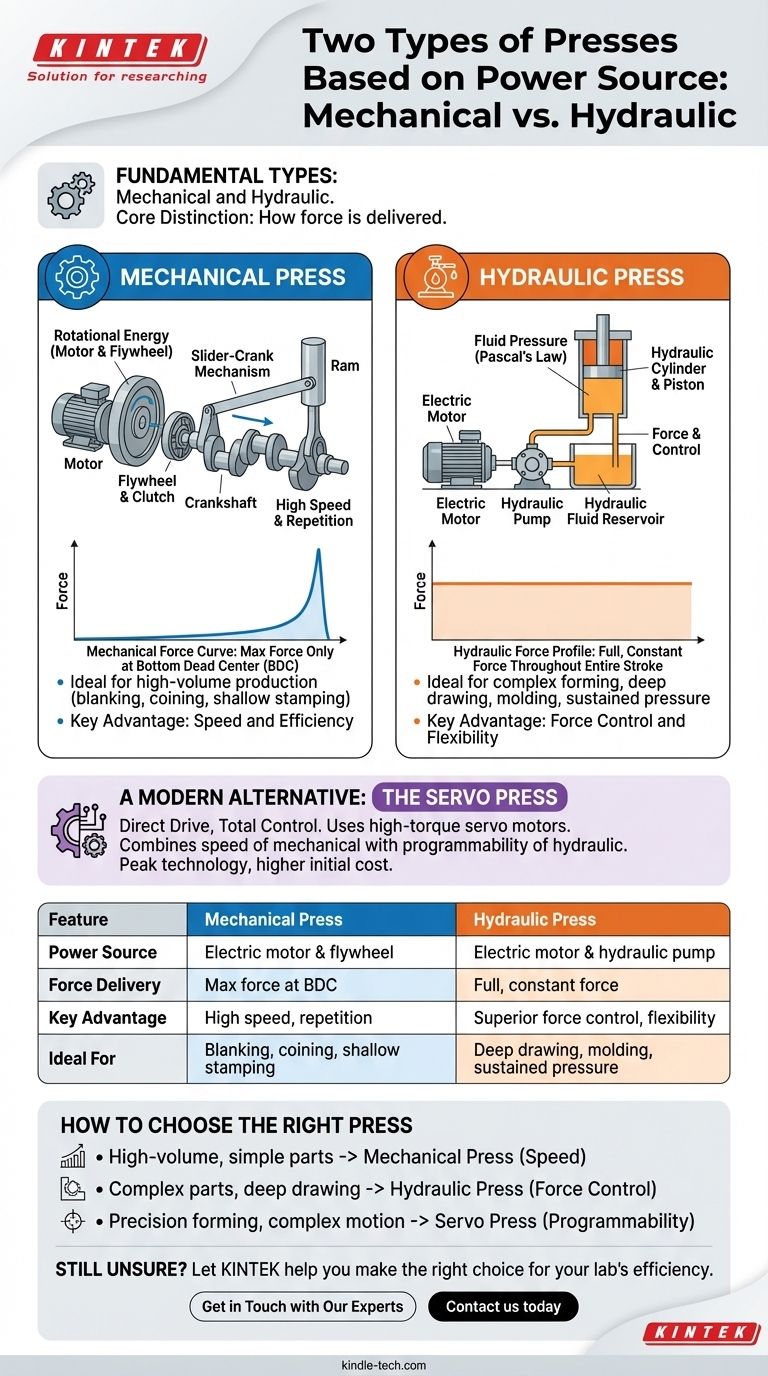
In the simplest terms, presses are categorized into two fundamental types based on their power source: mechanical presses and hydraulic presses. Mechanical presses derive their force from the stored rotational energy of a motor-driven flywheel, while hydraulic presses generate force by using a pump to pressurize fluid according to Pascal's Law.
The core distinction is not just the power source, but how that source delivers force. A mechanical press is built for speed and efficiency at a specific point in its stroke, whereas a hydraulic press is built for controlled, constant force throughout its entire stroke.

Understanding the Mechanical Press
A mechanical press is a system designed to efficiently convert rotational energy into immense linear force for high-speed operations.
The Power Source: Flywheel Energy
An electric motor runs continuously to spin a heavy flywheel, which acts like a mechanical battery, storing kinetic energy. This design allows for a smaller motor to deliver a massive amount of force in a short burst.
How It Works: The Slider-Crank Mechanism
When the press is activated, a clutch engages the flywheel with a crankshaft. This mechanism, similar to the one in a car's engine, converts the flywheel's rotation into the powerful, reciprocating up-and-down motion of the ram.
Key Characteristics: Speed and Repetition
The primary advantages of mechanical presses are speed and repeatability. They are capable of extremely high stroke rates, making them the standard for high-volume production like blanking, coining, and shallow stamping.
Understanding the Hydraulic Press
A hydraulic press is a system designed for versatility and the application of full, sustained force at any point in its operation.
The Power Source: Fluid Pressure
A hydraulic press uses an electric motor to power a pump. This pump moves hydraulic fluid into a cylinder, pushing against a piston. The force generated is a product of the fluid pressure and the piston's surface area.
How It Works: Pascal's Law in Action
This system leverages Pascal's Law, which states that pressure exerted on a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished. This allows the press to deliver its full rated tonnage at any position of the ram's stroke.
Key Characteristics: Force and Control
The defining features of a hydraulic press are its force control and flexibility. Operators have precise control over the stroke length, speed, pressure, and even the ability to "dwell" or hold the part under full pressure for an extended period. This makes them ideal for deep drawing, molding, and forming complex shapes.
The Core Difference: How Force is Delivered
The most critical distinction lies in the force curve—how each press applies force through its stroke.
The Mechanical Force Curve
A mechanical press only delivers its maximum rated force at the very bottom of its stroke, often called the Bottom Dead Center (BDC). The force available diminishes significantly as the ram moves higher up. Think of it like swinging a hammer; maximum impact happens at the very end of the swing.
The Hydraulic Force Profile
A hydraulic press delivers its full, constant tonnage throughout the entire stroke, from the moment it touches the workpiece until it retracts. This sustained pressure is like using a car jack—the force is consistent and controlled through the entire range of motion.
A Modern Alternative: The Servo Press
It's important to recognize a third category that combines the benefits of both: the servo-electric press.
Direct Drive, Total Control
Instead of a flywheel or hydraulics, a servo press uses high-torque servo motors to directly drive the ram, often with a ball screw. This provides the high speeds characteristic of a mechanical press while offering the full programmability and precise force control of a hydraulic press. They represent the peak of modern press technology, albeit at a higher initial cost.
How to Choose the Right Press for Your Application
Selecting the correct press is a function of your specific manufacturing goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple parts (blanking, piercing, coining): The speed and efficiency of a mechanical press are unmatched.
- If your primary focus is forming complex parts, deep drawing, or applications requiring sustained pressure: The force control and stroke versatility of a hydraulic press are necessary.
- If your primary focus is precision forming with complex motion profiles and a need for both speed and control: The advanced programmability of a servo press is the optimal choice.
Understanding this fundamental difference in how force is generated and applied is the key to selecting the most effective tool for your goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanical Press | Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric motor & flywheel (rotational energy) | Electric motor & hydraulic pump (fluid pressure) |
| Force Delivery | Maximum force only at bottom of stroke | Full, constant force throughout the entire stroke |
| Key Advantage | High speed and repetition for mass production | Superior force control and flexibility for complex forming |
| Ideal For | Blanking, coining, shallow stamping | Deep drawing, molding, applications requiring sustained pressure |
Still Unsure Which Press is Right for Your Application?
Choosing between a mechanical, hydraulic, or modern servo press is critical for your lab's efficiency and output quality. KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment, can help you make the right choice.
We specialize in providing the ideal press solutions for your specific needs, whether you require high-speed production or precise, controlled force. Our experts will work with you to understand your goals and recommend the perfect equipment to enhance your workflow.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK empower your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic hot press play in rice husk-based composite boards? Achieve Structural Density
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for nanocomposites? Ensure Precise Material Characterization
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- Why is a hydraulic press used for pre-deformation treatment? Enhance Coating Hardness & Thermal Stability
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing



















