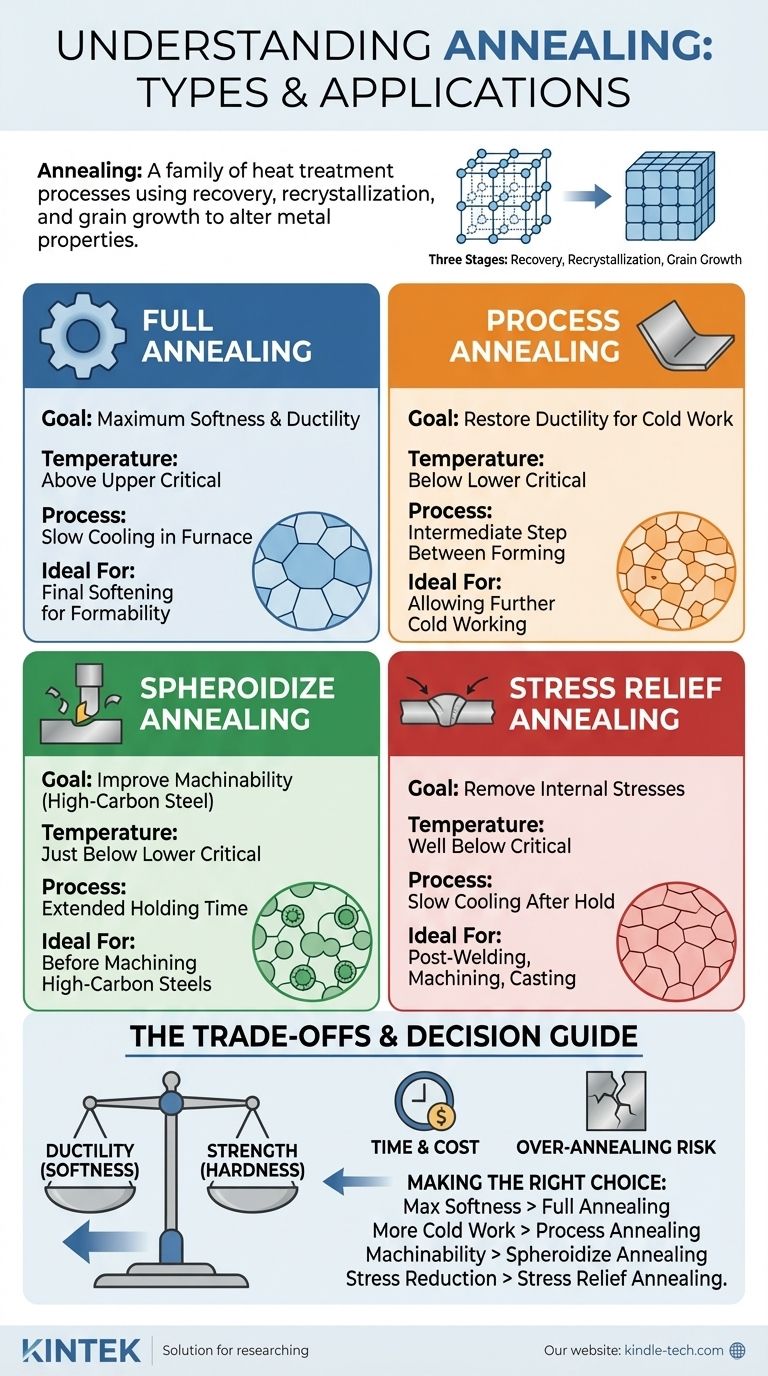
The primary types of annealing include Full Annealing, Process Annealing, Spheroidizing, and Stress Relief Annealing. While these are distinct industrial processes, they all operate on the fundamental principles of material recovery, recrystallization, and grain growth to alter a metal's internal structure and achieve specific properties like improved softness or machinability.
The term "annealing" does not refer to a single procedure but a family of heat treatment processes. The specific type of annealing you choose is dictated entirely by the starting material and the desired final mechanical properties, such as maximum softness, improved machinability, or simply the removal of internal stress.
The Fundamental Purpose of Annealing
Before examining the different types, it's critical to understand what problem annealing solves. It is a heat treatment process that alters the microstructure of a material to change its mechanical or electrical properties.
Softening for Workability
When a metal is plastically deformed at a low temperature (a process known as cold working or work hardening), it becomes progressively harder, stronger, and more brittle.
Annealing reverses this effect by reducing hardness and increasing ductility, making the material soft enough for further shaping, drawing, or forming operations.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding, casting, or heavy machining introduce significant internal stresses within a material. These residual stresses can lead to dimensional instability, premature failure, or cracking.
Annealing provides a path for these internal stresses to relax, resulting in a more stable and reliable component.
Improving Machinability
Some materials, particularly high-carbon steels, are difficult to cut or machine in their hardened state.
Specific annealing cycles can alter the microstructure to make the material much easier to machine, significantly reducing tool wear and improving surface finish.
How Annealing Works: The Three Stages
All annealing processes are governed by three consecutive stages that occur as the material's temperature is increased. The type of annealing is determined by which of these stages you allow to proceed and to what extent.
Stage 1: Recovery
At lower temperatures, the material undergoes recovery. During this stage, the internal stress within the crystal lattice is relieved. There is no significant change in the material's strength, but some restoration of ductility and conductivity occurs.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
As the temperature increases to the recrystallization temperature, new, strain-free grains begin to form and grow. These new grains replace the old, deformed grains that were created during work hardening.
This is the most critical stage for restoring the material's softness and ductility, as it effectively resets the microstructure.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
If the material is held at or above the recrystallization temperature for too long, the newly formed grains will start to merge and grow larger.
While this can further increase softness, excessive grain growth can sometimes be detrimental to other properties like toughness. Controlling this stage is key to achieving the desired final properties.
Key Types of Annealing Processes
Each process manipulates the three stages above by carefully controlling temperature, soak time, and cooling rate.
Full Annealing
This process involves heating the steel to a temperature well above its upper critical temperature and then cooling it very slowly, typically by leaving it in the furnace to cool.
The goal is to produce a coarse grain structure that results in maximum softness, ductility, and machinability. It allows all three stages, including significant grain growth, to occur.
Process Annealing
Also known as intermediate annealing, this is performed on a work-hardened part between forming operations. The material is heated to a temperature just below its lower critical temperature.
This temperature is high enough to induce recovery and recrystallization but not to fundamentally change the material's phase. Its sole purpose is to restore enough ductility to allow for further cold working.
Spheroidize Annealing
Used primarily for high-carbon steels, this process involves holding the material just below its lower critical temperature for an extended period (often many hours).
This doesn't just recrystallize the grains; it causes the hard carbide structures within the steel to transform into a spherical or globular shape. This microstructure provides the best possible machinability for these hard materials.
Stress Relief Annealing
This is a low-temperature process designed only to achieve the recovery stage. The material is heated to a temperature well below its critical point, held long enough to relieve stresses, and then slowly cooled.
The primary goal is to remove internal stresses from welding, machining, or casting without significantly reducing the material's hardness or strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an annealing process involves balancing competing priorities. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Ductility vs. Strength
The core trade-off in annealing is simple: as you increase ductility and softness, you almost always reduce hardness and strength. A fully annealed part will be very easy to form but will have low yield strength compared to its work-hardened or heat-treated state.
Time and Cost
Full annealing requires very slow cooling rates, often meaning the furnace is occupied for an entire shift or longer. This makes it a slow and energy-intensive process.
In contrast, process annealing or stress relief cycles are much shorter and therefore less expensive, as they don't require the same slow, controlled cooling.
The Risk of Over-Annealing
Heating a material for too long or at too high a temperature can lead to excessive grain growth. While this makes the material very soft, extremely large grains can negatively impact properties like fracture toughness and fatigue life, making the final part less durable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final objective dictates the correct process.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum softness and formability for a steel part: Use Full Annealing to create the most ductile and uniform microstructure possible.
- If your primary focus is restoring ductility to a work-hardened part to allow for more cold work: Use Process Annealing as a fast and efficient intermediate step.
- If your primary focus is improving the machinability of a high-carbon steel: Use Spheroidize Annealing to create the ideal microstructure for cutting operations.
- If your primary focus is simply to reduce internal stresses from welding or machining without losing strength: Use Stress Relief Annealing as a low-temperature, targeted solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct annealing process requires a clear understanding of your material's properties and your final engineering objective.
Summary Table:
| Type of Annealing | Primary Goal | Key Temperature Range | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Annealing | Maximum softness & ductility | Above upper critical temperature | Final softening for formability |
| Process Annealing | Restore ductility for further cold work | Below lower critical temperature | Intermediate step between forming operations |
| Spheroidize Annealing | Improve machinability of high-carbon steel | Just below lower critical temperature | High-carbon steels before machining |
| Stress Relief Annealing | Remove internal stresses without softening | Well below critical temperature | Post-welding, machining, or casting |
Achieve precise material properties with the right annealing process.
Choosing the correct annealing cycle is critical for achieving the desired softness, machinability, or stress relief in your metal parts. KINTEK's expertise in laboratory heating equipment ensures you have the precise control needed for every annealing application—from full annealing for maximum ductility to stress relief for dimensional stability.
Let us help you optimize your heat treatment process. Our team specializes in providing reliable lab furnaces and consumables tailored to your specific material science needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















