While the question asks for two types, the most important distinction in modern laboratory autoclaves is the method used to remove air from the sterilization chamber. The two primary mechanisms are Gravity Displacement and Pre-Vacuum (also known as dynamic air removal). The choice between them is determined entirely by the types of materials you need to sterilize, as ineffective air removal is a leading cause of sterilization failure.
The core difference between laboratory autoclaves is not their size or brand, but how they ensure steam makes contact with every surface. Gravity autoclaves passively push air out with steam, while Pre-Vacuum autoclaves actively pull air out with a pump, enabling far more effective sterilization of complex loads.
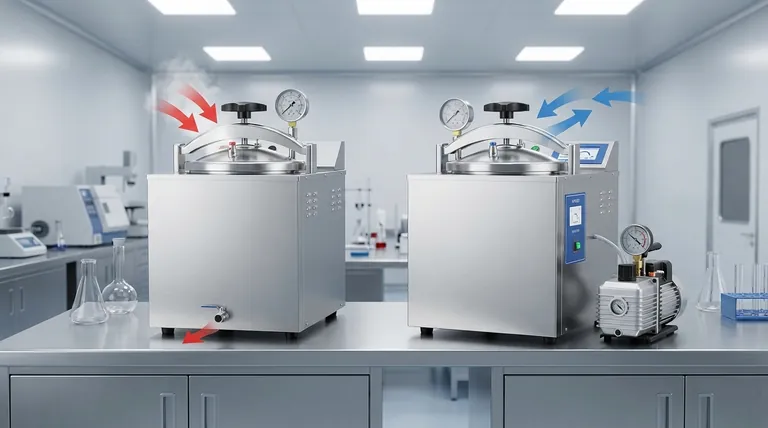

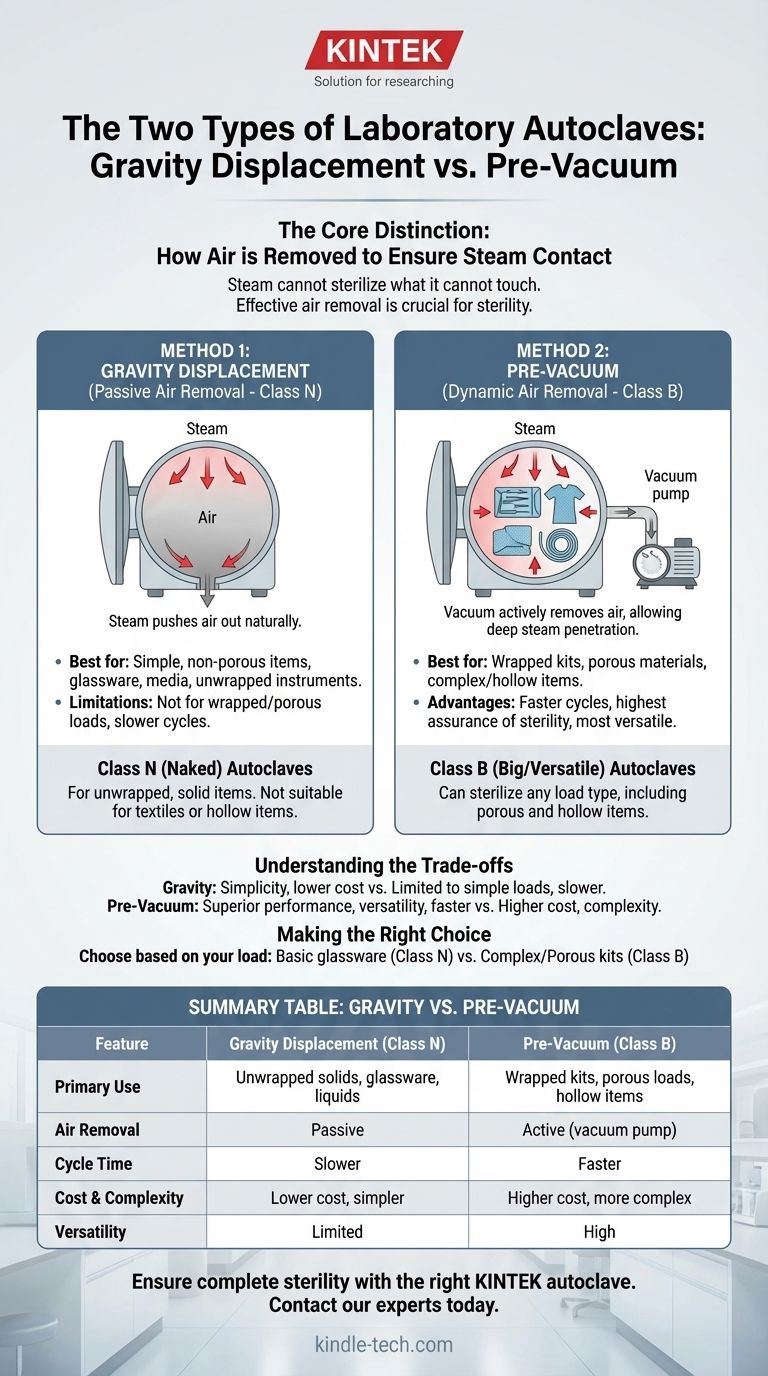
The Fundamental Challenge: Removing Air for Effective Sterilization
An autoclave works by using steam under pressure to achieve temperatures high enough to kill all microorganisms. However, steam cannot sterilize what it cannot touch.
The central challenge in any autoclave cycle is removing the ambient air from the chamber and the load. Trapped air pockets create cool spots that prevent steam from reaching surfaces, rendering the sterilization process ineffective. The two main types of autoclaves solve this problem in fundamentally different ways.
Method 1: Gravity Displacement
This is the simpler and more common method, especially in basic laboratory settings.
In a gravity displacement cycle, steam is slowly fed into the chamber, typically from the top or sides. Because steam is less dense than cool air, it fills the chamber from the top down, forcing the heavier, colder air out through a drain at the bottom.
These autoclaves are effective for sterilizing simple, non-porous items like laboratory glassware, media, and unwrapped metal instruments.
Method 2: Pre-Vacuum (Dynamic Air Removal)
This is a more advanced and robust method required for medical applications and complex laboratory loads.
Before steam is introduced, a vacuum pump actively removes most of the air from the chamber. This process may be repeated in a series of vacuum and pressure pulses. By creating a near-vacuum, the subsequent injection of steam is instantaneous and can penetrate deep into dense, porous, or complex loads.
This method is essential for sterilizing wrapped instrument kits, porous materials like surgical gowns, and items with long, narrow lumens like tubing.
Understanding the Autoclave "Class" System
To standardize performance, autoclaves are often categorized into three European classes (EN 13060), which are now widely recognized globally. These classes directly relate to the air removal method.
Class N Autoclaves
Class N autoclaves are designed for sterilizing naked, unwrapped, solid items. These almost always use the Gravity Displacement method. They are not suitable for textiles, porous loads, or even hollow items, as air may not be effectively removed.
Class B Autoclaves
Class B autoclaves can sterilize any type of load, including porous, hollow, and wrapped instruments. They are the most versatile and achieve this by using a Pre-Vacuum cycle. The "B" stands for "big," signifying their capability to handle the widest range of materials.
Class S Autoclaves
Class S autoclaves are for specific loads as defined by the manufacturer. They represent a middle ground, offering more capability than Class N but less than Class B. For example, a Class S unit might use an active drying cycle or a single vacuum pulse, but not the deep, multi-pulse vacuum of a Class B unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these systems involves balancing cost, complexity, and capability.
Gravity: Simplicity vs. Limitation
The primary advantage of a gravity displacement (Class N) autoclave is its lower cost and mechanical simplicity. With fewer moving parts, they are generally easier to maintain.
However, their major limitation is the inability to reliably sterilize wrapped or porous loads. Cycle times are also typically longer because the passive air removal process is less efficient.
Pre-Vacuum: Versatility vs. Complexity
A pre-vacuum (Class B) autoclave offers superior performance and versatility. Cycles are much faster, and it provides the highest level of assurance that steam has penetrated the entire load.
The trade-off is higher initial cost and increased complexity. The vacuum pump is an additional component that requires regular maintenance and can be a point of failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Lab
Your decision should be based entirely on what you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing basic glassware, media, and unwrapped instruments: A Class N (Gravity Displacement) autoclave is a reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If you need to sterilize wrapped surgical kits, porous materials like gowns, or complex hollow instruments: A Class B (Pre-Vacuum) autoclave is essential for ensuring complete steam penetration and sterility.
- If your needs are specialized and you must validate a specific, complex load type: A Class S autoclave may be an option, but a Class B unit often provides greater flexibility for future needs.
Understanding the method of air removal empowers you to select an autoclave that guarantees sterility and safety for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gravity Displacement (Class N) | Pre-Vacuum (Class B) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Unwrapped solids, glassware, liquids | Wrapped kits, porous loads, hollow items |
| Air Removal | Passive (steam pushes air out) | Active (vacuum pump removes air) |
| Cycle Time | Slower | Faster |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler maintenance | Higher cost, more complex |
| Versatility | Limited to simple loads | Handles complex, porous loads |
Ensure complete sterility for your laboratory with the right autoclave.
Whether you're sterilizing simple glassware or complex surgical kits, KINTEK provides reliable autoclave solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our range includes both Gravity Displacement and Pre-Vacuum models to ensure effective steam penetration and safety for all your lab equipment and consumables.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing



















