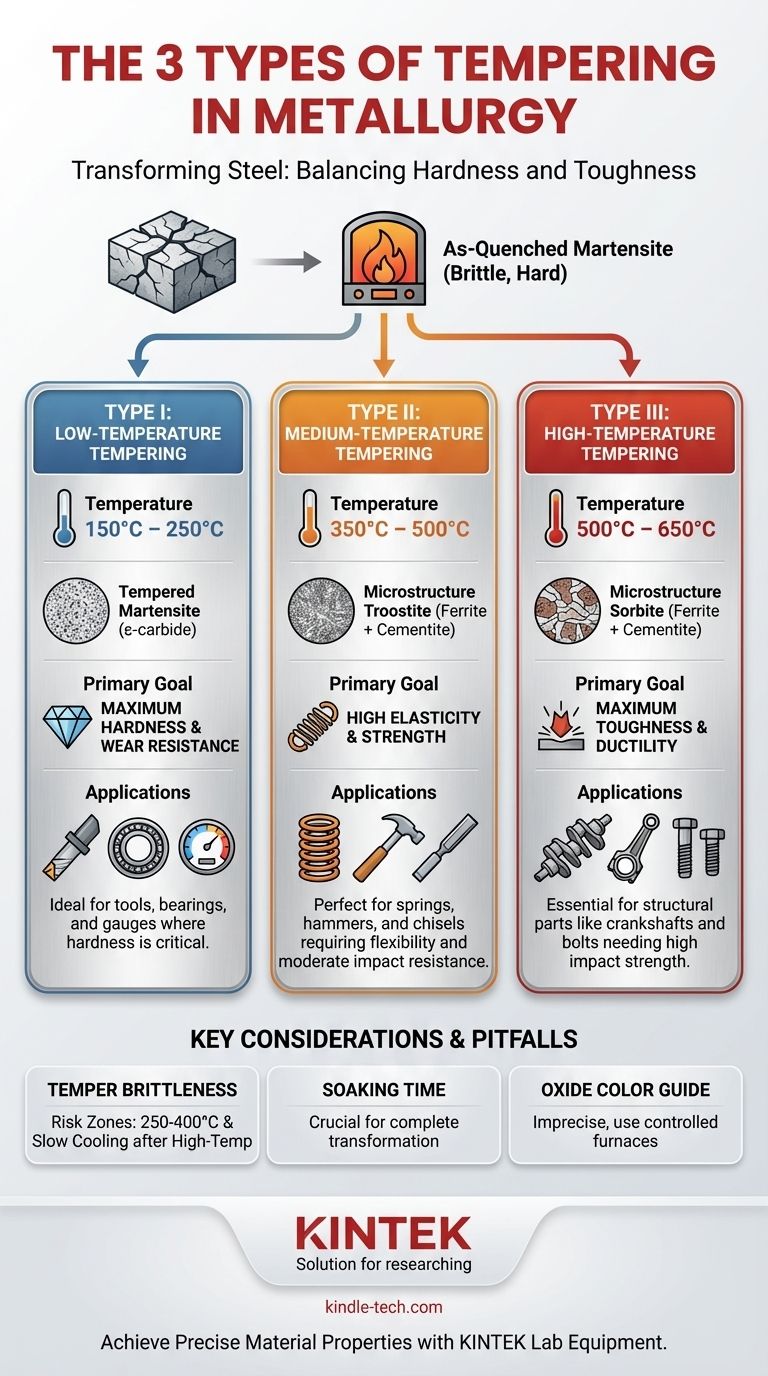
In metallurgy, tempering is classified into three distinct types based on the temperature range used. These are low-temperature tempering (150-250°C), medium-temperature tempering (350-500°C), and high-temperature tempering (500-650°C). Each range is chosen deliberately to transform the steel's brittle, as-quenched microstructure into one with a specific, desired balance of hardness and toughness.
The specific type of tempering you choose is not arbitrary; it is a direct engineering decision. Your choice of temperature range dictates the final trade-off between a component's ultimate hardness and its ability to absorb impact and resist fracture.
The Purpose of Tempering: From Brittle to Durable
Tempering is a heat-treatment process applied to hardened steels to achieve greater toughness by decreasing hardness. It always follows a hardening process like quenching.
The Problem with As-Quenched Steel
When steel is heated to a high temperature and then rapidly cooled (quenched), it forms a microstructure called martensite. This structure is extremely hard and wear-resistant, but it is also very brittle and filled with internal stresses, making it unsuitable for most applications. An as-quenched part can be as fragile as glass.
The Role of Temperature
Tempering involves reheating the quenched part to a specific temperature below its critical point, holding it for a set time, and then cooling it. This controlled heating allows carbon atoms to precipitate and form carbides, relieving internal stresses and transforming the brittle martensite into more ductile microstructures.
The Fundamental Trade-off
The core principle of tempering is the inverse relationship between hardness and toughness. The higher the tempering temperature, the more the hardness is reduced, but the greater the toughness and ductility become.
A Detailed Look at the Three Tempering Ranges
The classification of tempering into three types is based on the microstructural changes that occur at different temperature ranges and the resulting mechanical properties.
Type I: Low-Temperature Tempering (150°C – 250°C)
The primary goal here is to relieve internal stresses while retaining the highest possible hardness and wear resistance from the martensitic structure.
The microstructure produced is called tempered martensite. At this temperature, very fine particles of epsilon (ε) carbide precipitate.
This process is ideal for components where hardness is the most critical property. Common applications include cutting tools, gauges, bearings, and case-hardened parts.
Type II: Medium-Temperature Tempering (350°C – 500°C)
This range aims to produce a material with high elasticity, good strength, and sufficient toughness. Hardness is intentionally sacrificed to a greater degree than in low-temperature tempering.
The resulting microstructure is troostite, which is a very fine mixture of ferrite and cementite. This structure is known for its high elastic limit.
Typical applications include springs, leaf springs, hammers, and chisels, where the ability to flex or withstand moderate impact without deforming or breaking is key.
Type III: High-Temperature Tempering (500°C – 650°C)
The objective of high-temperature tempering is to achieve the best possible combination of strength and, most importantly, toughness and ductility. This process significantly reduces hardness.
This treatment produces a microstructure called sorbite, a coarser mixture of ferrite and cementite that excels at absorbing energy and resisting fracture under high stress.
This is used for highly stressed structural components that require high toughness and impact strength, such as automotive crankshafts, connecting rods, shafts, and bolts. This process is often referred to as "toughening" or "quench and temper."
Understanding the Pitfalls and Considerations
Choosing a tempering process requires awareness of potential issues that can compromise the final material properties.
The Risk of Temper Brittleness
Certain temperature ranges can induce brittleness, which must be avoided. There are two primary forms to be aware of.
The first, known as "temper martensite embrittlement" or "blue brittleness," occurs between approximately 250°C and 400°C. This range is typically avoided unless necessary for specific hardness targets.
The second form, "temper embrittlement," occurs when steel is slow-cooled after high-temperature tempering (or held for long periods between 375°C and 575°C). This is caused by the segregation of impurities to grain boundaries and is managed by rapid cooling after tempering.
The Importance of Soaking Time
While temperature is the dominant factor, the time the part is held at that temperature (soaking time) is also crucial. Insufficient time will result in an incomplete microstructural transformation and inconsistent properties throughout the component.
Color as an Imperfect Guide
Historically, blacksmiths used the color of the oxide layer that forms on steel during heating as a guide for tempering temperature. While useful, this method is imprecise and should not be relied upon for modern, critical applications where controlled furnaces provide far greater accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a tempering process must be driven by the component's end-use requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use low-temperature tempering for applications like cutting tools and bearings.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and elasticity: Use medium-temperature tempering for components like springs or impact tools.
- If your primary focus is maximum toughness and ductility: Use high-temperature tempering for critical structural parts that must absorb significant energy without fracturing.
By understanding these principles, you can precisely engineer the mechanical properties of steel to meet the demands of any application.

Summary Table:
| Tempering Type | Temperature Range | Key Microstructure | Primary Goal | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature | 150°C – 250°C | Tempered Martensite | Maximum Hardness & Wear Resistance | Cutting tools, bearings, gauges |
| Medium-Temperature | 350°C – 500°C | Troostite | High Elasticity & Strength | Springs, hammers, chisels |
| High-Temperature | 500°C – 650°C | Sorbite | Maximum Toughness & Ductility | Crankshafts, connecting rods, bolts |
Achieve Precise Material Properties with KINTEK
Selecting the correct tempering process is critical for the performance and longevity of your components. The precise temperature control required for consistent results demands reliable laboratory equipment.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of metallurgy and materials science laboratories. Our range of high-quality tempering furnaces and ovens ensures accurate temperature profiles and uniform heating, enabling you to execute low, medium, or high-temperature tempering with confidence.
Let us help you engineer superior materials:
- Achieve Consistent Results: Our furnaces provide the stable, controlled environment necessary for repeatable tempering cycles.
- Optimize Your Process: Get the exact balance of hardness, strength, and toughness your application demands.
- Enhance Lab Efficiency: Rely on durable, high-performance equipment built for rigorous metallurgical testing.
Ready to perfect your heat treatment process? Contact our experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C



















