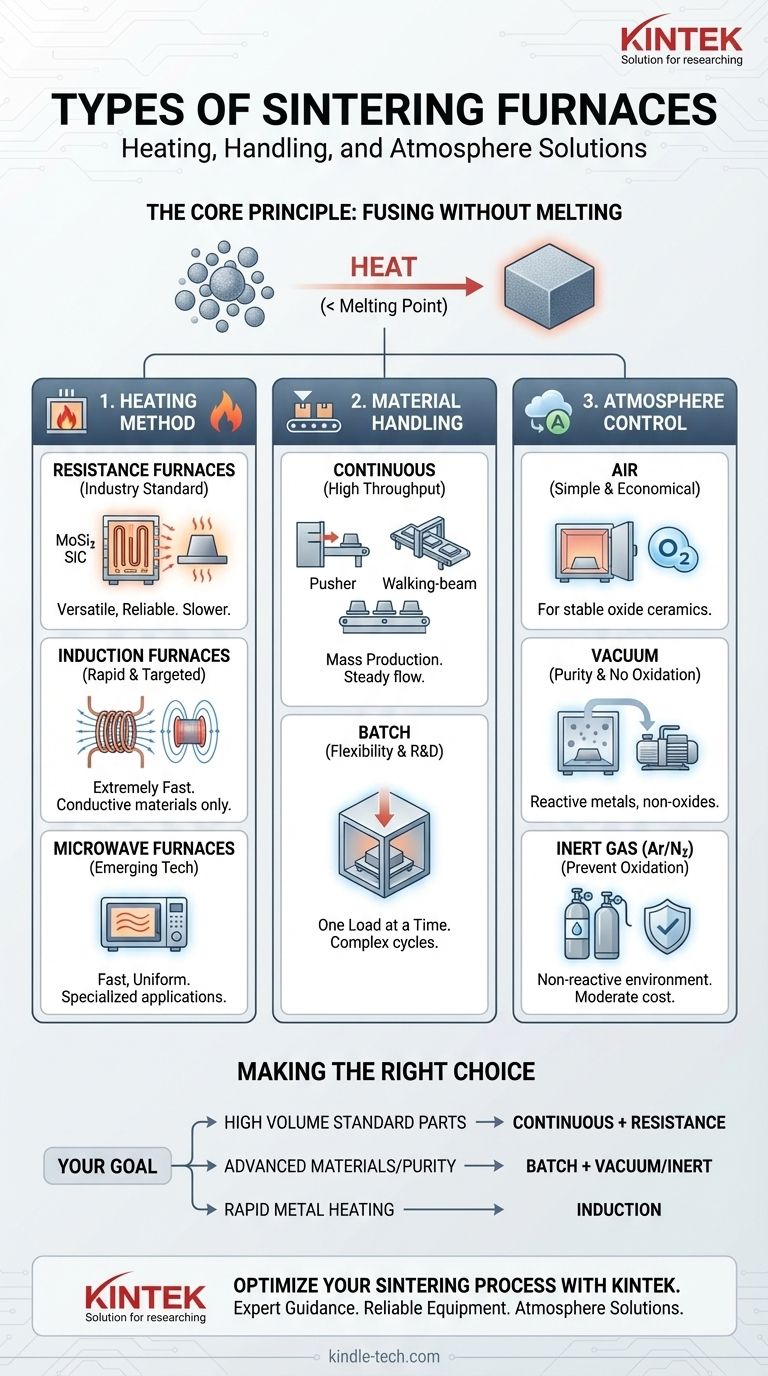
Sintering furnaces are primarily categorized by their heating method, material handling system, and atmospheric capabilities. The main heating methods are resistance and induction, while material handling is typically either continuous (like pusher or walking-beam furnaces) or batch-based. These designs can operate in various atmospheres, including air, vacuum, or inert gas, to achieve specific material properties.
The question isn't which type of sintering furnace is "best," but which combination of heating, material handling, and atmosphere control is correct for your specific material, production volume, and desired final properties. Understanding these core principles is the key to making the right investment.
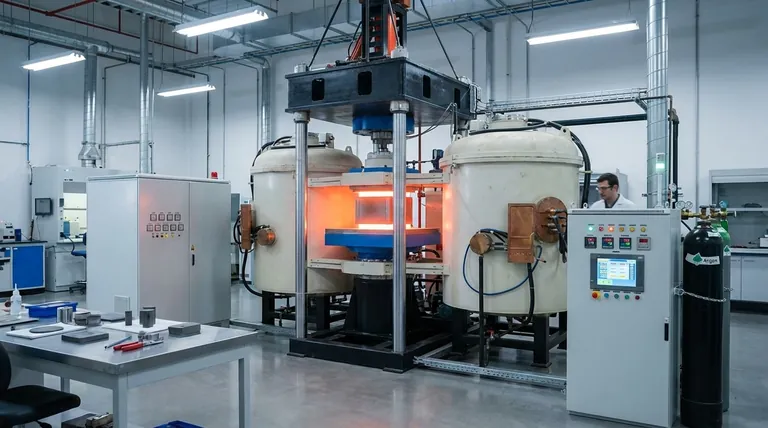

The Core Principle: How Sintering Works
Fusing Powder Without Melting
Sintering is a thermal process applied to a powder compact. The goal is to heat the material to a high temperature, but below its melting point.
This process causes the individual powder particles to bond together, increasing the material's density, mechanical strength, and in some cases, its translucency, transforming it into a solid, coherent object.
Classification by Heating Method
The furnace's heating method is its most fundamental characteristic, defining its speed, efficiency, and suitability for different materials.
Resistance Furnaces: The Industry Standard
Resistance furnaces generate heat by passing electricity through high-resistance heating elements. This heat then radiates to the parts being sintered.
These are the most common type of furnace due to their versatility and reliability. The heating elements are typically made from robust materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC).
Induction Furnaces: Rapid and Targeted Heating
Induction furnaces use powerful electromagnetic fields to induce an electric current directly within the material itself. This internal current generates heat rapidly and efficiently.
This method is extremely fast but is generally limited to electrically conductive materials, such as metals and certain types of ceramics.
Microwave Furnaces: An Emerging Technology
Microwave sintering is a newer approach that uses microwave energy to heat the material. It can offer very fast and more uniform heating compared to conventional methods for certain materials.
While promising, it is not as widely adopted as resistance or induction heating and is often used in more specialized applications.
Classification by Material Handling
How parts move through the furnace defines its throughput and suitability for different production scales.
Continuous Furnaces for High Throughput
Continuous furnaces are designed for mass production, where a steady flow of material is required.
- Pusher Furnaces: Parts are loaded onto ceramic "boats" or trays, which are pushed one after another to form a continuous train moving through the furnace.
- Walking-Beam Furnaces: This mechanism lifts the boats, moves them forward a set distance, and lowers them back onto stationary beams. This "walking" motion reduces friction and wear on both the parts and the furnace hearth.
Batch Furnaces for Flexibility
Batch furnaces process one load or "batch" of parts at a time. The entire chamber is heated and cooled according to a specific programmed cycle.
These are ideal for research and development, small production runs, or for parts requiring complex, multi-stage thermal cycles that are impractical in a continuous system.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
The atmosphere inside the furnace is crucial as it prevents or promotes chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Sintering in Air
This is the simplest and most economical option, suitable for materials like some oxide ceramics (e.g., zirconia in dental applications) that are stable and do not react with oxygen.
Vacuum Furnaces for Purity
Operating under a vacuum removes atmospheric gases, preventing oxidation and contamination. This is essential for sintering reactive metals, non-oxide ceramics, and materials where ultimate purity is required.
Vacuum furnaces can be configured with a horizontal orientation for easier loading or a vertical orientation, which can be advantageous for specific part geometries and minimizing distortion.
Inert Gas Atmospheres
Using an inert gas like Argon (Ar) or Nitrogen (N2) provides a non-reactive environment without the cost and complexity of a high-vacuum system. This is a common method for preventing oxidation in sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every furnace design involves compromises between performance, cost, and complexity.
Resistance vs. Induction
The primary trade-off is versatility versus speed. Resistance furnaces can heat almost any material but are slower. Induction furnaces are incredibly fast and efficient but work only with conductive materials.
Continuous vs. Batch
This is a choice between throughput and flexibility. Continuous furnaces are built for high-volume, standardized production. Batch furnaces offer the flexibility to run different parts with unique cycles but have lower overall throughput.
Atmosphere Costs
Controlling the atmosphere adds significant cost and complexity. Sintering in air is the cheapest. Inert gas is a moderate-cost solution for preventing oxidation, while high-vacuum systems provide the highest purity but are the most expensive to purchase and operate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its technology to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard parts: A continuous furnace (Pusher or Walking-Beam) with a resistance heating system is likely your most reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics or reactive metals: A batch furnace with vacuum or inert gas capabilities is essential to control material purity and prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating of conductive metal parts: An induction furnace offers unmatched speed and energy efficiency, making it ideal for specialized metal sintering.
- If your primary focus is small-scale production or R&D: A smaller, flexible batch furnace (often resistance-heated) provides the versatility needed for varied materials and process cycles.
Ultimately, the ideal sintering furnace is the one whose capabilities directly serve the specific needs of your material and your process.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Resistance, Induction, Microwave | Versatility vs. speed for conductive materials |
| Material Handling | Batch, Continuous (Pusher, Walking-Beam) | R&D/flexibility vs. high-volume production |
| Atmosphere | Air, Vacuum, Inert Gas (Argon/Nitrogen) | Material purity, preventing oxidation, cost control |
Still Unsure Which Sintering Furnace is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct combination of heating, handling, and atmosphere is critical for your material's properties and your production goals. KINTEK, your trusted partner in lab equipment, specializes in helping laboratories like yours select the ideal sintering furnace.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Match furnace technology to your specific materials (ceramics, metals) and production volume.
- Reliable Equipment: From high-throughput continuous furnaces to flexible R&D batch systems.
- Atmosphere Solutions: Vacuum and inert gas systems to ensure material purity and prevent oxidation.
Let's optimize your sintering process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize Densification of CNT/Al Matrix Composites
- Why must a high vacuum be maintained during Cu-CNT sintering? Ensure Optimal Bonding and Material Integrity
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production



















