In modern dentistry, ceramics are the cornerstone material for aesthetic and durable restorations. They are used to create a wide range of custom-fit devices, including crowns (caps), bridges, veneers, inlays, and onlays. Their primary advantage is an unparalleled ability to mimic the translucency, color, and texture of natural tooth enamel, delivering lifelike results that are also highly compatible with the body.
Dental ceramics are not a single substance but a diverse class of materials valued for their unique ability to balance strength, biocompatibility, and superior aesthetics. The fundamental challenge is selecting the right type of ceramic for a specific clinical need, as the strongest options are often less translucent and the most aesthetic options are less durable.

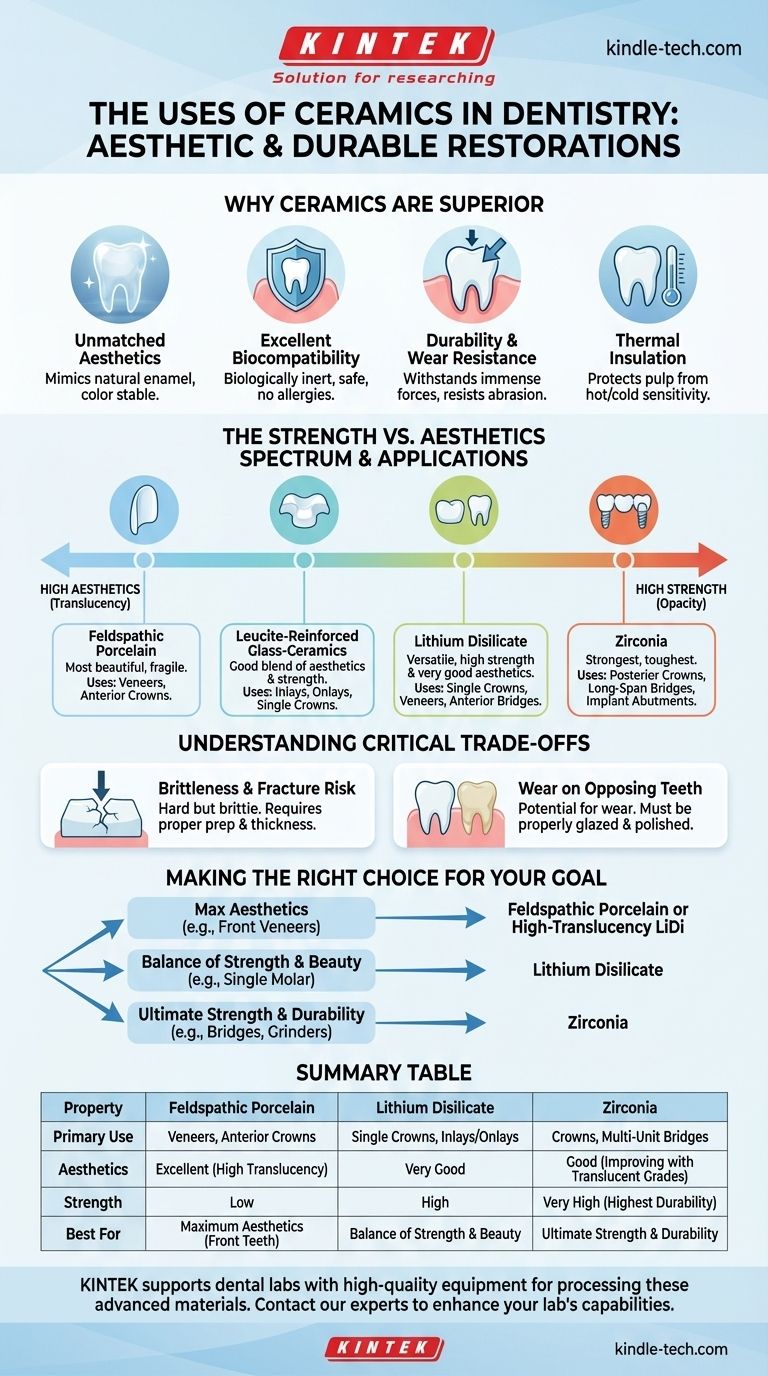
Why Ceramics are a Superior Choice in Dentistry
The adoption of ceramics over traditional materials like metal alloys is driven by a unique combination of beneficial properties that are perfectly suited for the oral environment.
Unmatched Aesthetics
Ceramics can be manufactured to match the precise shade and translucency of a patient's natural teeth. They absorb, reflect, and transmit light in a way that is remarkably similar to tooth enamel, making restorations virtually indistinguishable from their surroundings. This color stability also ensures they won't stain or discolor over time.
Excellent Biocompatibility
Dental ceramics are biologically inert, meaning they do not corrode, release substances, or cause allergic or inflammatory reactions in the surrounding gum tissues. This makes them an exceptionally safe material for long-term use in the body, unlike some metal alloys that can cause sensitivity or reactions in certain patients.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Modern dental ceramics are incredibly strong and hard, capable of withstanding the immense biting and chewing forces exerted in the mouth. They are highly resistant to wear and abrasion from opposing teeth and abrasive foods, maintaining their shape and function for many years.
Thermal Insulation
Unlike metal restorations, which can conduct hot and cold temperatures and cause tooth sensitivity, ceramics are excellent insulators. This property protects the underlying tooth nerve (pulp) from thermal shock, leading to a more comfortable experience for the patient.
Key Types of Dental Ceramics and Their Applications
The term "ceramic" encompasses several distinct materials, each with a different balance of strength and beauty. Choosing the right one is critical for a successful outcome.
Feldspathic Porcelain
This is the original, classic cosmetic dental ceramic. It is essentially a glass-based material prized for its exceptional translucency and aesthetic potential.
Because it is the most beautiful but also the most fragile ceramic, it is primarily used for cosmetic veneers and crowns on front teeth, where biting forces are lower.
Leucite-Reinforced Glass-Ceramics
This material enhances traditional porcelain by adding leucite crystals, which interrupt crack propagation and significantly increase its strength.
It offers a good blend of aesthetics and moderate strength, making it suitable for inlays, onlays, and single crowns on both front and back teeth.
Lithium Disilicate
This is arguably the most versatile and widely used ceramic in modern dentistry. It contains a high concentration of needle-like lithium disilicate crystals, which provides excellent strength and fracture resistance.
Its combination of high strength and very good aesthetics makes it an ideal choice for single crowns anywhere in the mouth, veneers, and even three-unit bridges in the anterior region.
Zirconia
Zirconia is a crystalline-based ceramic and is the strongest, toughest dental ceramic available. Often called "ceramic steel," its resistance to fracture is unparalleled.
Early versions were very strong but opaque, limiting them to posterior crowns and long-span bridges. However, newer translucent zirconias have improved aesthetics, expanding their use for anterior crowns and implant abutments where ultimate durability is the priority.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. Understanding the inherent compromises is key to making an informed decision.
The Strength vs. Aesthetics Spectrum
This is the core trade-off in dental ceramics. As you move from glass-based materials to crystalline-based ones, you gain strength but typically lose translucency.
Feldspathic porcelain sits at the peak of aesthetics but has the lowest strength. Zirconia is at the peak of strength but is traditionally the most opaque. Lithium disilicate occupies a highly effective middle ground.
Brittleness and Fracture Risk
While ceramics are incredibly hard, they are also brittle. Unlike metals, which may bend under excessive force, a ceramic will fracture if its strength limit is exceeded by a sharp, focused impact.
This risk is mitigated by proper tooth preparation by the dentist, ensuring the restoration has adequate thickness and is not subjected to improper bite forces.
Wear on Opposing Teeth
Because some ceramics are harder than natural tooth enamel, they can potentially cause wear on the opposing teeth over time.
This issue is largely eliminated by ensuring the ceramic is properly glazed and highly polished. A smooth, polished zirconia surface, for example, is extremely kind to opposing natural teeth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a ceramic material should always be tailored to the specific functional and aesthetic demands of the restoration's location in the mouth.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics (e.g., front tooth veneers): Feldspathic porcelain or a high-translucency lithium disilicate are the premier choices for their life-like appearance.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and beauty (e.g., a single molar crown): Lithium disilicate is often the ideal material, offering robust performance with excellent aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength and durability (e.g., a multi-tooth bridge or for a patient who grinds): Zirconia is the definitive material of choice due to its superior fracture resistance.
Understanding these material properties empowers clinicians and patients to choose a restoration that is not just a repair, but a long-term, functional, and aesthetic solution.
Summary Table:
| Property | Feldspathic Porcelain | Lithium Disilicate | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Veneers, Anterior Crowns | Single Crowns, Inlays/Onlays | Crowns, Multi-Unit Bridges |
| Aesthetics | Excellent (High Translucency) | Very Good | Good (Improving with Translucent Grades) |
| Strength | Low | High | Very High (Highest Durability) |
| Best For | Maximum Aesthetics (Front Teeth) | Balance of Strength & Beauty | Ultimate Strength & Durability |
Ready to select the perfect ceramic material for your dental restorations?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables essential for processing and fabricating these advanced dental ceramics. Whether you are creating precise veneers, durable crowns, or strong bridges, having the right tools is critical for success.
Our products support dental labs in achieving consistent, high-quality results with materials like zirconia, lithium disilicate, and feldspathic porcelain. Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities and deliver superior, long-lasting dental solutions to your patients.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations



















