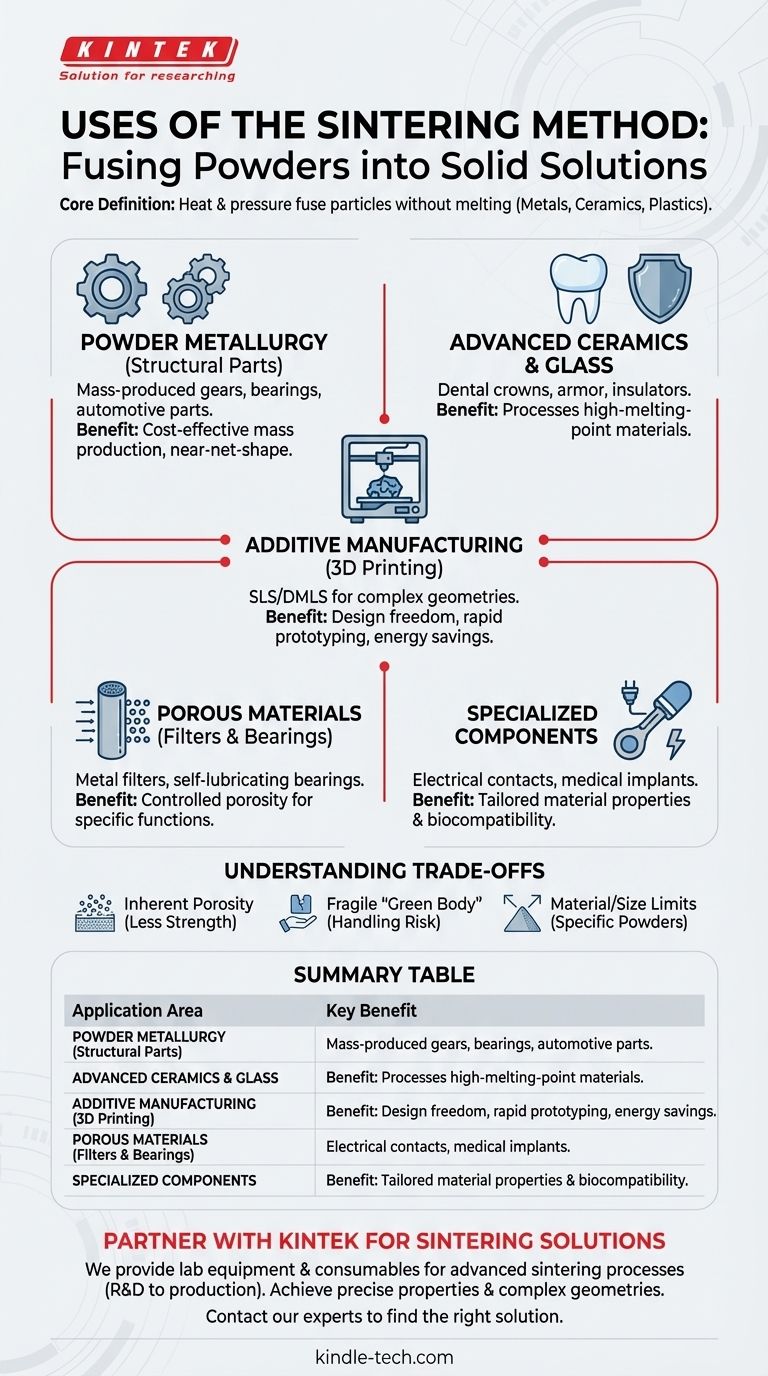
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing method used to create solid objects from powders, such as metals, ceramics, or plastics. It relies on heat and pressure to fuse particles together without melting them, making it essential for processing materials with very high melting points and for creating parts with unique properties through powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing.
Sintering's primary value lies in its ability to fabricate parts that are difficult or impossible to create through traditional melting and casting. It enables the production of components from high-temperature materials, the creation of complex shapes via 3D printing, and the engineering of materials with controlled porosity.

The Principle: Fusing Solids Without Melting
Sintering is fundamentally a process of atomic diffusion. By heating a compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point, you give the atoms enough energy to migrate across the boundaries of individual particles, fusing them into a solid, coherent mass.
Why This Matters for High-Melting-Point Materials
For materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and many advanced ceramics, their melting points are so high that melting and casting them is impractical, energy-intensive, or impossible.
Sintering provides a lower-energy pathway to consolidate these materials into useful, dense forms, making it the go-to method for applications like tungsten lamp filaments and high-performance cutting tools.
Achieving Near-Net-Shape Parts
Sintering begins with a powder compacted into a mold, a process that creates a "green body" that is very close to the final part's dimensions.
This near-net-shape capability drastically reduces the need for subsequent machining, minimizing material waste and production costs. This is a key advantage of the powder metallurgy (PM) process.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of the sintering process has led to its adoption in a wide range of fields, from mass-produced automotive parts to custom medical implants.
Powder Metallurgy for Structural Parts
This is the most common industrial use of sintering. It is used to mass-produce metal components like gears, self-lubricating bearings, and other structural steel parts for the automotive and industrial machinery sectors.
Advanced Ceramics and Glass
Sintering is the traditional and modern method for producing nearly all ceramic products, including porcelain insulators, dental crowns, and ballistic armor plates. It is also used in the production of certain types of glass.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Processes like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) use a laser to selectively sinter powder layer by layer. This builds complex, custom metal or plastic parts directly from a digital model, offering immense design freedom and energy savings compared to traditional fabrication.
Controlled Porosity for Filters and Bearings
While sintering is often used to create a dense, strong part, it can also be precisely controlled to create a network of interconnected pores. This is used to make porous metal or plastic filters, as well as self-lubricating bearings that are impregnated with oil.
Specialized Electrical and Medical Products
The unique capabilities of sintering are leveraged for specialized components. These include electrical contacts, magnetic materials, and biocompatible medical and dental implants that require specific material properties and shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is crucial for making an informed design choice.
Inherent Porosity and Strength
Unless combined with secondary processes like hot isostatic pressing (HIP), sintered parts almost always retain a small amount of residual porosity. This can make them less strong or durable than parts forged or machined from a solid billet of the same material.
The 'Green Body' Challenge
The initial powder compact, or "green body," is fragile and must be handled carefully before the final sintering process. This adds a step and a potential point of failure in the manufacturing workflow.
Material and Size Limitations
The process is best suited for materials available in a fine powder form. Furthermore, achieving uniform density and avoiding warping can be challenging for very large or geometrically complex parts, which may limit its application for certain designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific constraints and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Sintering via powder metallurgy is an outstanding choice for small to medium-sized metal parts with moderate complexity.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials: Sintering is often the most practical, or only, viable method for consolidating materials like tungsten and advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is complex geometries or rapid prototyping: Sintering-based 3D printing provides unmatched design freedom for creating custom, one-off, or low-volume parts.
- If your primary focus is engineering specific material properties: Sintering offers unique control over a material's density, enabling the creation of functional porous products like filters and self-lubricating bearings.
Understanding when to apply sintering unlocks a powerful tool for material fabrication and innovative product design.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Cases | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy | Gears, bearings, automotive parts | Cost-effective mass production, near-net-shape |
| Advanced Ceramics | Dental crowns, armor, insulators | Processes high-melting-point materials |
| Additive Manufacturing | SLS/DMLS 3D printing of complex parts | Design freedom, rapid prototyping |
| Porous Materials | Filters, self-lubricating bearings | Controlled porosity for specific functions |
| Specialized Components | Electrical contacts, medical implants | Tailored material properties and biocompatibility |
Need to fabricate complex or high-performance parts?
Sintering is a versatile method for creating components from metals, ceramics, and plastics. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for advanced sintering processes, whether for R&D or production. Our expertise helps you achieve precise material properties and complex geometries efficiently.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the right sintering solution for you.
Contact our experts today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory's sintering needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- How much psi can a hydraulic press make? From 2,000 PSI to over 50,000 PSI Explained
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



















