In a laboratory setting, ovens are categorized primarily by how they circulate air and their specialized functions. The most common types you will encounter are gravity convection, mechanical (or forced air) convection, and vacuum ovens. For more extreme applications, specialized high-temperature furnaces are also used.
The choice of a laboratory oven is not about finding the "best" model, but about matching the specific heating mechanism to the demands of your scientific application, whether that is speed, temperature uniformity, or gentle processing under a controlled atmosphere.

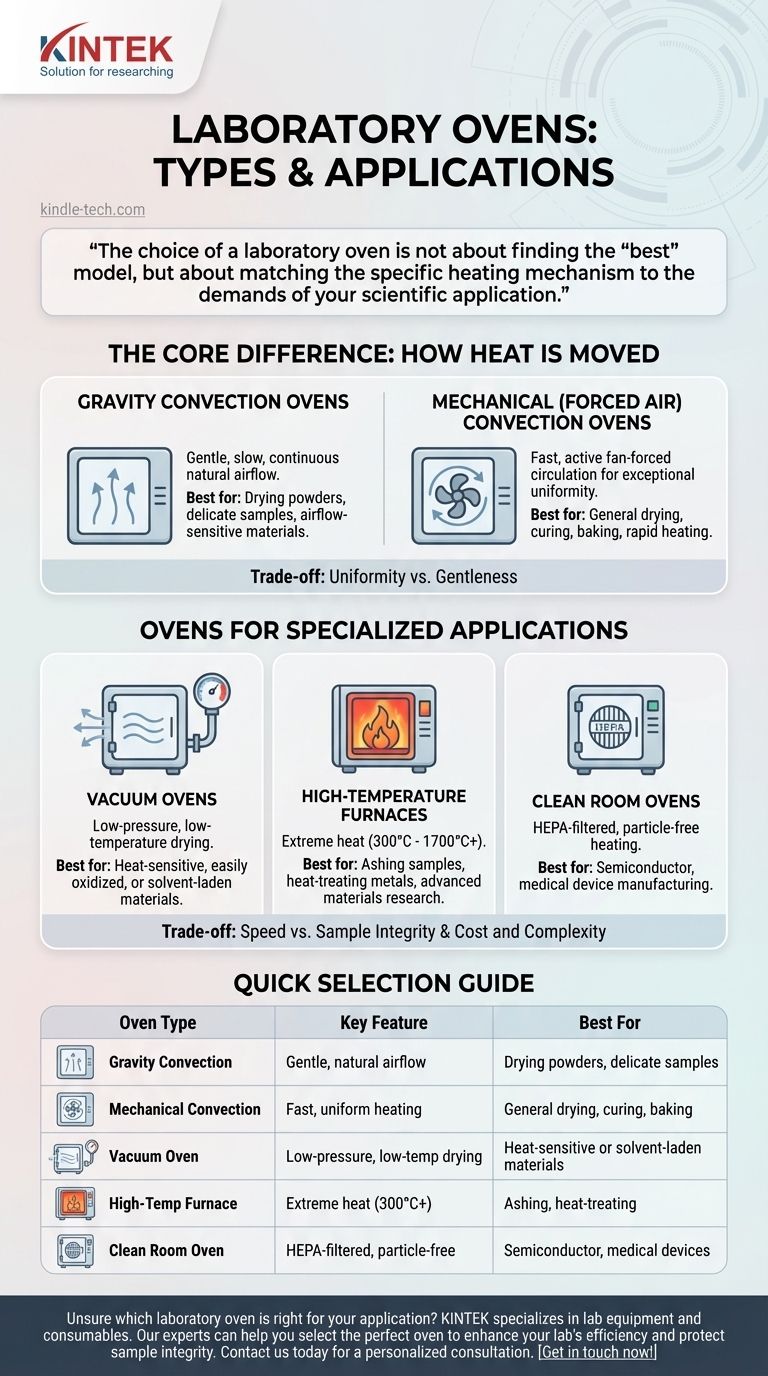
The Core Difference: How Heat is Moved
The most fundamental distinction between general-purpose lab ovens lies in their method of air circulation. This single factor dramatically influences their performance and ideal use cases.
Gravity Convection Ovens
Gravity convection ovens rely on the natural movement of heated air. As air is warmed by the heating elements at the bottom, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler, denser air sinks to be heated.
This process creates a slow, gentle, and continuous airflow. It is the preferred method for applications where a forceful airflow could disturb the sample.
Mechanical (Forced Air) Convection Ovens
Mechanical convection ovens, also known as forced air ovens, incorporate a fan to actively circulate the heated air throughout the chamber.
This forced circulation results in exceptional temperature uniformity and a much faster rate of heat-up and temperature recovery after a door is opened. They are the workhorses for most drying, curing, and general heating tasks.
Ovens for Specialized Applications
Beyond general heating, certain processes require precise control over the atmosphere or much higher temperatures, necessitating specialized equipment.
Vacuum Ovens
A vacuum oven allows for drying and heating in a low-pressure environment. By removing air with a vacuum pump, you significantly lower the boiling point of liquids.
This makes vacuum ovens essential for gently drying heat-sensitive materials that would decompose at higher temperatures. It also prevents oxidation of reactive samples and is ideal for removing flammable solvents.
High-Temperature Furnaces
While technically not "ovens," high-temperature furnaces are often discussed in the same context. Standard lab ovens typically operate up to 250°C or 350°C.
Furnaces, often called muffle furnaces, are designed for applications requiring temperatures from 300°C to over 1700°C, such as ashing samples, heat-treating metals, or advanced materials research.
Clean Room Ovens
Used in sensitive manufacturing environments like semiconductor or medical device production, these ovens have high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters.
Their purpose is to heat a product without introducing contaminating particles from the ambient air, ensuring the process remains sterile or particle-free.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an oven involves balancing performance, sample integrity, and cost. Each type presents a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages.
Uniformity vs. Gentleness
The primary trade-off is between a gravity and a mechanical convection oven. The fan in a mechanical oven ensures excellent temperature uniformity, but its airflow can disturb light powders or delicate samples. A gravity oven provides gentle heating but may have less precise temperature consistency throughout the chamber.
Speed vs. Sample Integrity
Forced air ovens are significantly faster at drying. However, this rapid surface heating can sometimes create a "skin" on a sample, trapping moisture inside. A vacuum oven is slower but provides a much more thorough and gentle drying process for delicate or complex materials.
Cost and Complexity
As features and capabilities increase, so do cost and operational complexity. A simple gravity convection oven is the most affordable and straightforward. Mechanical ovens are a moderate step up, while vacuum ovens and high-temperature furnaces represent a significant investment and require more user training.
Selecting the Right Oven for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the requirements of your specific procedure.
- If your primary focus is gentle drying of powders or samples sensitive to airflow: A gravity convection oven is the ideal and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is speed, rapid temperature recovery, and the highest temperature uniformity: A mechanical (forced air) convection oven is superior for most general-purpose applications.
- If your primary focus is drying heat-sensitive, easily oxidized, or solvent-laden materials at low temperatures: A vacuum oven is the only safe and effective option.
- If your primary focus is reaching temperatures above 350°C for processes like ashing or heat-treating: You must use a high-temperature furnace, not a standard laboratory oven.
Understanding these core distinctions ensures you select a tool that enhances, rather than compromises, the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Oven Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Gravity Convection | Gentle, natural airflow | Drying powders, delicate samples |
| Mechanical Convection | Fast, uniform heating | General drying, curing, baking |
| Vacuum Oven | Low-pressure, low-temperature drying | Heat-sensitive or solvent-laden materials |
| High-Temperature Furnace | Extreme heat (300°C - 1700°C+) | Ashing, heat-treating, materials research |
| Clean Room Oven | HEPA-filtered, particle-free | Semiconductor, medical device manufacturing |
Unsure which laboratory oven is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect oven—whether you need the gentle heating of a gravity convection model, the speed and uniformity of a mechanical convection oven, or the specialized capabilities of a vacuum oven or high-temperature furnace. We provide solutions that enhance your lab's efficiency and protect the integrity of your samples.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let us help you find the ideal heating solution for your specific workflow. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking



















