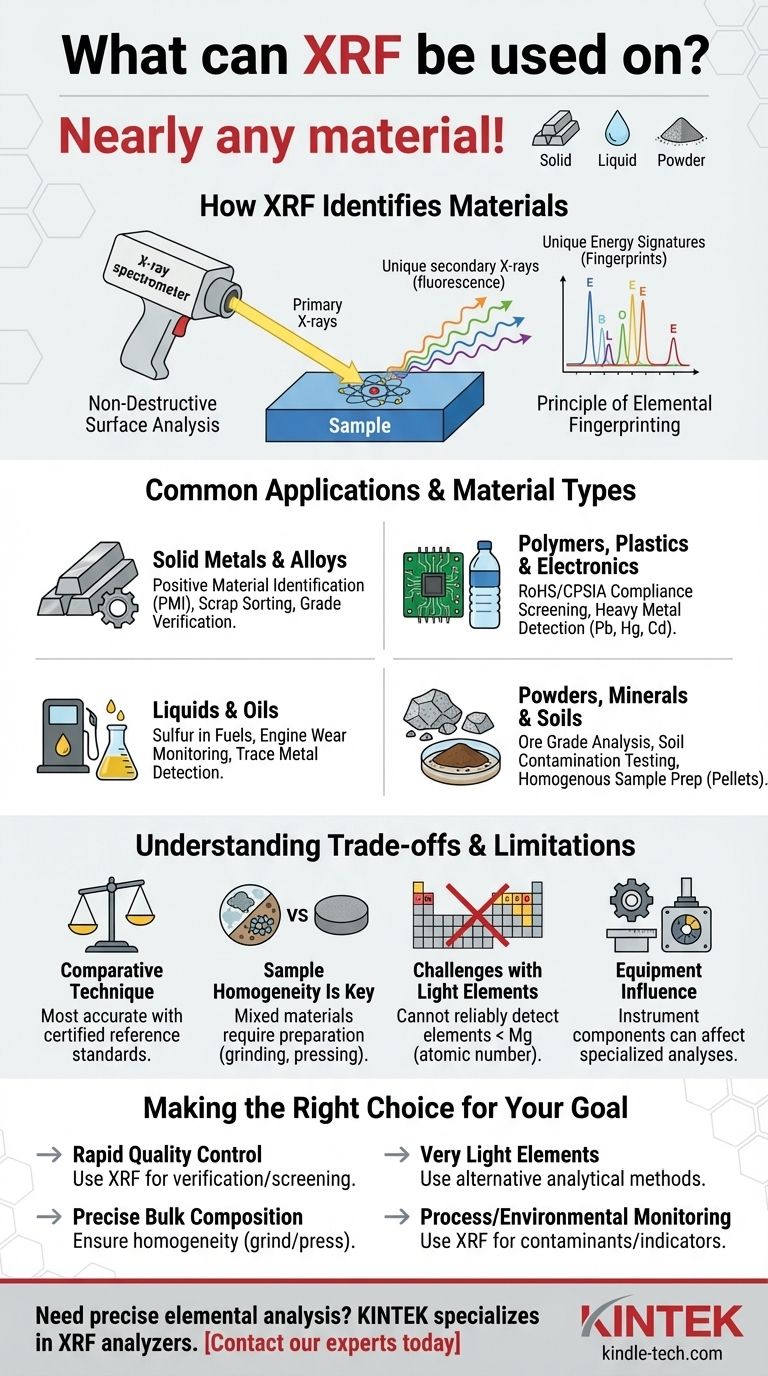
In short, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) can be used on nearly any material. It is a powerful, non-destructive technique used to determine the elemental composition of solids, liquids, powders, and even thin films. XRF is widely applied in quality control for metal alloys, compliance testing for heavy metals in plastics, and analyzing the elemental makeup of geological or petroleum products.
The central value of XRF is not just its versatility across material types, but its ability to provide rapid, on-the-spot elemental analysis. It answers the question "What elements is this made of?" without destroying the sample, making it an indispensable tool for quality control, screening, and research.
How XRF Identifies Materials
The Principle of Elemental Fingerprinting
XRF works by bombarding a sample with high-energy X-rays from a spectrometer. This energy excites the atoms within the material, causing them to emit their own secondary X-rays, known as fluorescence.
Each element on the periodic table produces a unique energy signature, or "fingerprint," when it fluoresces. By measuring these unique signatures, the XRF analyzer can instantly identify which elements are present and in what relative quantities.
A Non-Destructive Surface Analysis
A key characteristic of XRF is that it is a non-destructive technique. The analysis does not harm or alter the sample, which is critical when testing valuable or finished products.
However, it is important to understand that XRF is primarily a surface analysis tool. The X-rays only penetrate a small depth into the material, so the results reflect the composition of the surface layer being measured.
Common Applications and Material Types
Solid Metals and Alloys
This is one of the most common uses for XRF. It is used extensively for Positive Material Identification (PMI) in manufacturing and fabrication.
Applications include verifying the grade of stainless steel, confirming the composition of aerospace alloys, or sorting scrap metal with high accuracy and speed.
Polymers, Plastics, and Electronics
XRF is a cornerstone of regulatory compliance screening. It is used to quickly detect the presence of restricted heavy metals like lead, mercury, cadmium, and chromium in consumer products.
This is essential for complying with directives like the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) in electronics and the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA).
Liquids and Oils
The technique is also effective for analyzing liquids. A common industrial application is measuring the concentration of sulfur in fuels like gasoline and diesel to meet environmental standards.
It can also be used to analyze the elemental composition of lubricating oils to monitor for engine wear by detecting trace metal particles.
Powders, Minerals, and Soils
For materials that are not homogenous, samples are often ground into a fine powder and pressed into a pellet to ensure a consistent and representative reading.
This method is standard in mining and geology for analyzing ore grades, in environmental science for testing soil contamination, and in construction for verifying the composition of cement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
It Is a Comparative Technique
XRF provides its most accurate quantitative results when calibrated with certified reference materials or standards of a similar composition. Without proper calibration, its data is best used for relative comparisons and screening rather than absolute measurement.
Sample Homogeneity Is Key
Because XRF analyzes a small spot on the surface, the result is only representative of the bulk material if the sample is homogenous. For mixed materials or unrefined ores, results can vary significantly across the surface. This is why sample preparation, like grinding and pressing powders, is so important for accuracy.
Challenges with Light Elements
XRF technology has difficulty detecting very light elements, typically those with an atomic number lower than magnesium (Mg). Elements like lithium, beryllium, carbon, and oxygen cannot be reliably identified. For applications requiring analysis of these light elements, other techniques are necessary.
Equipment Can Influence Results
In specialized analyses, even the instrument components can be a factor. For example, when testing for iron, a standard stainless steel pressing face on a pellet die could potentially contaminate the reading. In such cases, alternative materials like tungsten carbide are used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding its capabilities and constraints, you can determine if XRF is the correct tool for your objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or sorting: XRF is an unmatched tool for quickly verifying alloy grades or screening products for restricted elements.
- If your primary focus is precise bulk composition of a solid: You must ensure your sample is homogenous, which may require grinding it into a powder and pressing it into a pellet for analysis.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for very light elements (e.g., lithium, carbon): You will need to consider an alternative analytical method, as XRF is not suitable for this task.
- If your primary focus is process or environmental monitoring: XRF provides a fast and reliable way to check for contaminants or key elemental indicators in everything from soil to fuel.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage XRF as a powerful and efficient tool for elemental analysis across a vast range of applications.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Applications | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Metals & Alloys | Positive Material Identification (PMI), scrap sorting | Rapid grade verification, non-destructive |
| Polymers & Electronics | RoHS/CPSIA compliance screening | Detects restricted heavy metals (Pb, Hg, Cd) |
| Liquids & Oils | Sulfur in fuels, wear metals in lubricants | Fast monitoring for environmental standards |
| Powders, Minerals & Soils | Ore grade analysis, soil contamination testing | Homogeneous sample preparation ensures accuracy |
Need precise elemental analysis for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in XRF analyzers and lab equipment for accurate, non-destructive testing. Whether you're in manufacturing, environmental monitoring, or R&D, our solutions deliver rapid results for quality control and compliance.
Contact our experts today to find the right XRF solution for your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What are laboratory mixers used for? Achieve Perfect Sample Homogeneity and Reliable Results
- How does a high-efficiency homogenizing mixer contribute to the preparation of Tobermorite and Xonotlite precursors?
- How does a constant temperature rotary shaker contribute to evaluating iron nanoparticles? Optimize Dye Degradation
- What function does a high-speed rotor-stator homogenizer perform in biomass processing? Optimize Structural Disruption
- What is the difference between mixer and disperser? Choose the Right Tool for Your Process















